Posts Tagged ‘DFW smog’
Power of the Press: Week after Trib Report on DFW Smog, First “Exceedences” of 1997 Standard
 It was only eight days ago the that online Texas Tribune did the first real overview of DFW air quality for this "ozone season." Borrowing heavily from the June 16th Downwinders at Risk presentation to the North Texas regional air quality committee, it concluded that there had been no discernible progress in regional air quality for the past five to six years despite a new state anti-smog plan aimed at getting the area below the 1997 standard of 85 parts per billion.
It was only eight days ago the that online Texas Tribune did the first real overview of DFW air quality for this "ozone season." Borrowing heavily from the June 16th Downwinders at Risk presentation to the North Texas regional air quality committee, it concluded that there had been no discernible progress in regional air quality for the past five to six years despite a new state anti-smog plan aimed at getting the area below the 1997 standard of 85 parts per billion.
Ironically, up to that point, DFW had been enjoying one of the wettest, coolest, most ozone alert-free summers on record. Not one 100 degree day until July and only one "bad air" days of note on June 11th. It looked like we might actually be able to meet the 1997 standard of 85 ppb for the very first time.
That's all changed with this past weeks' return to familiar form. In just seven days, they've been at least four official "ozone alerts" issued for DFW by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality. Those had produced four "exceedences" of the current 75 parts ppb standard, which the state is now aiming at with another "do nothing" plan under development and due out by the end of the year. On Wednesday the trend got more serious with the addition of the first two "exceedences" of the older 1997 standard we can't seem to conquer – a reading of 88 ppb at the NW Fort Worth monitor at Meacham Field and a 91 at the usually quiet Granbury monitor in Hood County. In the latter case, one mid-afternoon hourly reading reached as high as 113 – just 12ppb short of a violation of an even more ancient standard left over from the 1980's.
For comparison's sake, EPA scientists just sent a letter to EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy recommending that a new, lower federal standard for ozone be set at 60-70 ppb.
It will still take another week of 85 ppb plus days to produce the "fourth highest" readings at the Denton or Keller sites to combine with their 2013 averages and keep DFW in violation of a 17-year old ozone standard. But then again, we have all of August and September to go.
Not surprisingly, two of this summer's hot spots include traditionally troublesome monitors – the Denton and NW Fort Worth site. Tarrant and Denton Counties have historically been the places where the region's highest readings have originated. One reason is wind direction – smog accumulates from upwind sources like the Midlothian cement plants and blows Northwest during the summer. Another more recent reason is the mining of Barnett Shale gas deposits that release huge quantities of smog-forming pollution in the western half of the Metromess, a phenomenon that's been examined in a new UNT study that divided the region's ozone monitors into "Fracking" and "Non-Fracking" areas and found significantly higher readings among those in the Fracking area.
As we went to press with this post, Thursday's readings looked to be producing another round of 75 ppb or higher results. Adding to this year's ozone season irony is that over the last 20 years, July has traditionally been the summer month that produced the fewest number of high ozone readings, book-ended by higher numbers in June and August-September.
Depending on the weather, DFW may still be able to make it over the 1997 standard, 85 ppb hump. But based on this past week's results, that hump just got bigger. Stay tuned.
Ask the State and Holcim To Finally Give DFW “the Holy Grail” of Cement Pollution Control Technology
 Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
That's right. Holcim is asking the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) to OK a permit that will result in a "major modification" of its Midlothian plant and could produce significant amounts of new pollution before it even decides what the major modification is going to be. Anywhere else in the country this might be a bit odd, but hey, it's Texas, where Rick Perry's TCEQ has a rubber stamp standing by for anything industry requests.
Holcim's permit request is being prompted by a problem complying with new federal regulations limiting a kind of pollution called Total Hydrocarbons, or THCs. These are also sometimes referred to as "Volatile Organic Compounds." Think Benzene, and other kinds of hazardous flammable gases. In its permit application Holcim says it needs to add new controls to reduce THC to levels and come under the new federal standard. Fair enough. The company then says that it's still trying to decide between two different types of controls and will make up its mind after getting the permit and seeing how well its choice works out on one of its two separate giant kilns. That's the bogus part.
But wait, there's more! The two technologies Holcim is considering installing in Midlothian are: 1) A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, or RTO, which is a fancy way of saying setting them on fire and flaring them off, and, 2) A Selective Catalytic Reduction unit, or SCR, which is a tower of treated metal honeycombs that pick up pollution as the plant exhaust passes through them. RTOs are already installed on American cement plants, including TXI's huge Midlothian kiln just a few miles down Highway 67 from Holcim. On the other hand, up to now full-scale commercial SCR units have only been installed on European cement plants and in fact, the Portland Cement Association has lobbied long and hard to keep them out of the US for fear of raising the pollution control bar too high for all of the country's cement plants.
That's because SCR is more expensive to build and maintain than most cement plant control devices. But for the money, you get the Holy Grail of cement plant pollution control technology.
Most of the European cement plants that have SCR units install them to remove another type of pollution from their stacks – Nitrogen Oxides (NOx). If that sounds familiar, it's because NOx is a major smog-forming pollutant, and DFW has so much of it that the region has never been in compliance with the Clean Air Act standard for smog. And you'll never guess which facilities are the single largest sources of NOx pollution in North Texas. Or maybe you will: the Midlothian cement plants. That's why Downwinders at Risk has made it a point to campaign to require all three Midlothian cement plants – Holcim, TXI and Ash Grove – to install SCR….since all the way back in 2001, when the first European units were deemed a success at a German cement plant. SCR can remove 80 to more than 90% of all NOx coming out of a cement kiln. The 6500 tons of NOx a year that the Midlothian cement plants are permitted to release could be reduced to 650 tons with the application of SCR.
Now, as it turns out, SCR units are great not only at capturing large amounts of NOx pollution, but all kinds of other industrial pollution coming out of cement plants as well. Like THCs – up to 70% or so, but also Particulate Matter, Metals, Greenhouse Gases, Carbon Monoxide, and Dioxins. It's what's called a multi-pollutant control device because it does such a good job of eliminating a wide variety of nasty stuff from smoke stacks. This is what makes it the state-of-the-art technology for communities hosting kilns. In contrast, RTOs are single-purpose pollution devices aimed just at hydrocarbon removal and aren't designed to remove other kinds of emissions.
So even though Holcim is considering operating SCR because of its hydrocarbon problem, it would have a massive impact on the plant's air pollution across the board. And if Holcim were to set the precedent, the clock would begin ticking on bringing SCR to the other two Midlothian cement plants as well. It would only be a matter of time.
The public comment period for telling the state whether to accept or reject Holcim's permit application ends this Friday, July 11th at 5 pm. (If you're interested in jumping through the hoops to fill out the online form for official comments, you can go here and use Permit Number 8996)
Downwinders is submitting detailed comments praising Holcim for considering SCR, but urging the TCEQ to reject this permit because it's too vague and doesn't commit the company to any partciular technology, including SCR. We've also been collecting letters form local officials and stare legislators that urge Holcim to definitively choose SCR.
Now we're asking you to help us bombard both the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality and Holcim's US headquarters in Dundee Michigan in the next 48 hours with the same message to show public support for the company to do the right thing while rejecting a placeholder permit that doesn't commit it to do that right thing.
We want a permit request from the company that says Holcim will definitely install SCR, becoming the first commercial application of this state-of-the-art technology in America.
Using our "Featured Citizen Action" link, you can send such a message to Austin and Michigan in a matter of seconds right now. All you have to do is click here and then send the e-mails. We guarantee there's no more important or easier thing you can do for clean air in North Texas this week than sending these e-mails to the TCEQ Commisisoners and Holcim Corporate leadership. Please help us get the cement plant pollution control technology DFW deserves. It will only take a matter of seconds for you to help us achieve a goal we've been working toward for 14 years. We can do this. But we need your help. Now. Thanks.
EPA Scientists Say Current Smog Standard Not Protective Of Public Heath Even While TCEQ Blows Off Current One
 It's been a pretty nice summer in DFW so far hasn't it? Wetter and cooler than usual. More wind. According to the stats, this past month was the first June without any 100 degree days in seven years or so. Consequently, it's also the first June in forever that hasn't seen any "Orange" or "Red" ozone alert days. If this keeps up, DFW may actually come into compliance with the 1997 ozone standard of 85 parts per billion (ppb) over an 8-hour time period – a first as well.
It's been a pretty nice summer in DFW so far hasn't it? Wetter and cooler than usual. More wind. According to the stats, this past month was the first June without any 100 degree days in seven years or so. Consequently, it's also the first June in forever that hasn't seen any "Orange" or "Red" ozone alert days. If this keeps up, DFW may actually come into compliance with the 1997 ozone standard of 85 parts per billion (ppb) over an 8-hour time period – a first as well.
But unless you think "global weirding" is going to produce these kinds of summers routinely from here on out, there's little cause for comfort. This year's cleaner air is a direct result of cooler weather. Substitute the hellish summer of 2011 for this mild one and you'd be seeing ozone alerts filling up your e-mail box. As a result, it's not out of the question we could meet the standard this year, but flunk it in 2015 if the weather reverts back to "normal."
In addition, while we may come in under the 1987 smog standard for the first time, the public health goal posts have moved with better science. In 2008, the Bush Administration lowered the acceptable level of smog to 75 ppb. That's the goal of the clean air plan that Downwinders and other groups are fighting the state over right now, saying it's not adequate to even get to that 75 ppb level.
Texas Commission on Environmental Quality staff say we don't need to implement any major pollution control measures on cement kilns, power plants, or natural gas facilities to reach this 75 ppb goal by the deadline in 2018. All we have to do is sit back and let a new federal gasoline standard hit the market in 2017 and we'll all be fine – well, except for those millions of residents who'll be breathing-in smog greater than 75 ppb on the north and western side of the Metromess. But the TCEQ staff say we'll be "close enough." No harm, no foul say the folks from the agency where smog is not considered bad for you.
But close enough should only count in horseshoes and hand grenades, not what people breathe into their lungs. And while some of us are trying to make sure the new TCEQ plan is serious about reaching an air quality goal that's now six years old, the level of ozone considered "safe" by experts is once again going down.
In a letter to EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy last week, the Agency's own Clean Air Scientific Advisory Committee (CASAC) recommended a new smog standard of between 60 and 70 ppb, saying that there's a boatload of evidence showing that the 75 ppb level is not protective of human health, and even at 70 ppb there's significant public health harm done by bad air.
"At 70 ppb, there is substantial scientific evidence of adverse effects….including decrease in lung function, increase in respiratory symptoms, and increase in airway inflammation. Although a level of 70 ppb is more protective of public health than the current standard, it may not meet the statutory requirement to protect public health with an adequate margin of safety….our policy advice is to set the level of the standard lower than 70 ppb within a range down to 60 ppb…"
This recommendation was not unexpected. Every five years, the CASAC is legally obligated to review the scientific literature to make sure the federal ozone standard is giving adequate protection to public health. The last time it did so in 2008, the panel came to a similar conclusion to lower it somewhere between 65 and 70 ppb, but the Bush Administration ignored its own scientists and chose the higher standard instead. An Obama EPA was supposed to correct that mistake when it came into office, but then-EPA head Lisa Jackson got mugged on her way to the White House by the President's re-election campaign. Any changes were put on hold until that five year review clock began ticking again. And now the official alarm has gone off on that clock. The result is a re-affirmation of the earlier findings, this time with even more science to back up the changes.
As a result, EPA will have to decide whether or not to adopt the tougher recommendations of its scientists by December 1st of this year. If they do, a new standard will be officially adopted by 2015 and we'll have to write a new clean air plan in a couple of years to achieve that goal by the end of the decade. If it doesn't, they'll be sued, with the CASAC letter as exhibit #1, and they'll lose and have to set a new standard anyway.
Why is that important to the current debate over TCEQ's plan to meet the 75 standard? Because the TCEQ plan leaves at least four monitors, spread out from Denton, to Keller, to Eagle Mountain Lake above 75 ppb – a standard that EPA scientists now say conclusively is not protecting public health.
"Close enough" to that 75 ppb level turns out to be too far away from real protection in light of the new recommendations for a standard below 70 ppb from the Science Advisory Committee. And that assumes you believe the computer modeling TCEQ has done to support its plan. To date, the state is 0 for 5 going back to 1991 in being able to accurately predict these things. If history is any indication, the state's plan will fail to reach its goal of 75 ppb at just about every one of the 20 monitors in DFW, not just four.
If you know your target of 75 ppb of smog over an 8-hour period is no longer a safe standard, and your current plan condones levels above that, it's not really a clean air plan.
December is not only when EPA must decide if it's going to pursue a lower smog standard. It's also when the state is scheduled to take public comment on its current DFW anti-smog plan. So you have the surreal possibility of holding public hearings over the merits of an already obsolete plan that isn't even serious about reaching its obsolete goal.
This is why DFW residents must demand a plan from Austin that aims lower, not higher. It's why they must demand the EPA not allow TCEQ to get away with being "close enough" to a standard that's not protecting their health. A real clean air plan would be shooting for an average of 65-70 ppb knowing that that standard will be coming down the road sooner or later. A real clean air plan wouldn't allow any monitor to exceed the current 75 standard. A real clean air plan would try to do its best to protect public health by implementing pollution control measures on the sources of smog that are the cheapest and most effective to target – Midlothian's cement plants, east and central Texas coal plants, and the natural gas industry.
And that's exactly what Downwinders and other members of the new DFW Clean Air Network are trying to do. We're pushing for stricter EPA enforcement of the 75 ppb standard, and we're pushing for adoption of "Reasonably Available Control Measures" on the cement plants and gas compressors – now, not later. Because the only way DFW breathers are going to get a better clean air plan out of Austin and Washington is by organizing for one themselves.
Highlights from Monday: How the State Hides Gas Industry Pollution
 Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
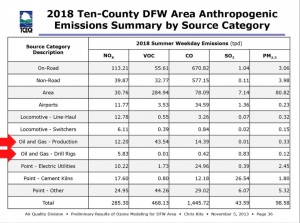
In the first you'll see how the state officially ranks all the "source categories" for human-made, or "Antrhopogenic," smog-forming Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) pollution in North Texas (all the numbers are Tons Per Day):
Yes the pic is fuzzy, (we can land a person on the Moon but can't seem to get charts to show up with a jpeg format online) but if you squint really hard, you'll notice there are two categories for Oil and Gas pollution numbers among the more traditional "Point Sources," Off-Road, "On-Road", etc – "Oil and Gas Production" and "Oil and Gas – Drill Rigs." Looking at these two categories you might think that adding them together would produce total Oil and Gas pollution numbers. You'd be wrong.
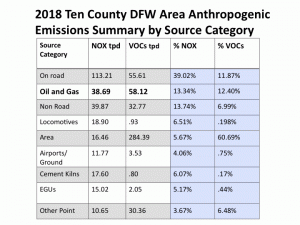
As it turns out, there are other Oil and Gas pollution numbers hidden away in other categories in this chart not labeled "Oil and Gas." For example, in both the "Area" and "Point-Other" categories are the numbers for NOx and VOCs pollution from gas compressors. But wait, you object, aren't gas compressors an integral part of any kind of "Oil and Gas Production?" Yes, yes they are. So why aren't they included in that category instead of being stuffed anonymously in these other categories? Great question. Perhaps it has something to do with the volume of pollution they release. Because when you finally wrestle the numbers from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (the TCEQ didn't voluntarily offer this information), compressor pollution turns out to double the amount of smog-forming NOx released from the Oil and Gas industry in the DFW 10-county "non-attainment area." And NOx pollution is what the TCEQ keeps saying is driving our chronic smog problem. Here's the way Schermbeck presented the same TCEQ "source categories" with the compressor numbers now teased out and added to the ones already identified as Oil and Gas: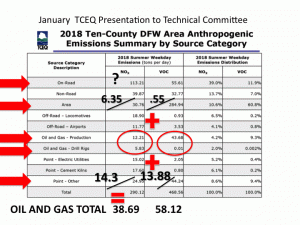
These additions raise the industry's polluter profile significantly. And that's what this next slide is doing. It's totaling all the Oil and Gas pollution and then re-ranking the categories based on these new numbers. Same totals, just different, and more honest, organization of the individual source figures. Instead of Oil and Gas emissions looking relatively small in relation to other sources like cement kilns and power plants and even locomotives, it escalates the Oil and Gas industry into one of the region's foremost industrial air polluters:
And even this much larger number is still underplaying the total amount of air pollution fracking adds to regional air quality because the state hasn't bothered to try to tease-out the "on-road" pollution that all those fracking waste and water trucks adds to the mix. State air modelers shrugged their shoulders and said they couldn't figure out how on earth to do that. Just by "Googling" the subject, Schermbeck found at least two previous studies that did that very thing – a 2005 Denton report and a 2013 Rand Corporation report that even estimated the amount of dust pollution raised by those trucks.
While those truck totals remain a mystery for now, using the TCEQ's own numbers, compressors make up at least 53% of the total NOx pollution released by the Oil and Gas industry in North Texas, and a full quarter of all VOC pollution released. According to Schermbeck, that's why they make such good targets for electrification, an air pollution control measure he was recommending as part of his larger presentation to the regional air planning committee on Monday.
This is just one example of the kind of duplicitous behavior the state of Texas is resorting to in trying to hide the true environmental and public health impact of the Oil and Gas industry. No slight of hand is too petty. Only by diligent digging by citizens is the truth coming out, ton by ton.
Schembeck's entire (unfuzzy) presentation is now online at the North Central Texas Council of Governments website as part of the June 16th agenda. It loses something without his accompanying narration but the jest of it is easily discerned for those who want to plod through it: TCEQ is doing anything but a sincere job of building a serious clean air plan for DFW. But then again, we bet you already knew that.
Rick Perry, with a Smoking Gun, in the COG Headquarters: Monday at 10 am
 The latest chapter in a decades old mystery game of "Get a Clue" happens tomorrow morning, Monday, June 16th when representatives of the Sierra Club and Downwinders at Risk present their case against the current state anti-smog plan during the regional air planning meeting at the headquarters of the North Texas Council of Governments, 616 Six Flags Road in Arlington. Come find out who and/or what keeps the DFW area from ever meeting federal clean air standards year after year and what can be done about it. The meeting starts at 10 am. Citizen groups are expected to do their presentations in the 11 to 12 hour. Then we'll all have a debriefing lunch at the Subway's down the street hosted by State Representative Lon Burnam. Y'all come.
The latest chapter in a decades old mystery game of "Get a Clue" happens tomorrow morning, Monday, June 16th when representatives of the Sierra Club and Downwinders at Risk present their case against the current state anti-smog plan during the regional air planning meeting at the headquarters of the North Texas Council of Governments, 616 Six Flags Road in Arlington. Come find out who and/or what keeps the DFW area from ever meeting federal clean air standards year after year and what can be done about it. The meeting starts at 10 am. Citizen groups are expected to do their presentations in the 11 to 12 hour. Then we'll all have a debriefing lunch at the Subway's down the street hosted by State Representative Lon Burnam. Y'all come.
Sierra Club Sues EPA Over Delayed “Bump Up” for DFW Smog Status
 DALLAS, TX – The U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) missed a key deadline in 2013 to classify smog air pollution in Dallas-Fort Worth as ‘severe,’ prompting the Sierra Club to file suit against the agency yesterday afternoon in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia for failing to properly act to protect the health of the people of North Texas.
DALLAS, TX – The U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) missed a key deadline in 2013 to classify smog air pollution in Dallas-Fort Worth as ‘severe,’ prompting the Sierra Club to file suit against the agency yesterday afternoon in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia for failing to properly act to protect the health of the people of North Texas.
The levels of smog in Dallas-Fort Worth are among the highest in the country, and only smoggy California, Houston and Baltimore have levels higher than North Texas. Ozone is the main ingredient in the smog in Dallas-Fort Worth. It triggers asthma attacks in children and is responsible for the red and orange bad air alert days the region sees every year.
“While we recognize that the Environmental Protection Agency has many priorities, nothing is more important than protecting our children from the dangers of smog and the asthma attacks that it can trigger,” said Dr. Neil Carman of the Lone Star Chapter of the Sierra Club. “The Clean Air Act has mechanisms in place to reduce pollution for areas with long-standing smog problems like Dallas-Fort Worth, but those mechanisms don’t get triggered unless EPA acts.”
The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) had a federal deadline to meet the public health standard by 2009, and when the state’s clean air plan failed to reduce pollution levels to meet the protective standards of the Clean Air Act, regulators received an extension to meet the standard by the end of the 2012.
State regulators again failed to develop a plan that would lower smog levels to protect people living in the region. After both failures, the law required EPA to classify Dallas-Fort Worth as having a “severe” ozone problem and publish the notice in the Federal Register in 2013. This action would have required polluters to take additional steps to clean our air. Unfortunately, U.S. EPA missed the deadline, prompting the Sierra Club to file suit late Tuesday, May 20, 2014.
"The Clean Air Act requires polluters to take extra steps in places like Dallas-Fort Worth that have been chronic violators of smog standards," said Jim Schermbeck with Downwinders at Risk, a clean air group based in Dallas-Fort Worth. "But asking Rick Perry to enforce the Clean Air Act in 2014 is like asking Wall Street tycoons to care about low-income families. That's why six million residents need the EPA to do its job and guarantee North Texas safe and legal air."
Because the EPA missed the 2013 deadline to properly classify the Dallas-Fort Worth area as a “severe” ozone smog area, industries are being allowed pollute more than they would otherwise, delaying the protections children, the elderly and people with respiratory illnesses in the region need.
"Today's action is the first step in requiring the EPA to finally solve the ozone problem in D-FW. Too many Texas children end up in the emergency room or miss school because of asthma and other breathing difficulties. We have to hold EPA to its legal requirements to give these families a chance to breathe easier," said Nia Martin-Robinson, Beyond Coal organizer with the Sierra Club in Texas.
Coal-fired power plants across Texas, cement plants in Midlothian and fracking in the Barnett Shale are significant contributors to smog-forming pollution to the region. State regulators have failed to require the most up to date pollution controls on these sources, contributing to the repeated failure of state clean air plans.
Thank You. Citizens Might Have Just Saved The Local Air Planning Process…From Itself
 A year from now, last Thursday' meeting in Arlington may be seen as a turning point.
A year from now, last Thursday' meeting in Arlington may be seen as a turning point.
Local residents refused to let the air quality planning process die, showing up in numbers that forced officials to switch to a larger room, and making sure their opposition to another state "do-nothing" air plan was heard loud and clear.
Their participation had already changed the day's agenda. Included was a breakthrough UNT study that directly challenges the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality's claim that natural gas emissions don't increase DFW smog.
UNT's Dr. Kuruvilla John's presentation of the new study received quite a bit of media coverage, before, during, and after Thursday's meeting. You can find some of the best coverage by clicking on the links below.
UT-Austin Study Reveals "Underestimates"
Dr. John's presentation influenced another researcher's slide show as well. Scheduled to speak about older, more generic ambient air measurements for ozone, Dr. David Allen of UT Austin instead presented more recent research into gas pollution as well.
Overlooked in the debut of the UNT study, Allen's constant monitoring of one drill site in Fort Worth revealed that the TCEQ was underestimating emissions from the pneumatic valves at the site by 159%.
That was news to both citizens and TCEQ, who said they hadn't looked at Allen's research and hadn't corrected their inventories to account for such underestimates. Valves like these are powered by natural gas, are quite numerous on gas equipment, and account for a large percentage of VOCs released from a fracking site.
A Better Picture of Oil and Gas Pollution
Citizen cross-examination of TCEQ staff members present at the meeting also revealed a different look at the volume of Oil and Gas industry pollution in the 10-county DFW "non-attainment area"
Up to Thursday, TCEQ was dispersing Oil and Gas pollution across several categories, making it impossible to show the true total impacts.
Here's an example of the way TCEQ likes to present the info:
SOURCES OF SMOG-FORMING NITROGEN OXIDE POLLUTION (NOx)
IN DFW's NON-ATTAINMENT AREA
1. "On Road" vehicles 113.21 tons per day
2. "Non-Road" vehicles" 39.87 tpd
3. "Area" 30.76 tpd
4. "Other Point Sources" 24.95 tpd
5. "Locomotives" 18.90 tpd
6. "Cement Kilns" 17.60 tpd
7. "Electric Utilities" 15.02 tpd
8. Oil and Gas Production 12.21 tpd
9."Airports" 11.77 tpd
10. Oil and Gas Drill Rigs 5.83 tpd
TOTAL 290.12 tpd
This makes it look like Oil and Gas pollution is not that big a deal.
But it turns out TCEQ is hiding 28.44 tpd of NOx gas compressor pollution in the "Area" and "Other Point Source" categories.
This was brought out in questioning on Thursday. Once you add these figures to the other Oil and Gas emission numbers spread out over different categories, this is what you get:
SOURCES OF SMOG-FORMING NITROGEN OXIDE POLLUTION (NOx)
IN DFW's NON-ATTAINMENT AREA
1. "On Road" vehicles 113.21 tpd
2. Oil and Gas Industry 46.48 tpd
3. "Non-Road" vehicles 39.87 tpd
4. "Locomotives" 18.90 tpd
5. "Cement Kilns" 17.60 tpd
6. "Area" 15.93 tpd
7. "Electric Utilities" 15.02 tpd
8. "Other Point Sources" 11.34 tpd
9. "Airports" 11.77 tpd
TOTAL 290.12
(Earlier today we put out an e-mail alert that left 10 tons off the "Area" category in this second chart, greatly affecting its ranking. That mistake is corrected in this version of the chart and we apologize for any confusion that might have caused)
When you quit playing the state's shell game with Shale pollution, the Oil and Gas industry becomes the region's second largest source of NOx pollution – the kind of pollution TCEQ says is the main driver of smog in DFW (not even counting all the pollution from O&G fracking trucks still hiding in the "On Road" category).
There have been control measures for cars to reduce NOx. There have been controls on heavy duty equipment and trucks to reduce NOx. There have been new controls on locomotives to reduce NOx pollution. There have been controls on airport ground equipment to reduce NOx pollution. There's even been middling controls to reduce the NOx from the Midlothian cement kilns. But where's the controls to reduce NOx from the Oil and Gas industry – the one source in this list that hasn't had the same kind of regulatory attention? Good question – save it for next time.
Citizen Participation is Crucial
This is the kind of close examination the TCEQ hopes to avoid by limiting debate on this new clean air plan, scheduled to be submitted to EPA by July next year. And it's exactly why citizens need to keep showing up.
Because of the momentum and interest coming out of Thursday's meeting, citizens also got the next scheduled pow-wow of the local air planning process moved up to late May or early June instead of waiting until July.
We're already taking suggestions for what you want to see on that agenda, so don't be shy. And thank you again for restoring some tiny amounts of integrity into a process that's been swamped by Rick Perry's indifference.
You're making a difference, and that's all anybody can do. This last Thursday it was a big difference. Let's try to do the same in May.
Some Coverage of Thursday's Air Planning Mtg.
Channel 8: "UNT researchers say fracking a contributor to North Texas smog problem"
Texas Observer: "Studies: Links Between Fracking and Smog Pollution Stronger Than State Claims"
Star-Telegram: "Natural Gas Production Contributing to Higher Ozone Levels, study Finds"
Denton Record Chronicle: "Officials: No New Plans to Clean Up Air"
HOW YOU CAN SAY "THANK YOU" BACK
Here's what Downwinders at Risk did this past week to make sure Thursday's air quality meeting wasa success:
1) Pressed for and got the UNT study linking fracking to smog on the meeting agenda after being told it would not be included.
2) Sent out releases to the media advertising the UNT presentation.
3) Sent out alerts to you and others to let you know about the new UNT study and the meeting itself.
4) Sent out a "Citizens' Guide to the Meeting" so you could be prepared for Thursday.
5) Showed-up at Thursday's meeting with handouts showing the lack of air quality progress in DFW and the lack of a complete plan by TCEQ
6) Used our questions to reveal how TCEQ was hiding Oil and Gas industry pollution totals in their data
7) Pressed for and got an earlier "next meeting" of the local air quality planning group
8) Sent out this follow-up so that everyone knows what went on and what the news is from the meeting
A local forum for clean air issues was about to disappear.
Only the last month's mobilization of citizens prevented that from happening on Thursday.
Who began that mobilization?
We did.
We really need your financial help to keep doing this. We don't get state or national funding – just local money from people like yourself.
Thanks. We very much appreciate it.
We Won a Small Victory – Now Come Take Advantage of It
 This is why citizen participation matters.
This is why citizen participation matters.
Last week, local officials were balking at reserving a slot at next Thursday's regional air planning meeting for a presentation by UNT researchers on how gas industry emissions from the Barnett Shale could be adding to DFW's chronic smog.
After reading about the UNT research in the Denton Record Chronicle, Downwinders at Risk and State Representative Lon Burnam specifically asked the local Council of Governments to include the UNT work on the agenda.
At first, we were told that there was already one technical presentation scheduled for the meeting and there wouldn't be any time for a second.
That struck us as strange, since in the past, every such meeting has always had more than one technical presentation.
When we pointed this out in an e-mail with links to past meeting agendas to prove the point, we quickly got a different response. Suddenly, there would be time for the UNT presentation.
That wasn't so hard was it? All it took was a little logical push back. But if we hadn't supplied it, Thursday would be looking a lot different.
Now, we're asking you to please come and help us push back a little more.
State environmental officials are on record as saying the air pollution from gas mining and production in the Barnett Shale is not adding to DFW's smog.
A lot of us think otherwise.
Come next Thursday, on the 17th, you can listen to the new UNT research on fracking air pollution and ask Texas Commission on Environmental Quality officials directly what makes them so sure that gas pollution isn't hurting local air quality.
Because the format of these regional clean air meetings are now so informal, anyone in the audience can ask questions of a presenter. That means you – if you show up.
It doesn't matter if you don't know the technical lingo. This is all about wind direction, weather, and things that pollute. There are no stupid questions.
The new anti-smog plan that the state is building needs all the public scrutiny it can get. It needs tough examination by people who care about clean air and the truth.
Next Thursday, you can help us put the state on the spot.
This is the first opportunity in 2014 to speak up and sound off about our decades-long smog problem. Don't let the TCEQ leave town without hearing from you.
We fought and won the right for you to listen to this research because we thought it was important. Won't you please come and take advantage of this victory?
We need a good showing to prove DFW residents are still mad about breathing dirty air.
NEXT THURSDAY, APRIL 17th
10 am to 12pm
North Central Texas Council of Government headquarters
616 Six Flags Drive
(After the meeting, State Representative Lon Burnam and Downwinders will be hosting a lunch time de-briefing, location to be decided, so stay tuned.)
Look, we know this is a small victory. But state officials don't want to talk about how gas industry pollution may be making our local smog worse, even though there's evidence that it is.
That's exactly why we think we need to keep bringing it up.
Winning the right to hear a new scientific presentation on the connection between gas pollution and smog may not seem like much of a win, but it is when the Powers-That-Be don't want you to hear it.
We know that small victories like this can lead to larger successes.
In the 1990's the same state agency that's now denying gas pollution has any impact on DFW smog was saying exactly the same thing about the Midlothian cement plants.
It took lots of push back from citizens who knew better before we got the state to admit it was wrong.
Now, Ellis County is in the DFW non-attainment area and the cement plants have controls on them they would otherwise never have.
We need the same effort in 2014 to show the state is as wrong about gas industry pollution as it was about the cement plants.
Right now, Downwinders is the only group committed to organizing citizens around clean air issues in DFW.
But we just lost a funding source that was critical to us and we need your help to keep the pressure on. This money paid for staff work in the field.It's very easy to give securely online here, or you can send checks to our P.O. Box at the bottom of the page.
We really need your help. Thank you.
2013 DFW Smog Report: Failure….Again
 (Dallas)— On the eve of constructing yet another DFW clean air plan, the 2013 Ozone Season ended on Thursday the same way the previous 16 have ended: with North Texas out of compliance with the 1997 federal clean air standard.
(Dallas)— On the eve of constructing yet another DFW clean air plan, the 2013 Ozone Season ended on Thursday the same way the previous 16 have ended: with North Texas out of compliance with the 1997 federal clean air standard.
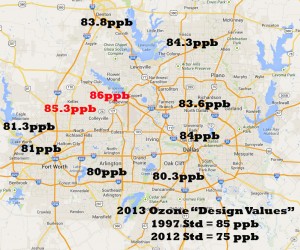
Even a mild summer with lower temperatures and more rain couldn't save the numbers from exceeding an illegal three-year running average of 85 parts per billion at monitors in Keller and Grapevine.
According to Jim Schermbeck with the clean air group Downwinders at Risk, what makes this year’s violation particularly troublesome is that the 1997 standard has been replaced with a more protective one that's 10 ppb lower. “For the next DFW air plan to succeed, it will have to reduce smog to levels that no DFW monitors have ever recorded. I don’t know anyone outside of Austin who thinks the state is up to that task.”
That new plan has its official kick-off event next Tuesday, November 5th, beginning at 9am in Arlington at the Council of Governments Headquarters. It's the first briefing from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality on the computer model it will be using to base the plan on. Everything about one of these plans is based on such a computer model, a model only the state can run. The plan must be submitted to EPA by June of 2015.
Even though extremely high ozone numbers were rarer this year, there were enough bad air days to cause the running averages of 10 out of 17 monitors, called "design values" to rise – not the kind of trend you want when you're next task is complying with a tougher standard.
Schermbeck was particularly concerned about a monitor near Mockingbird and I-35 in Central Dallas that’s seen its ozone average rise dramatically for three years in a row. “This is a monitor that had a "design value" of 67 parts per billion in 2010 – that is, it was in compliance with the new 75 ppb standard just three years ago. But now it’s up to 84 ppb and almost out of compliance with the 1997 standard. That's quite an increase in three years, and in a place where smog hasn’t been a problem for awhile.”
Every monitor inside the DFW metro area and even most "rural" monitors had a design value above the new standard of 75 ppb. Only Kaufman and Greenville made it under the wire, barely, with readings of 74 ppb.
As usual, the worst ozone levels were found in the northwest quadrant of the DFW area. This is a well-known historical pattern caused by the predominant southeast to northwest winds that blow pollution from the coast up through the coal and gas patches of East and Central Texas, over the Midlothian Industrial Complex and North Texas central urban cores into Northwest Tarrant Wise and Denton counties
This pattern has been the target of the last three state clean air plans, but has never been overcome. Schermbeck noted that last clean air plan to make a dent was the 2006 effort that produced lower numbers in steady fashion. Since 2008 however, air quality that was supposed to be getting better has gotten worse, or stagnated.
While cars have gotten cleaner during this time, and pollution from cement and coal plants has been reduced, there's one "source category" of pollution that's increased significantly since 2008: the gas industry.
In submitting the last DFW air plan to EPA in 2011, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality estimated there were more tons of smog-forming Volatile Organic Compounds being released by the gas industry in the official DFW "non-attainment area" than by all the cars and trucks on the road combined. That wasn't true in 2008.
Moreover, this is new air pollution in a smog non-attainment area that doesn't have to be off-set by reductions in pollution elsewhere in DFW. Unlike every other large industry, the gas industry is exempt from this offset requirement of the Clean Air Act.
Denton's Airport monitor's 4th highest reading of 85 ppb this summer, the one that officially counts toward its running average, was the highest such reading in the entire state, including Houston.
There's no doubt Denton is in the middle of the local gas patch, as are the Keller and Grapevine monitors that had the highest design values this year. Given the decreases in pollution from other categories, are gas patch emissions keeping these numbers from coming down they way they were supposed to? Austin keeps saying no, but the evidence is compelling.
Just last year there was a study out of Houston showing how a single flare or compressor station could significantly impact local ozone levels by as much as 5 or 10 ppbs. TCEQ itself just produced a study this last summer showing how Eagle Ford Shale gas pollution is increasing ozone levels in San Antonio.
Local Barnett Shale gas pollution might explain these Tarrant and Denton county monitors' problems, but they don't explain the rise in numbers of the Dallas monitors, since the wind during ozone season comes in from the south to southeast.
What new pollution is coming from that direction? Gas industry pollution from numerous compressor stations and processing plants stations in Freestone, Anderson, Limestone and other counties just about 90 to 100 miles south-southeast of Dallas. If one adds up all the emissions these facilities are allowed under their "standard permits." it exceeds the pollution from coal plants like Big Brown. That's a huge hit from sources that weren't there 10 years ago.
In effect, DFW is getting squeezed between gas pollution being produced in the middle of its urban areas, and gas pollution blowing in from the south.
“Officials with Rick Perry's TCEQ would rather drink lye than admit gas pollution is causing smog problems for DFW” says Schermbeck, “but such an admission might be the only way to bring DFW into compliance with the Clean Air Act.”
“This is why local DFW municipal and county governments serious about air quality must divorce themselves from Austin's politicized science and begin to seek their own solutions. Austin really isn't interested in solving DFWs chronic smog problems. Heck, the Commissioners who run TCEQ don't even believe smog IS a health problem.”
Take Another Hit – It Was the Best June for DFW Breathing Since 2007
 If this unseasonable cooler weather is making it seem like you're spending summer someplace other than DFW, it's also been the best "ozone season" in the region in seven years.
If this unseasonable cooler weather is making it seem like you're spending summer someplace other than DFW, it's also been the best "ozone season" in the region in seven years.
In the month that just ended, we only had four monitors on four days that violated the new 75 parts per billion smog standard that takes effect in 2018, and zero violations of the obsolete 1997 85 ppb standard. The maximum 8-hour reading was an 83 at the Denton Airport on June 3rd. Contrast that with last June: 54 violations of the 75 ppb standard and 27 violations of the 85 ppb standard over 9 days. Or 2011 – 24 violations of the 75 ppb standard, 7 violations of the 85 standard.
In fact, you have to go back all the way to 2007 when we had five violations of the 75 ppb standard but no "exceedences" of the 85 ppb, to find as good a June for air quality as we just had. And there are only a couple of other Junes – in 2010 and 2000 that even come close to being as full of safe and legal air. That's the good news.
The bad news is that these years were all followed by worsening air quality trends, that is, they turned out to be aberrations. So if this pattern holds, we'll have to wait until next summer to put it in context. As always, weather has a lot to do with how bad or good our ozone season is. The cooler and wetter, the better. The dryer and hotter, the worse. Just as this summer's cooler temps seem like they're out of place, by next June we could be thinking the same thing about our reprieve from smog.
The good news is that there's no questions that declining emissions in almost every category (we're looking at you oil and gas) have had a positive impact on the numbers. That's your doing. After 20 years of citizen effort, there's a lot less pollution from the cement plant complex in Midlothian, the coal plant belt in East Texas, and the millions of vehicles on and off the road.
For the EPA and the state, 2013 comes a year too late to help them recover from a terrible 2011 "clean air plan" that was supposed to get us down below 85 ppb by watching people purchase new cars. The clock officially ran out on that plan June 15th. Sales of new vehicles are dramatically up, so there's real displacement as old gas guzzlers get traded in for more efficient models. Whether those trade-ins are enough to cancel out the still-exploding growth rate of the area and rising gas and oil activity remains to be seen. That's why the EPA uses a three-year rolling average to determine transgressions against the Clean Air Act, to minimize the impact of anomalies.
You're just going to have to stay tuned to find out whether the summer of 2013 is the exception to the rule, or the re-writing of the rules.