Posts Tagged ‘DFW SIP’
Going Backwards: DFW’s Annual Smog Average Went Up Twice in Two Days Last Week
 State officials and industry PR types thought they'd caught a break last summer when two things produced a much lower annual smog average, called a "Design Value."
State officials and industry PR types thought they'd caught a break last summer when two things produced a much lower annual smog average, called a "Design Value."
Since it's a three-year rolling average of smog numbers, past years roll off as new ones come on. Smog numbers from 2011 that had been so high they'd sent the average soaring, were finally rolling off and wouldn't be included in the average.
Second, unusually cooler temperatures and rain kept a new round of numbers lower. Combined, these factors resulted in a significant decrease in the smog average for 2014.
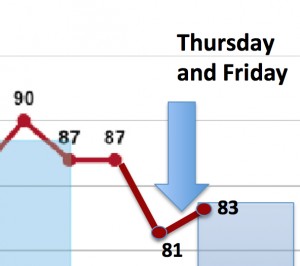
But in 2015, a more typical summer, or at least August, is bringing the average back up (Over 60% of the 100 highest recorded levels of smog this summer occurred in the last 30 days). Smog levels are higher across the board this year than last. There are more monitors recording more "exceedences" of the national smog standard. Leading them all is the Denton monitor, which saw ozone levels rise on Thursday and then skyrocket on Friday. The numbers were so high on both days they moved the needle of the annual smog average, the DFW Design Value, up from 81 to 82 parts per billion (ppb) on Thursday and up to 83 ppb on Friday. The standard is 75 ppb.
Even though Houston has recorded higher smog numbers than DFW this year, 2014's lower smog numbers was even more anomalous for that city than for North Texas. Last year's much lower numbers in the Bayou City are canceling out this year's much higher numbers. So that in 2015, DFW's Denton monitor's annual average of 83 ppb is the highest in the State of Texas.
And that means that according to the official accounting of the Clean Air Act, DFW has dirtier air than Houston. And not for the first time.
It also means we're rolling backwards in terms of air quality progress. With at least a whole month of "ozone season" to go, DFW's smog average is now only a little lower than it was in 2009. It would only take one or two more bad days to raise the average again.
This is the second time in four years that DFW's smog average has increased during the implementation of a state clean air plan for the area. Neither plan required new controls on large industrial polluters significantly contributing to the problem, like the gas industry, East Texas coal plants, and Midlothian cement kilns. There may be some connection there.
Given the state's stellar two decade-old track record of never meeting a clean air plan deadline, its latest plan was always likely to fail. But a federal court roll back of the deadline to get to the 75 ppb standard at all DFW monitors, from 2018 to 2017, plus these new 2015 smog numbers, make it DOA in the real world.
However, in the regulatory world governing these things officially, the plan is still being reviewed by the EPA and, believe it or not, could get approved if citizens don't make a big stink.
That's why you need to sign our Change.org petition to EPA to reject the state's plan and send an email to EPA officials requesting they write a new clean air plan instead of the state of Texas.
Many clean air advocates cautioned that 2014 should be seen as a outlier, and this summer is justifying that caution. If the experts are right, climate change will mean future summers will be more like 2011 than 2014. We've got to have a more realistic approach to the goal of safe and legal air. The State of Texas will not provide that. EPA can.
Citizens To Form Posse, Demand State Enforce the Clean Air Act at Thursday Hearing on New DFW Air Plan
 (Arlington) Critics of a new plan to clean the air in Dallas-Ft. Worth are using a public hearing on Thursday evening to accuse the state of Texas of breaking the law by not requiring the implementation of pollution control technologies already in widespread use to help lower smog levels in North Texas.
(Arlington) Critics of a new plan to clean the air in Dallas-Ft. Worth are using a public hearing on Thursday evening to accuse the state of Texas of breaking the law by not requiring the implementation of pollution control technologies already in widespread use to help lower smog levels in North Texas.
“We’re asking residents to come out and get sworn into a citizens posse to help us make the state follow the Clean Air Act,” said Jim Schermbeck, Director of the local clean air group Downwinders at risk, one of the leading opponents of he new plan. “Austin is going to ridiculous, Monty Python-like lengths to avoid new controls on the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas coal plants, and local gas facilities in this new plan – even though those controls are now commonplace in each industry.”
Thursday’s public hearing centers on a new plan to comply with the federal ozone standard of 75 parts per billion (ppb) by 2018. DFW has never achieved such a low level of smog, and only this last year dipped below the 1997 standard of 85 ppb for the first time with the help of cooler, wetter summer.
EPA says a state plan like the one the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality is proposing for DFW must include “all Reasonable Available Control Technologies,” and “all Reasonable Available Control Measures” to get lower smog levels as “expeditiously as possible.” EPA defines these as technologies as ones that are “technically and economically feasible.” But according to Schermbeck, the state of Texas is deliberately ruling out local use of pollution controls already adopted by industry that could speed cleaner air.
He cited three examples. Selective Catalytic Reduction, or SCR acts much like the catalyst on cars, only on a much larger scale for industrial plants. It’s already in use on at least half a dozen European cement plants where it’s reduced smog-forming pollution by up to 90%, and on many coal-fired power plants across the world and in the US, where it achieves the same results. Yet the TCEQ DFW air plan doesn’t require SCR on the largest single sources of smog pollution in the region, the Midlothian cement plants, or the East Texas coal plants that are known to impact DFW air quality, saying the technology isn’t “feasible.” TCEQ maintains this stance even though the Holcim cement plant in Midlothian has announced plans to include an SCR unit on one of its own kilns.
“Here’s a pollution control technology already in operation and achieving great results, with a cement plant in North Texas already adopting it, but the state’s position is that it isn’t ‘feasible’. It’d be comical if it wasn’t delaying cleaner air for over 6 million people that haven’t had it in decades.”
Besides ignoring SCR on cement and coal plants, Schermbeck said the TCEQ has also ruled-out electrification of large gas compressors as “infeasible” – despite the widespread use of electric compressors In the Barnett Shale already and the requirement of municipalities like Dallas and Southlake to allow nothing but electric compressors within their city limits. According to a 2012 study by the Houston Advance Research Consortium, compressors could increase downwind ozone levels as much as 3 to 10 parts per billion. There are at least 647 large compressors in the DFW “non-attainment area” covered by the TCEQ air plan.
“Requiring just these three technologies that are already on the market and being used in their respective industries could reduce air pollution by thousands of tons a year and help us achieve compliance with the new federal ozone standard much quicker,“ said Schermbeck. He said they all pass the test of being feasible according to EPA definitions. “By law, they should be required.”
Instead, the state is relying exclusively on a new federal gasoline mix being introduced in 2017 to achieve the required 75 ppb standard by 2018. Although it’s expected to help lower ozone levels across the country, it won’t get DFW down to the level of 75 ppb alone. To make the plan work on paper, the state has had to estimate oil and gas pollution downward in a way Schermbeck and others claim is unrealistic.
“Basically, the state’s approach is to do absolutely nothing for the next three years and hope the federal gasoline change brings it “close enough” to the lower standard. But hope is not a plan.”
Schermbeck said his group would be passing out badges to members of their clean air posse and recruiting residents to persuade the EPA to reject the state’s proposal. The federal agency has the final say. But there’s also always court – where many clean air rules for the state of Texas have been decided over the last 20 years. “If government won’t enforce the law, we may have to do it ourselves.”
TCEQ’s Terrible, Horrible, No Good, Very Bad Air Plan for DFW

TCEQ Public Hearing on the new DFW Anti-Smog Plan
Thursday, January 15th 6:30 pm
Arlington City Hall, 101 W. Abram
Over the last two decades, we've seen some pretty lame DFW clean air plans produced by the state, but the newest one, scheduled for a public hearing a week from now, may be the most pathetic of the bunch.
From a philosophical perspective, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality stopped pretending to care about smog in DFW once Rick Perry decided to run for president around 2010 or so. Computer modeling was scaled back, staff was slashed, and the employees that were left had to be ideologically aligned with Perry's demand that no new controls on industry (i.e potential or existing campaign contributors) was preferable to six or seven million people continuing to breathe unsafe and illegal air.
TCEQ's 2011 anti-smog plan reflected that administrative nonchalance by concluding – in the the middle of the Great Recession – that consumers buying new cars would single-handedly deliver the lowest smog levels in decades. It did not. It went down in history as the first clean air plan for the area to ever result in higher ozone levels. The first, but maybe not the last.
This time around, it's not the cars themselves playing the role of atmospheric savior for TCEQ, but the fuel they'll run on. Beginning in 2017, the federal government is scheduled to introduce a new, low-sulfur gasoline that is predicted to bring down smog by quite a bit in most urban areas. Quite a bit, but not enough to reach the ozone standard of 75 ppb that's necessary to comply with the Clean Air Act by 2018. It's the gap between this official prediction and the standard where the state is doing a lot of hemming and hawing.
TCEQ staffers really did tell a summertime audience in Arlington that that estimated 2018 gap of between 1 and 2 ppb was "close enough" to count as a success. Now, you might give them the benefit of the doubt, but remember this is an agency that has never, ever been correct is its estimation of future ozone levels. After five attempts over the last two decades, TCEQ has never reached an ozone standard in DFW by the official deadline. Precedent says this plan won't even get "close enough."
Plus, we know getting "close" to 75 ppb isn't protecting public health in DFW. Even as this clean air plan is being proposed by Austin, the EPA is moving to lower the national ozone standard to somewhere between 60 and 70 ppb (There's a hearing on that at Arlington City Hall on January 29th). That new EPA ozone standard is due to be adopted by the end of this year. So this entire state plan is obsolete from a medical perspective. Instead of aiming for a level of ozone pollution closer to 70 ppb as soon as possible, it's not even getting down to a flat 75 ppb at all DFW monitors by 2018. It wil take an entirely new plan, and pulling TCEQ teeth, to do that much later. In other words, millions of people will have to wait as much as a five to seven years longer to get levels of air quality we know we need now in 2015.
What are the major flaws this time?
1. TCEQ is Using 2006 in 2014 to Predict 2018.
The EPA recommends that states use an "episode" of bad air days from the last three years – 2009-2013 – in trying to estimate what ozone levels will be three years from now. The more recent the data, the better the prediction.
TCEQ is ignoring that recommendation, relying on a computer model that's already nine years old. This has all kinds of ramifications on the final prediction of compliance. Instead of having more recent weather data, you have to "update" that variable. TCEQ doesn't have to compensate for the drought DFW is experiencing now or factor in a year like 2011 where the drought caused a worst case scenario for ozone formation.
TCEQ isn't using more recent data on how sensitive monitors are to Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) – the major kinds of pollution that cause smog . That's important because gas production in the Barnett Shale has put a lot more VOCs in the air. But instead of getting a more accurate post-drilling boom read on what's driving smog creation, the TCEQ is relying on a picture that starts out before the boom ever started.
The further you reach back in time for a model to predict future levels of smog, the fuzzier that future gets, and the less accurate the results. TCEQ is using a model that's twice to three times older than EPA guidance recommends. What are the odds that TCEQ estimates will be correct based on this kind of methodology?
2. TCEQ is Downplaying OIl and Gas Pollution
Citizens attending the air quality meetings in Arlington over the past year have seen the TCEQ try and hide the true volume and impact of oil and gas pollution at every turn. Instead of all the industry emissions being listed under the single banner of "Oil and Gas Pollution," the Commission has tried to disperse and cloak them under a variety of categories in every public presentation.
"Other Point Sources," a classification that had never been seen before, was the place where pollution from the 647 large compressor stations in DFW could be found – if you bothered to ask. "Area Sources" was where the emissions from the thousands of other, smaller compressors could be found – again, only if you asked. "Drilling" was separate from "Production." And despite other agencies being able to tease out what kind of pollution came from the truck traffic associated with fracking within their jurisdictions, the TCEQ never bothered to estimate how much of the emissions under "Mobile Sources" was generated by the Oil and Gas industry.
The reason the TCEQ has tried so hard to hide the true volumes of oil and gas pollution is because once you add up all of these disparate sources, the industry becomes the second largest single category of smog-forming pollution in DFW, second only to on-road cars and trucks (and remember many of those trucks are fracking-related). According to TCEQ's own estimates, oil and gas facilities in North Texas produce more smog-forming VOC pollution than all of the cars and trucks in the area combined, and more smog-forming NOx pollution than the Midlothian cement plants and all the area's power plants combined.
TCEQ is loathe to admit the true size of these emissions and place them side-by-side next to other, traditional sources, lest the public understand just how huge a impact the oil and gas industry has on air quality. Austin's party line is that this pollution isn't contributing to DFW smog – that it's had no impact on local air quality. But such a claim isn't plausible. If cars are a source of smog, and cement kilns and power plants are a source of smog, how can a category of VOC and NOx pollution dwarfing those sources not also be a source of smog? Think how much less air pollution we'd have if the Barnett Shale boom of the last eight years had not taken place?
In it's last public presentation in August, the TCEQ made the impact of oil and gas pollution clear despite itself. According to the staff, oil and gas emissions were going to be decreasing in the future more than they had previously estimated. As a result, a new chart showed that certain ozone monitors, including the one in Denton, would see their levels of smog come down significantly. It was exactly the proof of a causal link between gas and smog that TCEQ had been arguing wasn't there. Only it was.
In terms of forecasting future smog pollution, TCEQ is underplaying the growth of emissions in the gas patch. Everything it's basing its 2018 predictions on is years out-of-date, leftover from its last plan.
Drilling rig pollution is extrapolated from a 2011 report that counts feet drilled instead of the actual number of rigs. TCEQ predicts a decline in drilling and production in the Barnett Shale without actually estimating what that means in terms of the number of wells or their location. It also assumes a huge drop-off in gas pollution after 2009 that hasn't been documented by any updated information. It's only on paper.
While recent declines in the price of oil and gas have certainly put a damper on a lot of drilling activity, there's still a significant amount going on. Look no further than Mansfield, where Edge is now applying for permit to build a new compressor and dozens of new wells on an old pad.
In 2011, nobody was building Liquified Natural Gas terminals up and down the Gulf Coast for an export market the way they are now. Analysts say those overseas markets could produce a "second boom" in drilling activity between now and 2018, but the TCEQ forecasts don't take that into account.
Gas production pollution numbers – emissions from compressors, dehydrators, storage tanks – are even more tenuous. Every gas industry textbook explains that as gas plays get older, the number of lift compressors increases in order to squeeze out more product. Increase the number of compressors and you increase the amount of compressor pollution. But TCEQ numbers fly in the face of that textbook wisdom and predict a decline in compressor pollution because wells in the Barnett Shale are getting older!
The best analogy for how TCEQ is estimating oil and gas pollution is its poor understanding of where those thousands of smaller compressor are and how much pollution they're actually producing. No staff member at TCEQ can tell you how many of those compressors there are in the region – they literally have no idea and no idea of how to count them in the real world. There are just too many, their locations are unknown, and they were never individually permitted.
Instead, the TCEQ takes production figures from the Railroad Commission and guesses how many of those small compressors there are, as well as their location, based on where the RRC tells it production is going on in the Shale. Then staff guesses again about the emissions being emitted by those compressors, because there's no data telling them what those emissions actually are. In the end you have a series of lowballed guestimates, stacked one atop the other, presented as fact. It's smoke and mirrors.
3. TCEQ Isn't Requiring Any New Controls on Any Major Sources of Air Pollution
Like its previous 2011 DFW air plan, which resulted in an increase in North Texas ozone levels, TCEQ's new plan requires no new controls on any major sources of air pollution, despite evidence showing that such controls in smog-forming emissions from the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas coal plants, and Barnett Shale gas facilities could cut ozone levels significantly.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is already used extensively in the cement plant industry in Europe to reduce smog pollution by up to 90%. Over a half dozen different plants have used the technology since 2000. The TCEQ's own 2006 report on SCR concluded it was "commercially available." Holcim Cement has already announced it will install SCR in its Midlothian cement plant. Yet the TCEQ makes no mention of this in its plan.
That's right, a cement plant in Midlothian has decided SCR is commercially viable, but the State is looking the other way and pretending this development in its own backyard isn't even happening. TCEQ is stating in its proposed plan that SCR just isn't feasible!
In 2013, a UTA Department of Engineering study looked at what happened if you reduced Midlothian cement plant pollution by 90% between 6 am and 12 Noon on weekdays. Ozone levels went down in Denton by 2 parts per billion. That may not seem like a lot, but in smog terms it's the difference between the Denton air monitor violating the 75 ppb standard under the TCEQ plan and complying with the Clean Air Act.
In 2012 a UTA College of Nursing study found higher rates of childhood asthma in Tarrant County "in a linear configuration" with the plumes of pollution coming from the Midlothian cement plants. SCR means less pollution of all kinds: smog, dioxins and the particulate matter the Nursing College thought was causing those increased rates of childhood asthma. By delaying the requirement that all the Midlothian cement plants install SCR by 2018, the state is turning its back on a problem that Cook Children's hospital described as "an epidemic."
The same is true of SCR in the East Texas coal plants. The technology is being used in other coal plants around the world and in the US to reduce smog pollution. There's no reason it shouldn’t be required for the dirtiest coal plants in Texas that impact DFW air quality. After decades of being out of compliance with the Clean Air Act, DFW is one of the places the technology is needed most.
Last year the Dallas County Medical Society, led by Dr. Robert Haley, petitioned the TCEQ to either close those coal plants or install SCR on them. The doctors' petition was rejected by TCEQ Commissioners and they were told their concerns would be addressed in the DFW air plan. They aren't. Those concerns, along with the proof they presented about the impact of the plants on local air quality, are being ignored.
Electrification of gas compressors is a commonly used technology that could cut smog pollution as well, and yet the TCEQ is not requiring new performance standards that would force operators of hundreds of diesel and gas-powered compressors in North Texas to switch to electricity.
A 2012 Houston Advanced Research Center study found that pollution from a single compressor could raise local ozone levels by as much as 3 to 10 ppb as far away as ten miles. There are at least 647 large compressor stations in the western part of the DFW area. Dallas and other North Texas cities have written ordinances requiring only electric-powered compressors within their city limits based on testimony from industry that electrification was a commonly used technology in the industry. And yet, TCEQ's official position is that electrification isn't feasible.
In ignoring these types of new controls the TCEQ is violating provisions of the Clean Air Act to implement "all reasonably available control technologies and measures" to insure a speedy decrease in ozone levels. Each of these technologies is on the market, being used in their respective industries, and readily available. Studies have shown that each of these technologies could cut ozone levels in DFW significantly, but the TCEQ is refusing to implement them. In doing so, many observers believe it's blatantly in violation of the law.
We don't expect TCEQ to change its position. That well has been poisoned for the foreseeable future. But we do expect a higher standard of enforcement from the Obama Administration EPA. That's why we're asking you to show-up at the public hearing and oppose this dreadful state air plan a week from now in Arlington. We need to demonstrate to the federal government that citizens are concerned about getting cleaner air now, not in the next plan or the one after that. Now. We need to put pressure on the EPA to reject this TCEQ plan, to either send it back to the drawing board or substitute one of its own. Without you showing up, that pressure isn't there.
Between now and Thursday – and all the way through January 30th, you can send prepared comments opposing the TCEQ plan to Austin and the EPA Regional Administrator with a simple click here – and add your own comments as well.
As a reward for coming over and venting your frustration, we'd like you to stay and party with us at the official "retirement party" of State Representative Lon Burnam, beginning at 7:30 pm just four blocks down the street. It's a roasting and toasting of the best friend environmentalists ever had in the Texas Legislature, as well as a fundraiser for Downwinders to continue our work to defend your air. JUST CLICK HERE FOR TICKETS.
Next Thursday you can support clean air two ways in one evening. Help us beat back a terrible, horrible, no good, very bad air plan, and then come celebrate the wonderful, righteous, very good work of a dedicated public servant. See you there.
Power of the Press: Week after Trib Report on DFW Smog, First “Exceedences” of 1997 Standard
 It was only eight days ago the that online Texas Tribune did the first real overview of DFW air quality for this "ozone season." Borrowing heavily from the June 16th Downwinders at Risk presentation to the North Texas regional air quality committee, it concluded that there had been no discernible progress in regional air quality for the past five to six years despite a new state anti-smog plan aimed at getting the area below the 1997 standard of 85 parts per billion.
It was only eight days ago the that online Texas Tribune did the first real overview of DFW air quality for this "ozone season." Borrowing heavily from the June 16th Downwinders at Risk presentation to the North Texas regional air quality committee, it concluded that there had been no discernible progress in regional air quality for the past five to six years despite a new state anti-smog plan aimed at getting the area below the 1997 standard of 85 parts per billion.
Ironically, up to that point, DFW had been enjoying one of the wettest, coolest, most ozone alert-free summers on record. Not one 100 degree day until July and only one "bad air" days of note on June 11th. It looked like we might actually be able to meet the 1997 standard of 85 ppb for the very first time.
That's all changed with this past weeks' return to familiar form. In just seven days, they've been at least four official "ozone alerts" issued for DFW by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality. Those had produced four "exceedences" of the current 75 parts ppb standard, which the state is now aiming at with another "do nothing" plan under development and due out by the end of the year. On Wednesday the trend got more serious with the addition of the first two "exceedences" of the older 1997 standard we can't seem to conquer – a reading of 88 ppb at the NW Fort Worth monitor at Meacham Field and a 91 at the usually quiet Granbury monitor in Hood County. In the latter case, one mid-afternoon hourly reading reached as high as 113 – just 12ppb short of a violation of an even more ancient standard left over from the 1980's.
For comparison's sake, EPA scientists just sent a letter to EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy recommending that a new, lower federal standard for ozone be set at 60-70 ppb.
It will still take another week of 85 ppb plus days to produce the "fourth highest" readings at the Denton or Keller sites to combine with their 2013 averages and keep DFW in violation of a 17-year old ozone standard. But then again, we have all of August and September to go.
Not surprisingly, two of this summer's hot spots include traditionally troublesome monitors – the Denton and NW Fort Worth site. Tarrant and Denton Counties have historically been the places where the region's highest readings have originated. One reason is wind direction – smog accumulates from upwind sources like the Midlothian cement plants and blows Northwest during the summer. Another more recent reason is the mining of Barnett Shale gas deposits that release huge quantities of smog-forming pollution in the western half of the Metromess, a phenomenon that's been examined in a new UNT study that divided the region's ozone monitors into "Fracking" and "Non-Fracking" areas and found significantly higher readings among those in the Fracking area.
As we went to press with this post, Thursday's readings looked to be producing another round of 75 ppb or higher results. Adding to this year's ozone season irony is that over the last 20 years, July has traditionally been the summer month that produced the fewest number of high ozone readings, book-ended by higher numbers in June and August-September.
Depending on the weather, DFW may still be able to make it over the 1997 standard, 85 ppb hump. But based on this past week's results, that hump just got bigger. Stay tuned.
Highlights from Monday: How the State Hides Gas Industry Pollution
 Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
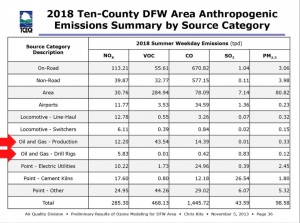
In the first you'll see how the state officially ranks all the "source categories" for human-made, or "Antrhopogenic," smog-forming Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) pollution in North Texas (all the numbers are Tons Per Day):
Yes the pic is fuzzy, (we can land a person on the Moon but can't seem to get charts to show up with a jpeg format online) but if you squint really hard, you'll notice there are two categories for Oil and Gas pollution numbers among the more traditional "Point Sources," Off-Road, "On-Road", etc – "Oil and Gas Production" and "Oil and Gas – Drill Rigs." Looking at these two categories you might think that adding them together would produce total Oil and Gas pollution numbers. You'd be wrong.
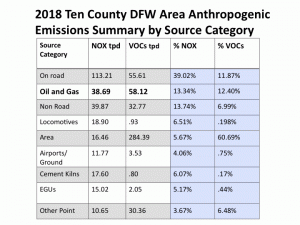
As it turns out, there are other Oil and Gas pollution numbers hidden away in other categories in this chart not labeled "Oil and Gas." For example, in both the "Area" and "Point-Other" categories are the numbers for NOx and VOCs pollution from gas compressors. But wait, you object, aren't gas compressors an integral part of any kind of "Oil and Gas Production?" Yes, yes they are. So why aren't they included in that category instead of being stuffed anonymously in these other categories? Great question. Perhaps it has something to do with the volume of pollution they release. Because when you finally wrestle the numbers from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (the TCEQ didn't voluntarily offer this information), compressor pollution turns out to double the amount of smog-forming NOx released from the Oil and Gas industry in the DFW 10-county "non-attainment area." And NOx pollution is what the TCEQ keeps saying is driving our chronic smog problem. Here's the way Schermbeck presented the same TCEQ "source categories" with the compressor numbers now teased out and added to the ones already identified as Oil and Gas: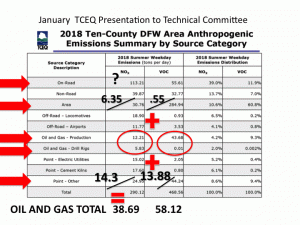
These additions raise the industry's polluter profile significantly. And that's what this next slide is doing. It's totaling all the Oil and Gas pollution and then re-ranking the categories based on these new numbers. Same totals, just different, and more honest, organization of the individual source figures. Instead of Oil and Gas emissions looking relatively small in relation to other sources like cement kilns and power plants and even locomotives, it escalates the Oil and Gas industry into one of the region's foremost industrial air polluters:
And even this much larger number is still underplaying the total amount of air pollution fracking adds to regional air quality because the state hasn't bothered to try to tease-out the "on-road" pollution that all those fracking waste and water trucks adds to the mix. State air modelers shrugged their shoulders and said they couldn't figure out how on earth to do that. Just by "Googling" the subject, Schermbeck found at least two previous studies that did that very thing – a 2005 Denton report and a 2013 Rand Corporation report that even estimated the amount of dust pollution raised by those trucks.
While those truck totals remain a mystery for now, using the TCEQ's own numbers, compressors make up at least 53% of the total NOx pollution released by the Oil and Gas industry in North Texas, and a full quarter of all VOC pollution released. According to Schermbeck, that's why they make such good targets for electrification, an air pollution control measure he was recommending as part of his larger presentation to the regional air planning committee on Monday.
This is just one example of the kind of duplicitous behavior the state of Texas is resorting to in trying to hide the true environmental and public health impact of the Oil and Gas industry. No slight of hand is too petty. Only by diligent digging by citizens is the truth coming out, ton by ton.
Schembeck's entire (unfuzzy) presentation is now online at the North Central Texas Council of Governments website as part of the June 16th agenda. It loses something without his accompanying narration but the jest of it is easily discerned for those who want to plod through it: TCEQ is doing anything but a sincere job of building a serious clean air plan for DFW. But then again, we bet you already knew that.
The Biggest Fracking Fight That Isn’t Being Fought – DFW Air Plan Mtgs This Month
 Since fights over fracking began in the Barnett Shale, they've been mostly fights over specific permits, leases, or rules fought in one city at a time.
Since fights over fracking began in the Barnett Shale, they've been mostly fights over specific permits, leases, or rules fought in one city at a time.
Other than an occasional trip to Austin or DC to stop or support some piece of legislation, the action takes place in whatever community is putting up the most resistance. Front lines are fragmented and move around a lot. There's not a single cause that's united the energy from the multitude of ad hoc groups and individual "fracktivists" into a focused campaign for regional change. The closest thing to more encompassing battles have been the recent victories in Dallas and the current kickass campaign in Denton. These feel like old Cold War skirmishes – proxy clashes standing in for the on-going larger war over the Barnett Shale's soul.
But from now until the summer of 2015 there's a regional fracking fight waiting to be fought. It involves new bureaucracies and terms and mechanics, so it makes a lot of traditional fracking foes nervous. But the payoff is the potential to affect change throughout a 10-county area, including the heart of the urban Barnett Shale – Tarrant, Parker, Denton, Johnson, Wise and Ellis – as well as Dallas, Collin, Kaufman, and Rockwall.
What's the fight? It's over the new regional anti-smog plan, called a State Implementation Plan, or SIP. When a region hasn't met the federal standard for smog, also called ozone, it has to submit a plan to the EPA to explain how it's going to comply by the end of a three-year deadline. Despite at least three previous plans, DFW has never met the 1997 federal standard for smog. It's 85 ppb, or "parts per billion" concentration over 8 hours measured by approximately 20 stationary monitors scattered over the area. The closest we've come has been 86 ppb of ozone in 2009.
The new DFW plan is supposed to be designed to meet an even more ambitious target – no monitor higher than a three-year running average of 75 ppb of ambient air by 2018. We're at 87 ppb now. To reach the new goal, DFW would have to drop 12 parts per billion in ambient smog levels in four years -something that's never happened before.
Ozone/smog is created by a combination of Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) from combustion sources and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from combustion sources and evaporation sources mixing in daylight. The more sun, the more ozone.
What are combustion sources of NOx and VOCs? Power plants and cement kilns. Every boiler and furnace and oven. Every internal combustion engine. Every diesel engine. Anything with a flame or a spark.
What are evaporation sources of VOCs? Gasoline pumps,tanks and paint shops.
An anti-smog plan is supposed to look at all the sources of smog-forming pollution in a region and find the cheapest and easiest ways to reduce it. Past plans have been responsible for putting more controls on coal-fired power plants and the Midlothian cement plants, as well as creating HOV lanes and tightening inspection standards for vehicles. But one large category of smog-forming emissions has been left largely untouched by past air plans – the gas and oil industry.
It's not because gas and oil sources aren't capable of contributing to DFW smog. Start with all the trucks that are needed for each well and the NOx and VOC emissions they produce. Then the drilling rig itself. Some cities now require electric motors, others still allow diesel and the NOx and VOCs they produce. Think about all the chemicals being dumped into a well and then flowing back out, many of them VOCs. Flares are sources of both NOx and VOCs. Storage tanks and pipelines are huge sources of escaped evaporated VOCs. Diesel compressors are huge sources of NOx. There isn't a part of the oil and gas fuel cycle that doesn't produce smog-forming pollution.
It's not because the oil and gas emissions are insignificant. In 2011, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality estimated that the VOCs being released by all the oil and gas facilities in the DFW area were greater than the volume of VOCs being released by all the cars and trucks on the road in the same region. In 2012, a Houston Area Research Council report estimated that a single flare or compressor could raise downwind ozone levels 3 to 5 parts per billion as far as five to ten miles away.
No, the oil and gas industry haven't been touched by these state anti-smog plans because the state doesn't want to impose new regional regulations on an industry. It's nothing personal. Austin doesn't want to impose new regulations on any industry. The last serious SIP was in 2007 – before the Barnett Shale boom and Rick Perry's presidential campaign. Since then, it's been one excuse after another from TCEQ about why no new controls are necessary – even though DFW air quality progress has stopped and we're still in violation of a 20-year old smog standard.
It's also true that the oil and gas industry hasn't been touched by an air plan because no one's made them. No DFW anti-smog plan has been the focus of a fracking campaign like the recent Dallas Trinity East permits, or the Denton petition drive. There been no pressure on state government to respond to a regional demand for action.
But the new DFW air plan does offer gas activists a chance to get reforms outside of their own city limits. For example, it could be the goal to include mandatory electrification of compressors in this plan. It's been estimated that 60 % or more of the air pollution from the gas fuel cycle comes from compressors. Electrification doesn't solve all their air pollution problems but it takes a huge bite out of them because the compressors are no longer being run by locomotive size diesel engines. Electrification of new compressors and a phase-in to replace existing diesel engines could reduce not just smog pollution, but toxic air pollution and greenhouse gases by thousands of tons a year.
Even if Austin rejects such proposals, there's a part of every plan called the "Weight of Evidence" category that's more inclusive to voluntary measures. A recommendation for cities and counties to demand electrification of all compressors in the DFW region isn't as immediate as a state-sponsored mandate, but it's an official good housekeeping seal you can take to local city councils and pass one by one until it does become a de facto regional policy. This is exactly what happened with Downwinders' Green Cement procurement campaign from 2007-2011 aimed at getting rid of old wet cement kilns in Midlothian. A short recommendation to local governments about where to buy their cement in the 2007 SIP was turned into a model ordinance by Dallas and then passed by a dozen other entities, one by one, over the next two years. by the end of this year, there will be no wet kilns lift in Midlothian.
The same thing could happen with compressors in this new plan, or green completions, or tanks, or pipelines in this new DFW air plan – if activists are willing to invest the same amount of time and energy into a regional fight as they do in their own backyard battles.
You have a couple of chances in April to dip your toes into the SIP Process. This coming Sunday, April 6th, from 3 to 5 pm at the Texas Campaign for the Environment office in Dallas, State Rep Lon Burnam and Downwinders at Risk will be hosting a strategy meeting for folks who want to know more about how to take advantage of this new air plan. Central to this strategy is involving more gas activists to win a regional fight, so y'all come.
Then on April 17th, at 10 am at the North Central Council of Governments Headquarters in Arlington, there's a meeting of the SIP "technical committee" that will be hearing presentations from the state and others about DFW's smog problem. Don't let the "technical committee" name fool you. These are open to the public and anyone can attend. In fact, this is your chance to ask questions of the state and the experts.
And to make it more interesting, we think we've managed to convince the Powers That Be to include UNT graduate student Mahdi Ahmadi's presentation on Barnett Shale contributions to DFW ozone as part of the April 17th meeting. This was the study recently featured by Peggy Heinkel-Wolfe in the Denton Record Chronicle:
According to the results, the air monitoring sites surrounded by oil and gas production activities, generally on the west side of DFW, show worse long-term trends in ozone reduction than those located farther from wells on the east side of DFW.
His spatial analysis of the data showed that ozone distribution has been disproportionally changed and appears linked to production activities, perhaps an explanation why residents on the western side of DFW are seeing more locally produced ozone, particularly since 2008.
If this one fails, another new air plan will not be due until at least 2019 or 2020 at the earliest. This is our only chance until then to affect the gas industry over a wide area instead of just one permit or one city at a time. Let's try to make it count.
DFW Anti-Smog Plan Strategy Meeting
Sunday April 6th 2-5 pm
Texas Campaign for the Environment Offices –
3303 Lee Parkway #402 • Dallas, TX 75219 – across from Lee Park
Hosted by St. Rep. Lon Burnam and Downwinders at Risk
DFW Air Plan Committee Meeting – open to the public
10 am to 12 noon
Thursday April 17th
North Central Texas Council of Governments
616 Six Flags Drive, Arlington – across the street from the amusement park