DFW SIP
The Politics of Smog, in the US and Texas
 One of things about basing your health or exposure standards on science is that as research gets more sophisticated, the standards tend to get revised, usually downward. The more you know about how a substance affects the human body, the more subtle the health effects you discover. This has happned most spectacularly with substances like lead and benzene, but it's also happened routinely with smog, or as it's know in government regulations lingo, ozone.
One of things about basing your health or exposure standards on science is that as research gets more sophisticated, the standards tend to get revised, usually downward. The more you know about how a substance affects the human body, the more subtle the health effects you discover. This has happned most spectacularly with substances like lead and benzene, but it's also happened routinely with smog, or as it's know in government regulations lingo, ozone.
Unlike those other chemicals and substances however, the Clean AIr Act says standards for ozone exposure must be reviewed every five years to see if they're keeping up with the science. Standards must be protective fo public health. If new research discovers they're not, then they must get lowered. It's one of the most progressive and pro-active enforcement mechanisms that was included in the Act in a series of 1991 amendments.
As a result, in the past 20 years, the levels of ozone that were believed to be "safe" have come down dramatically as the science has gotten better. In the mid-1990's, an area wasn't out of violation unless it had over 125 parts per billion (ppb) of ozone as a one hour average. Dallas-Fort Worth more than matched that level, sometimes seeing one-hour readings as high as 135 ppb an hour. North Texas was out of compliance with the standard the moment it was passed.
As more research was published, scientists saw health effects at lower levels of smog exposure and so the standard was changed, as well as how it got measured. in 1998, the one-hour standard was tossed out and an eight-hour average began being used to reflect more realistic exposure patterns. And instead of 125 ppb, the number came down to 85 ppb.
Since 2006, the EPA panel of independent scientists in charge of those five year reviews mandated by the Clean Air Act have been concluding that the standard needed to come down to an eight-hour average of 60 to 70 ppb. But politics has interfered twice in trying to reach that goal. During the last Bush Administration it was brought down to only 75 ppb, where it stands now, and immediately before the 2012 elections, the Obama administration delayed another review that might have brought a lower number.
Now the process is cycling back and once again the EPA's own panel of researchers has recommended an ozone standard of 60 to 70 ppb. The EPA is said its looking at a range fo 65 to 70 ppb. Because the regulations haven't caught up with the science yet, it means, according to a new series of articles published by the Center for Public Integrity that,
"… people in a wide swath of the country breathe air that doesn’t violate any rules — and thus doesn’t trigger any warnings — and yet, according to research, is unhealthy."
There's no better example than DFW to demonstrate this behind-the-curve approach. Even while the state is in the final stages of submitting a new clean air plan for the region aimed at reaching the Bush Administration-era 75 ppb standard (by doing nothing but waiting for cleaner federal gasoline mandates to kick-in) the EPA acknowledges that number is obsolete and should come down to protect human health. Yet the state isn't penalized for not aiming lower, and isn't rewarded for reaching a lower number sooner than the deadline of 2018. The two tracks of regulation never intertwine, as if they were regulating two different kind of air pollution. In effect, government is blessing another half decade of unhealthy air in DFW.
Despite this lenient strategy it will come as no surprise that the State of Texas is fighting the current proposed revision downward in the ozone standard. It's at least consistent. Texas has always fought the lowering of the smog standard. Had it been up to Austin, we'd be living with the 125 ppb levels of 20 years ago – the smog equivalent of smoking two packs a day. As part of its look at the politics of ozone, the Center for Public Integrity's journalists spotlight the the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality's efforts to use industry researchers to make its case the standard is just fine where it is. One of the few pieces of good news is the involvement of local physicians with the Dallas County Medical Society stepping up and taking on Austin over its stance. Dr. Robert Haley of UT-Southwestern has become a well-known opponent of the TCEQ in his and the Medical Society's battle over the East Texas coal plants.
As the Center's articles indicate, court battles are an inherent part of the fight for better standards. Often environmental groups have had to sue the EPA to get the agency to implement the standards recommended by its own panel of scientists. Often, the EPA like it that way, because then it can say it was forced to lower standard by the courts instead of on its own. In Texas, with the submission of a state plan for DFW smog that many feel doesn't meet the Clean Air Act requirements for new controls, a court challenge could be facing the the EPA for the first time in a long time if it approves Austin's lax approach to providing safe and legal air to over six million residents.
The Center's articles are required reading for anyone trying to understand how the machinery of government works both to advance and retard the protection fo public health from a very basic threat. For DFW citizens, they could be a primer for an upcoming fight.
Downwinders and Sierra Club File Joint Comments on the State’s DFW “Do Nothing”Air Plan
 Wednesday of last week saw the deadline for filing official comments on the dreadful "plan" the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality has proposed to lower smog levels in DFW by 2018. In effect, the plan is to wait for federal gasoline changes in 2017 and hope for the best.
Wednesday of last week saw the deadline for filing official comments on the dreadful "plan" the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality has proposed to lower smog levels in DFW by 2018. In effect, the plan is to wait for federal gasoline changes in 2017 and hope for the best.
Shortly before closing time Wednesday, Downwinders at Risk and the Lone Star Chapter of the Sierra Club submitted 62 pages of criticisms concerning the plan. Not because either organization believes the TCEQ Commissioners will change heir minds, but because we're trying to establish a record that might eventually lead to a court challenge of the plan.
Although lengthy, the basic approach of the groups is two fold – call into question the state's computer modeling that's predicting success and challenge the state's exclusion of new pollution control measures on the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas Coal plants and Barnett Shale gas compressors.
Some of the highlights:
– The computer modeling the TCEQ is using for its new plan is the same it used for plans in 2006 and 2011, neither one of them successful at meeting its goal of cleaner air by the assigned deadline. In fact, the last clean air plan using this same model underestimated smog levels by almost 10 parts ber billion and actually saw a slight rise in smog at its conclusion – the first time a DFW plan ever resulted in higher ozone levels.
– In defiance of EPA guidance, the computer model TCEQ is using is more than five years old. EPA specifically recommends using an "ozone season" from 2009 to 2013. TCEQ's model is leftover from 2006, or three years older than the oldest year EPA says is appropriate.
– Also contrary to EPA rules, the TCEQ 2006 computer model ignores including the most relevant “meteorological conditions conducive to elevated air quality.” 2011 was the worst year for ozone levels in DFW since the beginning of this decade, in large part because it reflected the worst drought conditions. The three-year rolling average for the worst monitor, called the "design value" rose back up to 90 parts per billion after years of floating in the mid to upper 80's. But instead of using that year as a worst case baseline, the state defaulted to its 2006 model that doesn't incorporate the current drought.
– TCEQ's prediction of success is built on a series of unrealistic assumptions about the quantity of oil and gas pollution. For example, it underestimates the number and impact of air pollution from hundreds of large compressor stations and thousands of smaller "lift" compressors as the Barnett Shale ages. Fully 60 to 70% of all air pollution from the gas industry comes from these kinds fo facilities, so a mistake in estimating their impact could have a large chain reaction at downwind air quality monitoring sites in Tarrant, Denton, Parker and Johnson counties.
TCEQ also assumes that production levels in the Barnett will fall steeply. If they do not, there could be hundreds of tons more air pollution from the industry annually than what TCEQ assumes in its model.
That's important because the model predicts that the region will only barely squeak-by the 75 ppb standard required by 2018, with levels coming in at 75.87 at the Denton monitor site, 75.15 at Eagle Mountain Lake, and 75.04 in Grapevine. A jump in oil and gas pollution – or any other surge in pollution from any other source – could make those numbers obsolete and ruin our chances fo complying with the Clean Air Act on time…again.
– TCEQ's "Contingency Measures" are illegal. Every smog plan must have a series of quantifiable back-up contingency pans in case the options the plan relies on fail to achieve success. In this case, the state is only relying on unquantified and voluntary actions, such as "incentive" programs, the effectiveness of which cannot be measured. Since you can't measure them, you can't count them.
– TCEQ failed to consider all "reasonably available control technologies" and "measures." Nearly 40 pages is devoted to the wrong-headed, irrational, and illegal way TCEQ rejects off-the-shelf air pollution controls for the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas coal plants, and large gas compressors.
Under the Clean Air Act, a state's plan “shall provide for the implementation of all reasonably available control measures as expeditiously as practicable (including such reductions in emissions from existing sources in the area as may be obtained through the adoption, at a minimum, of reasonably available control technology) and shall provide for attainment of the national primary ambient air quality standards.” In order for the EPA to determine whether an area has provided for implementation as "expeditiously as practicable,” the State "must explain why the selected implementation schedule is the earliest schedule based on the specific circumstances of that area. Such claims cannot be general claims that more time is needed but rather should be specifically grounded in evidence of economic or technologic infeasibility.”
Step-by-step, Downwinders and the Sierra Club explains why Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is a reasonable control technology for the Midlothian cement plants and East Texas coal plants. Even as the owners of one of the Midlothian cement plants applies for a permit to install the technology, TCEQ is claiming its still not ready for prime time. The groups demonstrate how requiring SCR on these major polluters would have a large impact on DFW ozone levels.
The same level of absurdity if reveled in TCEQ's rejection of electrification of gas compressors. Despite being able to significantly lower smog-pollution in the very areas where its needed most, and despite electrification even being required by many Barnett shale municipalities, the state maintains that this option is unrealistic and unachievable.
There's probably no better compendium of the various sins committed by the TCEQ plan than these comments. If you're looking for the most solid case for compressor electrification, or SCR adaptation, or just TCEQ malfeasance, this is your one-stop shop.
You may think this is a technical document, or one full of legal mumbo-jumbo. It's not, at least not for the most part. Instead it's the kind of logical, evidenced case you'd assemble for a debate with the TCEQ. It's a blow-by-blow comprehensive look at why the state isn't any more likely to meet this clean air deadline than it has any other. A case we hope is capable of persuading EPA to reject the TCEQ plan.
Both Gas Industry Spinmeister and Mansfield Compressor Spew During Thursday’s EPA Hearing
 There was at least one truth uttered by Steve Everley, the professional PR spokesperson for Energy in Depth, itself the PR arm of the Gas Industry, during his testimony at last Thursday's EPA ozone standard hearing in Arlington:
There was at least one truth uttered by Steve Everley, the professional PR spokesperson for Energy in Depth, itself the PR arm of the Gas Industry, during his testimony at last Thursday's EPA ozone standard hearing in Arlington:
"…natural gas producers will be significantly impacted by EPA’s proposal to reduce the National Ambient Air Quality Standard for ozone from 75 parts per billion to between 65 and 70 ppb."
Indeed. At the rate things are going in Austin and DC, it might be the only thing to impact the industry's large emissions of pollution for many years to come. Left unsaid by Everley was why the industry would be impacted by such a lower ozone standard – because in many parts of the country now, including the DFW area, smog-forming pollution from the gas industry is contributing significantly to higher ozone levels.
Even the governmental affairs branch of the gas industry, otherwise known as the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, admits that facilities like compressors, storage tanks, pipelines, and de-hydrators found by the thousands in the western part of the Metromess contribute more smog-forming Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) than all the "on-road" vehicles in North Texas combined. This is true not only at the present time, but will be true at least three years into the future, according to TCEQ's own estimates.
Gas facilities also account for the third largest source of smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide pollution in DFW, according to TCEQ numbers included in their recent air plan submitted to EPA – only a ton per day less than all "non-road" vehicles in North Texas like construction equipment, and well ahead of "point sources" like the Midlothian cement kilns and local power plants.
In all, TCEQ predicts that 35,335 tons per year of smog-forming pollution will still be coming from the region's gas industry in 2018. That's a lot. It's so much that, as the TCEQ also demonstrates with its computer modeling, even a tweak here and there in gas pollution estimates can make big differences in the levels of ozone at monitors in places like Denton and Keller and Eagle Mountain Lake – traditionally the worst-performing air quality monitors in North Texas.
And that's why a lower ozone standard is a threat to the industry. The very air quality monitors the industry affects most with its pollution are the ones driving the region's high smog levels. Lowering the ozone standard means it would have to spend money to reduce those emissions significantly. It means it would have to spend money to prevent the kind of huge "accidental" releases of smog-forming pollution released by the Mansfield compressor on Thursday even while Steve Everley was testifying to EPA.
After giving her own testimony to EPA on Thursday morning, Earthworks' Sharon Wilson and Mansfield Gas Well Awareness board member Lance Irwin headed out to the Summit Midstream Partners Compressor Station behind Mansfield's Performing Arts Center, with an infrared, or FLIR "thermal imaging" camera. Such a device is capable of recording the kinds of VOC emissions that are often smelled and inhaled by surrounding residents, but can't be seen with the naked eye.
The Summit compressor and the two nearby Eagleridge gas wells have been the scene of many different complaints from the surrounding Mansfield neighborhood – everything from airborne foam landing in backyards to oily deposits landing on car finishes. On Thursday, Wilson and Irwin were responding to a new series of complaints about awful smells. When they showed up, what the two recorded was a massive "emergency blowdown" (versus the "planned" kind). While filming the event, Wilson suffered health effects familiar to gas facility neighbors and was overwhelmed by the obvious hydrocarbon fumes. Once you see her video, you understand why:
Such a blowdown was exactly what Lance Irwin had warned the Mansfield City Council about only three days before, during comments directed at slowing down or denying the permit for a new compressor, 34 wells, 12 tanks and a assortment of other facilities at an Edge pad site near Debbie Lane in town. He pointed out that industry and government estimates about emissions never take these kind of catastrophic events into account – form a short-term toxic exposure perspective, or as it turns out, from an air quality, smog-creating perspective. And he's right.
In this regard, these kinds of accidents are no different than the infamous industrial "burps" from refineries and chemical plants along the Houston Ship Channel that lead to smog spikes downwind. There are 650 large compressor stations in the DFW "non-attainment" area. How many are experiencing blowdowns on any given day? How many are affecting ozone levels in the spring and summer? The TCEQ estimates included in its DFW air plan don't even try to quanify them.
Because gas facilities like compressors are subject only to "standard permits," are located diffusely around a region, and don't officially emit a de minimus amount of air pollution, they're not subject to the federal rule of off-setting. That's when a new polluting facility locates in an already smoggy area like DFW and has to pay to cut smog pollution elsewhere if it wants to emit the stuff itself. If a new cement plant or power plant were to locate in DFW, it would have to pay to reduce a ton and a half of smog-forming pollution for every ton it wanted to release. Gas facilities don't have to do this – even though collectively they emit more smog-forming pollution than all the cement plants and power plant in the non-attainment area!
EPA has tried to argue that a company's different facilities are all tied together and should be counted as a single source, and so subject to off-setting regulations. But the courts have ruled against them.
Rising gas industry pollution and the absence of any official brake on its growth like off-setting is a large reason, maybe the primary reason, why DFW hasn't seen the kind of air quality progress it should have by now. Until this last summer's cooler and wetter weather gave us relief, ozone levels had been stagnating or even rising since 2009 – or about the time the industry invaded North Texas in large numbers. There's no question that had the Barnett Shale boom not happened, we'd have much cleaner air by now.
But it did and we don't. And so that's why a lower ozone standard is perhaps the only way that the gas industry will ever be forced to clean-up its act – especially on the widespread regional level we require to get to safe and legal air. Just like it has with the Midlothian cement plants, the need for lower smog levels can force the state's and industry's to act to add controls. It's a long-term fight, but one of the only paths to across-the-board change versus the city-by-city slog activists have had to rely on.
National Resources Defense Council lawyer John Walke has a great takedown of Steve Everley's spin on Thursday. And the tireless cross-country DeSmogblog reporter and photographer Julie Dermansky has a good read on the Mansfield fight that you should check out. But the most compelling rebuttal to both industry PR and local governments who want to ignore their own responsibility in this mess is probably Wilson and Irwin's two and a half minutes of video.
Don’t put away those gas masks yet: EPA’s National Ozone Public Hearing is Next Thursday in Arlington
All Day NATIONAL Public Hearing on a New Federal Ozone Standard
Thursday, January 29th, 9am to 7:30 pm
Arlington City Hall, 101 W. Abram
(To secure a 3-minute speaking slot, e-mail Eloise Shepard and ask for one in the time period most convenient for you. Slots are going fast (and not necessarily to citizens), so do it asap: shepherd.eloise@epa.gov)
It's Round Two of January's clean air public hearing marathon, and the biggest has been saved until last.
One of only three national public hearings on lowering the federal ozone, or smog standard, is taking place here in DFW, at Arlington City Hall all day next Thursday January 29th, from 9 am to 7:30 pm.
Last week saw a state-sponsored hearing on another TCEQ do-nothing DFW clean air plan. But the state wouldn't even have to pay lip service to such plans were it not for the requirement to meet a federal ozone level and the region's inability to do so over the last two decades.
Lowering the federal ozone level means it will be tougher in the future for the state to claim it doesn't have to implement any new pollution controls on cement kilns, coal plants, or gas facilities. More importantly, enforcement of a tougher standard means better public health: fewer "bad air days," fewer asthma attacks, fewer trips to the emergency room because your child can't breath, and fewer deaths caused by dirty air.
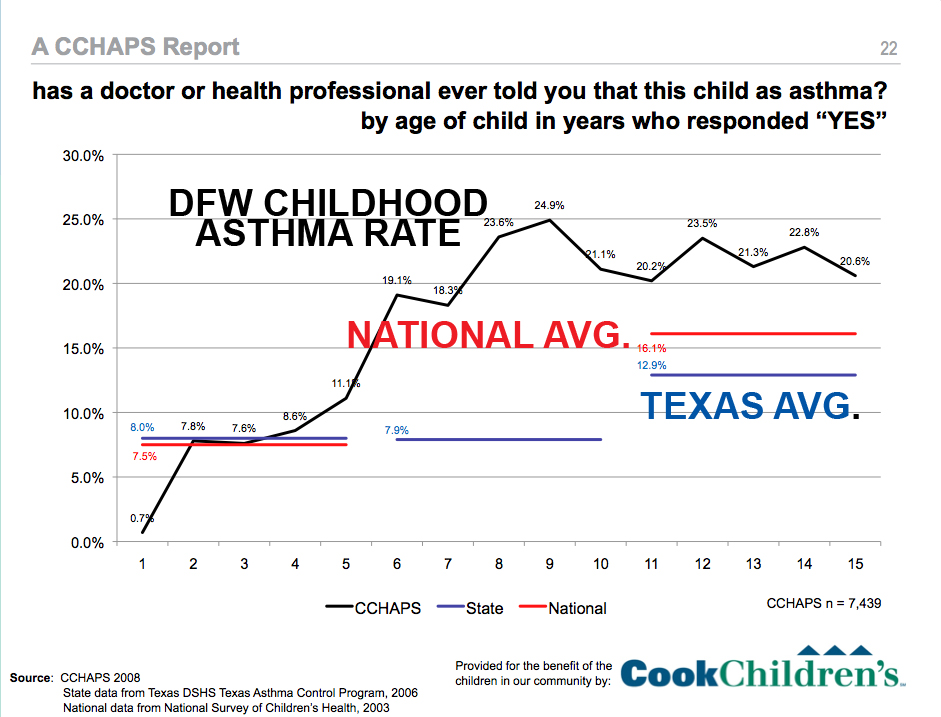
That's important because reports like the child heath survey from Cook Children's hospital in 2009 showed that childhood asthma rates in DFW were twice the state average and almost 10% higher than the national average. It called the prevalence of asthma among local children an "epidemic."
Currently, the national ozone standard is 75 parts per billion (ppb) – which DFW is still at least three years away from reaching even under the rosiest of scenarios. (Right now our average is 81 ppb, and that's only because of a wetter and cooler summer in 2014). But that 75 ppb number is a political compromise – not one grounded in science. Based on public health studies the EPA's own independent board of specialists has recommended a range of 60 to 70 ppb at least three times since 2008, with an emphasis on the lower end of that range. Now it looks as if the EPA is finally willing to follow through on that recommendation.
EPA's national ozone standard sets the goal of cleaner air that every state must work toward. It drives all new clean air plans. like the one the state of Texas is proposing for DFW right now. The lower the standard, the more pollution has to be reduced. The more pollution has to be reduced, the more controls have to be added to major sources of air pollution to get that reduction. That's how you get long-term clean air progress in states like Texas that refuse to act on their own.
A significant reduction in the federal standard – from 75 (ppb) to as low as 60 ppb would make it much, much harder for Texas to avoid new controls on industry. To give you some idea of how much harder, consider that the state's "plan" for compliance with the current 75 ppb level is completely dependent on a new EPA gasoline mix coming onto the market in 2017. Even then, it's own estimates say that it won't get down below 75 at least three or four monitoring sites. Just one monitor site out of compliance means the whole region is in violation. Short of a huge rise in the use of electric cars, more huge decreases in vehicle pollution aren't expected. Additional significant drops in smog that would be required under a new, lower standard would have to include controls on major industrial sources – like the cement kilns, coal plant and, yes even gas facilities.
When you have a much lower ozone standard, you have to reduce smog by addressing ALL sources of air pollution.
Finding a way to comply with a lower national ozone standard is how more modern pollution controls were mandated almost a decade ago at the Midlothian cement plants. Meeting that new ozone standard meant pollution from the kilns had to be reduced and that made it more possible for Downwinders' "Green Cement" campaign to work with local governments. Today, there are no obsolete "wet kilns" left in Texas – they've all been replaced with more modern dry kiln operations. This has resulted in a reduction of hundreds, even thousands, of tons of smog-forming air pollution from these huge sources every year. We still have to require state-of-the-art Selective Calaytic Reduction (SCR) on the kilns, but they're releasing far less pollution than they were even five years ago because they've had to comply with a new federal ozone level.
With a new, lower ozone standard, the same could be true of new controls on gas facilities, like the 650 large compressors in North Texas, and the East Texas coal plants. That's why it's important for Texas residents to fight for the lowest possible standard this time around. When you testify, please make sure you request a new standard of NOT MORE THAN 60 PARTS PER BILLION.
According to a recent EPA staff analysis, an ozone standard of 60 ppb would reduce asthma deaths in the US by 95%, compared to only a 50% reduction under a 70 ppb level. If you want air that can eliminate all but a small fraction of respiratory problems associated with outdoor pollution, you need to press for a 60 ppb standard.
Needless to say industry is fighting back hard against such a standard, using its usual doom and gloom forecasts of economic hardship. This is the same argument that was used against the current ozone standard – the one we have now in the middle of the biggest economic boom in a decade. In fact, the technology for bringing down pollution levels currently exists in many industries – including kilns, coal plants and compressors. It's not experimental and it's not too expensive to use, as demonstrated by its use right now in those industries. We just have to require its use in states like Texas that are refusing to implement progress. That's why this new standard is so important – it will make the state take action it would not otherwise take. It's one of the only ways citizens who care about cleaner air in Texas can force progress.
Likewise, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality's own toxicologist, Michael "Smog Ain't Bad For You" Honeycutt will also be testifying. TCEQ knows that a lower standard will force its hand on new controls. It will be pulling out all the stops to use its influence and that of sympathetic elected officials to scuttle any change. Using ideologically-based arguments supported by industry-financed studies, the TCEQ will say there are no real benefits to reducing DFW smog. Those of you that know better have to show up and say so.
Speaking slots for the 29th are going very fast. Industry will be well-represented. Please don't get left out. We need your voice that day to call for a 60 ppb national ozone standard. E-mail the EPA at shepherd.eloise@epa.gov and reserve your time today.
Bottom Line: If You Think DFW Still Has A Smog Problem, Be in Arlington Tonight
 You don't have to have any special technical knowledge. You don't have to know regulatory or legal jargon. You just have to believe we still have a problem with smog in Dallas-Fort Worth. That's all it takes to participate in the air quality extravaganza happening tonight in Arlington. It's a rare two-for one chance to help the fight for cleaner air.
You don't have to have any special technical knowledge. You don't have to know regulatory or legal jargon. You just have to believe we still have a problem with smog in Dallas-Fort Worth. That's all it takes to participate in the air quality extravaganza happening tonight in Arlington. It's a rare two-for one chance to help the fight for cleaner air.
Public Hearing on the State's New DFW Air Plan 6:30 pm Tonight, Arlington City Hall, 101. W Abram
All you have to do is sign-up to speak, wait for your name to be called, and tell the state and the EPA representatives who'll be present that you want something better than a clean air plan that does nothing to get cleaner air except wait for a new federal gasoline formula to hit the market a year before the plan's deadline. The more people that do this, the more pressure EPA is under to reject this terrible state plan. Nothing fancy. Just show up and say you want better – that this region deserves better after two decades of being in violation of the Clean Air Act.
Click here to send prepared written comments to the state and EPA. You can add your own as well.
Roasting and Toasting of Retiring State Representative Lon Burnam – A Fundraiser for Downwinders at Risk, 7:30 -10 pm, Tonight, South Street Patio, 400 South Street – about four blocks east of Arlington City Hall
If you think DFW smog is still a problem, after you say your piece at the state hearing come and support the only group committed to trying making its elimination a priority – Downwinders at Risk. Since the mid-1990's we've been using these air plans to raise issues, get information, and sometimes even win victories that actually do lead to cleaner air. A big reason there's no more burning of hazardous waste in the Midlothian cement plants, and all of those cement plants have upgraded their equipment is because of the work we did around smog. Lately, we've been using them to drive home how much gas and oil pollution contribute to regional smog.
But we need your help – in terms of attendance at public hearings, and in terms of financial assistance. For your donation of $35 to this roasting and toasting of Lon, you get an evening of entertainment and take part in a salute to a real local clean air hero. And you make it more possible to keep challenging the status quo on behalf of your lungs.
CLICK HERE TO GET YOUR TICKETS ONLINE OR GET THEM AT THE DOOR TONIGHT
If you still think we have a smog problem, there's two things you can do about it tonight. Thanks.
Citizens To Form Posse, Demand State Enforce the Clean Air Act at Thursday Hearing on New DFW Air Plan
 (Arlington) Critics of a new plan to clean the air in Dallas-Ft. Worth are using a public hearing on Thursday evening to accuse the state of Texas of breaking the law by not requiring the implementation of pollution control technologies already in widespread use to help lower smog levels in North Texas.
(Arlington) Critics of a new plan to clean the air in Dallas-Ft. Worth are using a public hearing on Thursday evening to accuse the state of Texas of breaking the law by not requiring the implementation of pollution control technologies already in widespread use to help lower smog levels in North Texas.
“We’re asking residents to come out and get sworn into a citizens posse to help us make the state follow the Clean Air Act,” said Jim Schermbeck, Director of the local clean air group Downwinders at risk, one of the leading opponents of he new plan. “Austin is going to ridiculous, Monty Python-like lengths to avoid new controls on the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas coal plants, and local gas facilities in this new plan – even though those controls are now commonplace in each industry.”
Thursday’s public hearing centers on a new plan to comply with the federal ozone standard of 75 parts per billion (ppb) by 2018. DFW has never achieved such a low level of smog, and only this last year dipped below the 1997 standard of 85 ppb for the first time with the help of cooler, wetter summer.
EPA says a state plan like the one the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality is proposing for DFW must include “all Reasonable Available Control Technologies,” and “all Reasonable Available Control Measures” to get lower smog levels as “expeditiously as possible.” EPA defines these as technologies as ones that are “technically and economically feasible.” But according to Schermbeck, the state of Texas is deliberately ruling out local use of pollution controls already adopted by industry that could speed cleaner air.
He cited three examples. Selective Catalytic Reduction, or SCR acts much like the catalyst on cars, only on a much larger scale for industrial plants. It’s already in use on at least half a dozen European cement plants where it’s reduced smog-forming pollution by up to 90%, and on many coal-fired power plants across the world and in the US, where it achieves the same results. Yet the TCEQ DFW air plan doesn’t require SCR on the largest single sources of smog pollution in the region, the Midlothian cement plants, or the East Texas coal plants that are known to impact DFW air quality, saying the technology isn’t “feasible.” TCEQ maintains this stance even though the Holcim cement plant in Midlothian has announced plans to include an SCR unit on one of its own kilns.
“Here’s a pollution control technology already in operation and achieving great results, with a cement plant in North Texas already adopting it, but the state’s position is that it isn’t ‘feasible’. It’d be comical if it wasn’t delaying cleaner air for over 6 million people that haven’t had it in decades.”
Besides ignoring SCR on cement and coal plants, Schermbeck said the TCEQ has also ruled-out electrification of large gas compressors as “infeasible” – despite the widespread use of electric compressors In the Barnett Shale already and the requirement of municipalities like Dallas and Southlake to allow nothing but electric compressors within their city limits. According to a 2012 study by the Houston Advance Research Consortium, compressors could increase downwind ozone levels as much as 3 to 10 parts per billion. There are at least 647 large compressors in the DFW “non-attainment area” covered by the TCEQ air plan.
“Requiring just these three technologies that are already on the market and being used in their respective industries could reduce air pollution by thousands of tons a year and help us achieve compliance with the new federal ozone standard much quicker,“ said Schermbeck. He said they all pass the test of being feasible according to EPA definitions. “By law, they should be required.”
Instead, the state is relying exclusively on a new federal gasoline mix being introduced in 2017 to achieve the required 75 ppb standard by 2018. Although it’s expected to help lower ozone levels across the country, it won’t get DFW down to the level of 75 ppb alone. To make the plan work on paper, the state has had to estimate oil and gas pollution downward in a way Schermbeck and others claim is unrealistic.
“Basically, the state’s approach is to do absolutely nothing for the next three years and hope the federal gasoline change brings it “close enough” to the lower standard. But hope is not a plan.”
Schermbeck said his group would be passing out badges to members of their clean air posse and recruiting residents to persuade the EPA to reject the state’s proposal. The federal agency has the final say. But there’s also always court – where many clean air rules for the state of Texas have been decided over the last 20 years. “If government won’t enforce the law, we may have to do it ourselves.”
TCEQ’s Terrible, Horrible, No Good, Very Bad Air Plan for DFW

TCEQ Public Hearing on the new DFW Anti-Smog Plan
Thursday, January 15th 6:30 pm
Arlington City Hall, 101 W. Abram
Over the last two decades, we've seen some pretty lame DFW clean air plans produced by the state, but the newest one, scheduled for a public hearing a week from now, may be the most pathetic of the bunch.
From a philosophical perspective, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality stopped pretending to care about smog in DFW once Rick Perry decided to run for president around 2010 or so. Computer modeling was scaled back, staff was slashed, and the employees that were left had to be ideologically aligned with Perry's demand that no new controls on industry (i.e potential or existing campaign contributors) was preferable to six or seven million people continuing to breathe unsafe and illegal air.
TCEQ's 2011 anti-smog plan reflected that administrative nonchalance by concluding – in the the middle of the Great Recession – that consumers buying new cars would single-handedly deliver the lowest smog levels in decades. It did not. It went down in history as the first clean air plan for the area to ever result in higher ozone levels. The first, but maybe not the last.
This time around, it's not the cars themselves playing the role of atmospheric savior for TCEQ, but the fuel they'll run on. Beginning in 2017, the federal government is scheduled to introduce a new, low-sulfur gasoline that is predicted to bring down smog by quite a bit in most urban areas. Quite a bit, but not enough to reach the ozone standard of 75 ppb that's necessary to comply with the Clean Air Act by 2018. It's the gap between this official prediction and the standard where the state is doing a lot of hemming and hawing.
TCEQ staffers really did tell a summertime audience in Arlington that that estimated 2018 gap of between 1 and 2 ppb was "close enough" to count as a success. Now, you might give them the benefit of the doubt, but remember this is an agency that has never, ever been correct is its estimation of future ozone levels. After five attempts over the last two decades, TCEQ has never reached an ozone standard in DFW by the official deadline. Precedent says this plan won't even get "close enough."
Plus, we know getting "close" to 75 ppb isn't protecting public health in DFW. Even as this clean air plan is being proposed by Austin, the EPA is moving to lower the national ozone standard to somewhere between 60 and 70 ppb (There's a hearing on that at Arlington City Hall on January 29th). That new EPA ozone standard is due to be adopted by the end of this year. So this entire state plan is obsolete from a medical perspective. Instead of aiming for a level of ozone pollution closer to 70 ppb as soon as possible, it's not even getting down to a flat 75 ppb at all DFW monitors by 2018. It wil take an entirely new plan, and pulling TCEQ teeth, to do that much later. In other words, millions of people will have to wait as much as a five to seven years longer to get levels of air quality we know we need now in 2015.
What are the major flaws this time?
1. TCEQ is Using 2006 in 2014 to Predict 2018.
The EPA recommends that states use an "episode" of bad air days from the last three years – 2009-2013 – in trying to estimate what ozone levels will be three years from now. The more recent the data, the better the prediction.
TCEQ is ignoring that recommendation, relying on a computer model that's already nine years old. This has all kinds of ramifications on the final prediction of compliance. Instead of having more recent weather data, you have to "update" that variable. TCEQ doesn't have to compensate for the drought DFW is experiencing now or factor in a year like 2011 where the drought caused a worst case scenario for ozone formation.
TCEQ isn't using more recent data on how sensitive monitors are to Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) – the major kinds of pollution that cause smog . That's important because gas production in the Barnett Shale has put a lot more VOCs in the air. But instead of getting a more accurate post-drilling boom read on what's driving smog creation, the TCEQ is relying on a picture that starts out before the boom ever started.
The further you reach back in time for a model to predict future levels of smog, the fuzzier that future gets, and the less accurate the results. TCEQ is using a model that's twice to three times older than EPA guidance recommends. What are the odds that TCEQ estimates will be correct based on this kind of methodology?
2. TCEQ is Downplaying OIl and Gas Pollution
Citizens attending the air quality meetings in Arlington over the past year have seen the TCEQ try and hide the true volume and impact of oil and gas pollution at every turn. Instead of all the industry emissions being listed under the single banner of "Oil and Gas Pollution," the Commission has tried to disperse and cloak them under a variety of categories in every public presentation.
"Other Point Sources," a classification that had never been seen before, was the place where pollution from the 647 large compressor stations in DFW could be found – if you bothered to ask. "Area Sources" was where the emissions from the thousands of other, smaller compressors could be found – again, only if you asked. "Drilling" was separate from "Production." And despite other agencies being able to tease out what kind of pollution came from the truck traffic associated with fracking within their jurisdictions, the TCEQ never bothered to estimate how much of the emissions under "Mobile Sources" was generated by the Oil and Gas industry.
The reason the TCEQ has tried so hard to hide the true volumes of oil and gas pollution is because once you add up all of these disparate sources, the industry becomes the second largest single category of smog-forming pollution in DFW, second only to on-road cars and trucks (and remember many of those trucks are fracking-related). According to TCEQ's own estimates, oil and gas facilities in North Texas produce more smog-forming VOC pollution than all of the cars and trucks in the area combined, and more smog-forming NOx pollution than the Midlothian cement plants and all the area's power plants combined.
TCEQ is loathe to admit the true size of these emissions and place them side-by-side next to other, traditional sources, lest the public understand just how huge a impact the oil and gas industry has on air quality. Austin's party line is that this pollution isn't contributing to DFW smog – that it's had no impact on local air quality. But such a claim isn't plausible. If cars are a source of smog, and cement kilns and power plants are a source of smog, how can a category of VOC and NOx pollution dwarfing those sources not also be a source of smog? Think how much less air pollution we'd have if the Barnett Shale boom of the last eight years had not taken place?
In it's last public presentation in August, the TCEQ made the impact of oil and gas pollution clear despite itself. According to the staff, oil and gas emissions were going to be decreasing in the future more than they had previously estimated. As a result, a new chart showed that certain ozone monitors, including the one in Denton, would see their levels of smog come down significantly. It was exactly the proof of a causal link between gas and smog that TCEQ had been arguing wasn't there. Only it was.
In terms of forecasting future smog pollution, TCEQ is underplaying the growth of emissions in the gas patch. Everything it's basing its 2018 predictions on is years out-of-date, leftover from its last plan.
Drilling rig pollution is extrapolated from a 2011 report that counts feet drilled instead of the actual number of rigs. TCEQ predicts a decline in drilling and production in the Barnett Shale without actually estimating what that means in terms of the number of wells or their location. It also assumes a huge drop-off in gas pollution after 2009 that hasn't been documented by any updated information. It's only on paper.
While recent declines in the price of oil and gas have certainly put a damper on a lot of drilling activity, there's still a significant amount going on. Look no further than Mansfield, where Edge is now applying for permit to build a new compressor and dozens of new wells on an old pad.
In 2011, nobody was building Liquified Natural Gas terminals up and down the Gulf Coast for an export market the way they are now. Analysts say those overseas markets could produce a "second boom" in drilling activity between now and 2018, but the TCEQ forecasts don't take that into account.
Gas production pollution numbers – emissions from compressors, dehydrators, storage tanks – are even more tenuous. Every gas industry textbook explains that as gas plays get older, the number of lift compressors increases in order to squeeze out more product. Increase the number of compressors and you increase the amount of compressor pollution. But TCEQ numbers fly in the face of that textbook wisdom and predict a decline in compressor pollution because wells in the Barnett Shale are getting older!
The best analogy for how TCEQ is estimating oil and gas pollution is its poor understanding of where those thousands of smaller compressor are and how much pollution they're actually producing. No staff member at TCEQ can tell you how many of those compressors there are in the region – they literally have no idea and no idea of how to count them in the real world. There are just too many, their locations are unknown, and they were never individually permitted.
Instead, the TCEQ takes production figures from the Railroad Commission and guesses how many of those small compressors there are, as well as their location, based on where the RRC tells it production is going on in the Shale. Then staff guesses again about the emissions being emitted by those compressors, because there's no data telling them what those emissions actually are. In the end you have a series of lowballed guestimates, stacked one atop the other, presented as fact. It's smoke and mirrors.
3. TCEQ Isn't Requiring Any New Controls on Any Major Sources of Air Pollution
Like its previous 2011 DFW air plan, which resulted in an increase in North Texas ozone levels, TCEQ's new plan requires no new controls on any major sources of air pollution, despite evidence showing that such controls in smog-forming emissions from the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas coal plants, and Barnett Shale gas facilities could cut ozone levels significantly.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is already used extensively in the cement plant industry in Europe to reduce smog pollution by up to 90%. Over a half dozen different plants have used the technology since 2000. The TCEQ's own 2006 report on SCR concluded it was "commercially available." Holcim Cement has already announced it will install SCR in its Midlothian cement plant. Yet the TCEQ makes no mention of this in its plan.
That's right, a cement plant in Midlothian has decided SCR is commercially viable, but the State is looking the other way and pretending this development in its own backyard isn't even happening. TCEQ is stating in its proposed plan that SCR just isn't feasible!
In 2013, a UTA Department of Engineering study looked at what happened if you reduced Midlothian cement plant pollution by 90% between 6 am and 12 Noon on weekdays. Ozone levels went down in Denton by 2 parts per billion. That may not seem like a lot, but in smog terms it's the difference between the Denton air monitor violating the 75 ppb standard under the TCEQ plan and complying with the Clean Air Act.
In 2012 a UTA College of Nursing study found higher rates of childhood asthma in Tarrant County "in a linear configuration" with the plumes of pollution coming from the Midlothian cement plants. SCR means less pollution of all kinds: smog, dioxins and the particulate matter the Nursing College thought was causing those increased rates of childhood asthma. By delaying the requirement that all the Midlothian cement plants install SCR by 2018, the state is turning its back on a problem that Cook Children's hospital described as "an epidemic."
The same is true of SCR in the East Texas coal plants. The technology is being used in other coal plants around the world and in the US to reduce smog pollution. There's no reason it shouldn’t be required for the dirtiest coal plants in Texas that impact DFW air quality. After decades of being out of compliance with the Clean Air Act, DFW is one of the places the technology is needed most.
Last year the Dallas County Medical Society, led by Dr. Robert Haley, petitioned the TCEQ to either close those coal plants or install SCR on them. The doctors' petition was rejected by TCEQ Commissioners and they were told their concerns would be addressed in the DFW air plan. They aren't. Those concerns, along with the proof they presented about the impact of the plants on local air quality, are being ignored.
Electrification of gas compressors is a commonly used technology that could cut smog pollution as well, and yet the TCEQ is not requiring new performance standards that would force operators of hundreds of diesel and gas-powered compressors in North Texas to switch to electricity.
A 2012 Houston Advanced Research Center study found that pollution from a single compressor could raise local ozone levels by as much as 3 to 10 ppb as far away as ten miles. There are at least 647 large compressor stations in the western part of the DFW area. Dallas and other North Texas cities have written ordinances requiring only electric-powered compressors within their city limits based on testimony from industry that electrification was a commonly used technology in the industry. And yet, TCEQ's official position is that electrification isn't feasible.
In ignoring these types of new controls the TCEQ is violating provisions of the Clean Air Act to implement "all reasonably available control technologies and measures" to insure a speedy decrease in ozone levels. Each of these technologies is on the market, being used in their respective industries, and readily available. Studies have shown that each of these technologies could cut ozone levels in DFW significantly, but the TCEQ is refusing to implement them. In doing so, many observers believe it's blatantly in violation of the law.
We don't expect TCEQ to change its position. That well has been poisoned for the foreseeable future. But we do expect a higher standard of enforcement from the Obama Administration EPA. That's why we're asking you to show-up at the public hearing and oppose this dreadful state air plan a week from now in Arlington. We need to demonstrate to the federal government that citizens are concerned about getting cleaner air now, not in the next plan or the one after that. Now. We need to put pressure on the EPA to reject this TCEQ plan, to either send it back to the drawing board or substitute one of its own. Without you showing up, that pressure isn't there.
Between now and Thursday – and all the way through January 30th, you can send prepared comments opposing the TCEQ plan to Austin and the EPA Regional Administrator with a simple click here – and add your own comments as well.
As a reward for coming over and venting your frustration, we'd like you to stay and party with us at the official "retirement party" of State Representative Lon Burnam, beginning at 7:30 pm just four blocks down the street. It's a roasting and toasting of the best friend environmentalists ever had in the Texas Legislature, as well as a fundraiser for Downwinders to continue our work to defend your air. JUST CLICK HERE FOR TICKETS.
Next Thursday you can support clean air two ways in one evening. Help us beat back a terrible, horrible, no good, very bad air plan, and then come celebrate the wonderful, righteous, very good work of a dedicated public servant. See you there.
2014 DFW Smog Report: Good News But Don’t Hang Up the Gas Mask Yet
 For the first time since DFW began recording its smog levels, the region's three-year running average dipped below the 1997 eight-hour 85 parts per billion (ppb) standard. After years of leveling off at around 86-87, it's dropped to 81 ppb. That's good news.
For the first time since DFW began recording its smog levels, the region's three-year running average dipped below the 1997 eight-hour 85 parts per billion (ppb) standard. After years of leveling off at around 86-87, it's dropped to 81 ppb. That's good news.
DFW's decrease is attributed to 2011's terrible numbers rolling off the board and a wetter, cooler and windier summer than normal these last five months or so. As both drought-ridden 2011 and this year's results demonstrate, weather still plays an extremely critical role in how large or small our smog problem will be. Another summer or two like 2011 could easily put us back over the 1997 standard. More wet and cooler weather could see the decrease continue.
The news would be better except that we were supposed to have originally accomplished this milestone in 2009, then again last year after a second try, according to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ).
As it is, we still haven't reached the current, more protective 2008 national standard that was revised downward to 75 ppb after a review of the scientific literature.
In January, TCEQ will host a public hearing on its proposed "plan" to EPA to meet that goal that predicts most, but not all DFW monitors will reach 75 ppb by the summer of 2018.
Despite overwhelming evidence that new controls on the Midlothian cement plants and the reduction of gas industry pollution could speed this achievement, TCEQ's new plan contains no new pollution control measures on any major sources of smog polluters – cement kilns, coal plants, gas sources – but instead relies on the federal adoption of a new lower-sulfur gasoline mix for on-road vehicles. Like past proposals by Rick Perry's TCEQ, this one depends solely on the feds to get them into compliance. TCEQ isn't lifting a regulatory finger to help.
And its new plan once again aims high, not low. At last count, there were at least three Tarrant and Denton County monitors that TCEQ admitted would still be above the 75 ppb standard at the end of 2018. "Close enough" is the reply from Austin.
From a public health perspective, it's even worse. Why does the ozone standard keep routinely going down? Because new and better evidence keeps accumulating to show widespread health problems at levels of exposure to smog that were once considered "safe." About every five years, the EPA's scientific advisory committee must assess the evidence and decide if a new standard needs to be enforced to protect public health.
For most of the last ten years, the position of this independent panel of scientists is that the standard should be somewhere between 60 and 70 ppb. They were ignored in 2008. They were ignored in 2011. They once again came to this conclusion last May. What was the evidence that persuaded them? That the current 75 ppb standard for smog causes almost 20% of children in "non-attainment areas" to have asthma attacks, and leads to hundreds of thousands of deaths every year. Cutting the standard to 60 ppb reduces those deaths by 95%. Since the Clean Air Act states the EPA is duty bound to set a smog standard protective of human health, 60 ppb seems to be the threshold level that the current scientific literature says is actually safe for the majority of the population most vulnerable to the impact of bad air. By contrast, a smog level of 70 ppb only reduces those deaths by 50%. (Policy Assessment for the Review of the Ozone National Ambient Air Quality Standard, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air and Radiation, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, Health and Environmental Impacts Division, Ambient Standards Group, August 2014)
By December 1st, EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy must decide whether to officially recommend a standard in that 60-70 ppb range. It looks as though this time, the EPA might just endorse what the scientists are recommending, although it's unclear whether it'll be the upper or lower part of that range.
So even while the TCEQ is saying it's "close enough" to achieving the 75 ppb standard left over from George W's administration by 2018, the evidence is that level is too high to prevent large public health harms and must be lowered. A lot.
This is why it's so infuriating that the TCEQ is satisfied with getting only "close enough" to a 2008 standard that's about to become obsolete. Austin knows it could demand better air pollution control measures on the market right now that would accelerate the decrease in smog. It knows the pubic health would benefit from requiring such measures. But it's willing to condemn DFW children and others at risk for many more years for the sake of keeping its "business-friendly" reputation.
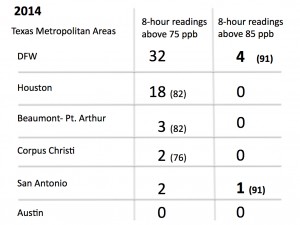
And while this year's slip below the 85 ppb standard is a sign of some progress, it remains true that DFW still has the worst air in Texas – a title we took from Houston years ago. Take a look at the chart summarizing the 2014 ozone season across Texas. Despite the nicer weather, DFW still had almost twice as many readings above 75 ppb as Houston and four above the 85 ppb standard. Houston had no readings above 85. In fact, San Antonio was the only other city to record a level so high – once.
 DFW still has a smog problem and all it takes is another hot and dry summer to see it escalate. We need the help more controls on major sources could give us. We need Selective Catalytic Reduction on ALL the Midlothian cement and East Texas coal plants. We need electrification of gas compressors in the Barnett Shale. This should be the message to both the TCEQ and EPA during the public hearing in January.
DFW still has a smog problem and all it takes is another hot and dry summer to see it escalate. We need the help more controls on major sources could give us. We need Selective Catalytic Reduction on ALL the Midlothian cement and East Texas coal plants. We need electrification of gas compressors in the Barnett Shale. This should be the message to both the TCEQ and EPA during the public hearing in January.
DFW smog in 2014: we've met the Clinton era standard for now, on the way to trying to get "close enough" to the W Standard, and still very far from a new Obama standard. Don't hang up the gas mask yet.
TCEQ: Link Between Fracking and Air Quality, No Cement Controls Just “Because”: Highlights From Tuesday’s Air Meeting
 Dallas Resident Liz Alexander showed up at the Council of Governments meeting room on Tuesday to lend her support to the effort to get more out of an anemic state ant-smog plan than the state wants to give. She was a warm body whose presence would be its own statement of concern. She was being a good trooper by just showing up.
Dallas Resident Liz Alexander showed up at the Council of Governments meeting room on Tuesday to lend her support to the effort to get more out of an anemic state ant-smog plan than the state wants to give. She was a warm body whose presence would be its own statement of concern. She was being a good trooper by just showing up.
At first she sat far from the action amidst the rows of seats for bystanders and, despite encouragement, was resigned to just listening, because as she explained, "she didn't know enough to ask questions."
Then someone urged her to move up to the rectangle of tables where the presenters stand and deliver, where there are microphones to raise the volume of concerns and questions that might be posed by mind-numbing reassurances that everything is going hunky-dory. As more of these air quality meetings have occurred, citizens have been less and less shy about taking up these front row seats that look more official than the rest; look like they should be reserved for guys in suits. Increasingly they're occupied by people in street clothes.
And then, after much information had been paraded in front of Liz, she did something she did not think she was qualified to do only about 90 minutes earlier. She asked a question. It was about what assumptions had been included in the information about unspent air pollution clean-up dollars that are piling up in Austin. She got an answer from a local COG staff person in real time that satisfied her. In the space of one meeting she moved from spectator to participant.
And she wasn't the only one. More than any other meeting so far, this one involved more citizens asking more questions about more subjects – and it revealed just how thin the state's rationale is for doing nothing.
As predicted, it was a day for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to explain why its new DFW anti-smog plan was really going to work this time – unlike the five previous failures – and why it wasn't going to be considering any new controls on the Midlothian cement plants or on gas compressors – a refutation of the case Downwinders at Risk had made in its June 16th presentation.
But here's what really happened: For the first time in these proceedings the state admitted that oil and gas emissions have a big influence on regional air quality. And when a former County Judge asked an TCEQ's Air Quality Manager specifically why anti-smog controls already being used on cement kilns in Europe were not being considered for the Midlothian kilns, the staffer couldn't say, offering up only the longest, most pregnant pause by any state staffer in the history of these meetings.
After being heavily criticized for months for leaving at least four monitors above the 75 ppb federal smog standard even after its plan had ended in 2018, the state came back to this meeting saying they only had three sites above 75 ppb now, and by margins that didn't exceed the standard by more than 1 part per billion. Between June and August, there had been a remarkable drop in future estimated smog levels at the area's monitoring sties in the state's computer modeling – particularly at the historically most stubborn monitoring sites in Denton and Northwest Tarrant County.
What had caused this drop? A relatively modest decrease in Nitrogen Oxide pollution of around seven tons a day and a decrease in Volatile Organic Compounds of about 15 tons per day. That's not a lot of pollution to produce such a large decrease in monitor readings in the computer model.
A more important question is: where did the decreases in air pollution come from that could produce such dramatic results in the modeling? The answer: primarily from oil and gas industry sources. Based on TCEQ's own formula relying on the declining number of new wells being drilled in the Barnett Shale.
For the moment forget the methodological qualms you might have about that declining well assumption. Instead, appreciate the fact that the same state agency that couldn't bring itself to ever say the Barnett Shale was producing air pollution holding DFW back from meeting Clean Air Act smog standards now says that it's decreases in that very kind of pollution that are having such a substantial effect on the monitors in the western part of the Metromess that have been the most resistant to other control strategies. TCEQ has just proven a causal link its been denying for over seven years now.
It can't be just a one-way street. If declining oil and gas air pollution equals better air quality in the TCEQ's computer model, so increases in oil and gas pollution must lead to worse air quality.
There are all kinds of reasons to doubt that the drop in total oil and gas air pollution will happen at all or drop as fast or as sharply as the TCEQ predicts. Afterall, they're 0 for 5 in such matters. They may be underestimating the amount of total air pollution from all gas and oil sources and so the drop will not be as sharp. They may be underestimating the impact of lots of new lift compressors that will be showing up to squeeze the last bits of gas from older wells even as new wells are not drilled as often. But as of Tuesday the link has been made by TCEQ itself that such a drop results in big decreases in smog levels in Denton and Northwest Tarrant County. That's something that citizens can use to argue as proof of the impact of oil and gas facilities on local air quality.
Of course, it only took the span of about 30 minutes for the TCEQ to internally contradict itself about those results.
According to TCEQ computer modelers, natural gas Compressor Stations large enough to be considered "point sources" just like cement kilns or power plants will be responsible for over 17 tons of Nitrogen Oxides, and 26 tons of VOCs a day in 2018 – well over the amount of oil and gas pollution decreases that resulted in those lower monitoring numbers in Denton and NW Tarrant County. But according to the TCEQ staff responsible for suggesting new controls in the new smog plan, those numbers are not large enough to have an impact on improving DFW air quality or warranting a policy of electrification for those compressors that could reduce their air pollution to a fraction of those volumes.
So while 7 tons of NOx reduction from Oil and Gas sources is large enough to bring some of the most stubborn monitors down a whole part per billion, reducing air pollution from Oil and Gas sources by another 17 tons of NOx reduction would have no effect on DFW air quality at all and it's just not worth it to make them electrify compressors. Honest, that was the logic in play on Monday, and it didn't hold up very well under questions from people like Liz Alexander.
And that was all before you got to why the Midlothian cement kilns could not, no way, no how, possibly, under any circumstance, be required to install Selective Catalytic Reduction controls, just like their European counterparts have done over the last 15 years.
Turns out, it's just because.
Oh, the TCEQ staffer cited four criteria for any new control measure to meet before it could be considered. Let's see, there was "technological feasibility." Since there are at least seven full-scale SCR units up and running in Europe, that couldn't be a problem. It's accepted technology by some of the same companies operating kilns in the US – including LaFarge-Holcim.
There was "economic feasibility." And since there are all those SCR examples already in the European market and no company has gone bankrupt running them, that's also off the table. Plus the fact that the TCEQ's own 2005 study of SCR concluded it was "available technology" then that would only cost $1000 to $3,000 per ton of NOx removed – versus the up to $15,000 per ton of NOx removed ratio allowed in the state's own official diesel engine replacement program. Coming in at one-fifth the cost of what the state already said was economically feasible, it certainly ruled out that one.
There was the third criterion – that controls couldn't cause ‘‘substantial widespread and long-term adverse impacts.’’ The state said that wasn't the reason they couldn't be considered either, although the TCEQ staffers seemed to hedge a bit here, seemingly wanting to say that, really, they didn't want to cause themselves adverse impact by admitting that they had been wrong for over a decade about this stuff.
The proposed control cannot be ‘‘absurd, unenforceable, or impracticable.’’ Clearly, if the Europeans are doing it on their kilns, it's none of those either. It's quantifiable, and up and running in power plants, cement kilns and incinerators.
And it has to speed the attainment deadline by a year. No problem. SCR could do that if it was installed in a timely fashion.
So at the end of the state's presentation, former Dallas County Judge Margaret Keliher asked the TCEQ staffer exactly why SCR wasn't considered a possible pollution control measure since none of these criteria that had been presented seem to rule it out. And the TCEQ's staffer's response was…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
No, really, that was the response. She couldn't say. It was that embarrassing. Because the rejection of SCR by TCEQ isn't based on any of those criteria. It's based on a political decision that's been made that no new pollution controls will be sought on the kilns or any other major industrial polluter as long as Rick Perry is running for President. Or "just because."
How ridiculous is this? At this point the TCEQ is taking an even more regressive view of SCR controls than the cement industry itself. In June, Holcim Cement's Midlothian plant requested a permit from the state that would allow it to build either a Thermal Oxidizer or an SCR until for the control of VOC pollution. Being the free market fanatics the Perry Administration claims to be, doesn't the fact that one of the Midlothian cement plants is asking for a permit that includes the possibility of installing SCR mean it's automatically technologically and economically feasible? The market is never wrong, right? Are the folks at Holcim so enamored of kinky, off-the-wall green technology that they'll just include it in a permit for laughs? These guys are Swiss engineers. They have no sense of humor.
Denial of SCR as a viable control measure that could reduce smog pollution is making the TCEQ contort into sillier and sillier positions. It's making them deny the conclusions of their own almost-decade old report that said it was available to put in a kiln in 2005. It's making them deny the fact that SCR is up and running at over half a dozen kilns in Europe. It's forcing them to once again use the "Midlothian limestone is magically special" defense that has been used to forestall any progress in pollution control there over the last 25 years. The arguments used against SCR are exactly the same as were used against the adoption of less effective SNCR technology before it was mandated. In case you hadn't noticed, they're still making cement in Midlothian despite the burden of having to nominally control their air pollution.
The state wants to power through this anti-smog plan just like they did the last one in 2011. They don't want to have to make industry do anything. But at this point the denial of SCR as a control measure to be included in the next DFW anti-smog plan is so absurd, as is the justification for electrification of gas compressors, that it might be fodder in the next citizens lawsuit over a DFW anti-smog plan, which usually follows these things like mushrooms after a rainstorm.
Want to get involved in this fight and make it more difficult for the state to get away with doing nothing at all about DFW smog – again? Please consider attending our next DFW Clean Air Network meeting – THIS SUNDAY, AUGUST 17th, from 3:30 pm to 5:30 pm at the offices of the Texas Campaign for the Environment across from Lee Park in Dallas, 3303 Lee Pkwy, Suite #402 (214) 599-7840. Citizens are the only force that can make this plan better. Be there, or breathe bad air.
Want to Quiz the State Over Crappy DFW Air? Tomorrow’s Your Chance As the Empire Strikes Back
 Rick Perry's minions at the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) are drafting a new anti-smog plan for DFW this summer and fall. The only access DFW residents have to how it's being done and why are through periodical regional air quality meetings hosted by the Council of Governments in Arlington. At these meetings staff from TCEQ make presentations on why the air in DFW is getting so much better and why no new pollution control measures are needed to reach smog standards required by the Clean Air Act – despite the fact that the state is 0 for 5 in plans to attain compliance with those standards. In fact, the last such plan from Austin actually resulted in slightly higher levels of smog.
Rick Perry's minions at the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) are drafting a new anti-smog plan for DFW this summer and fall. The only access DFW residents have to how it's being done and why are through periodical regional air quality meetings hosted by the Council of Governments in Arlington. At these meetings staff from TCEQ make presentations on why the air in DFW is getting so much better and why no new pollution control measures are needed to reach smog standards required by the Clean Air Act – despite the fact that the state is 0 for 5 in plans to attain compliance with those standards. In fact, the last such plan from Austin actually resulted in slightly higher levels of smog.
Tomorrow, Tuesday August 12th there will be another such regional air quality meeting. It's going on from 10 am to 12 noon at the Council of Government headquarters in Arlington at 616 Six Flags Road, right across from the amusement park (insert your own joke here). Of course, it's during business hours – you didn't think they're going to make it easy for the public to attend, did you?
Despite that, beginning in April more and more local residents have been showing up at these meetings to express their concern at the lack of progress in bringing safe and legal air to DFW. One of the reasons is that these meetings are the only forum available to citizens to question TCEQ staff in person – and then ask follow-up questions if you don't like the first answer. It's their only opportunity to be a kind of clean air Perry Mason and because it's a public meeting and everyone's looking at them, TCEQ staff have to at least make an attempt to answer those questions.
Things reached a high point at the last meeting in June when Downwinders and the Sierra Club were allowed to make their own presentations about why the state is falling down on its job. A roomful of concerned citizens and elected officials saw the case against the state was self-evident – all we had to do was quote from its own past press releases and memos to make our point.
Tomorrow's meeting is the first chance the state will have to give a rebuttal to those citizen group presentations. Staff will present all the reasons why we don't need new air pollution controls on the Midlothian cement plants, the gas industry, or the East Texas coal plants, and why another do-nothing anti-smog plan from Austin will be just dandy.
And so, if between inhaler bursts you ever wanted to quiz officials about Rick Perry's air pollution strategies, tomorrow's meeting is going to be your chance.
You may think you're not qualified, but you'd be wrong. Simple common sense questions are often the hardest ones for the TCEQ staff to answer, because you know, they're based on common sense, and so many of their policies aren't.
This is how citizens uncovered the fact that TCEQ was hiding oil and gas pollution in other categories not named oil and gas. This is how we got the TCEQ to release maps of where all the gas industry compressors in DFW are after first explaining there were no such maps. And so on.
All that you need is a curious mind. They're not prepared for those.
Tomorrow, 10 to 12 noon is your opportunity to show your concern about breathing bad air, your desire to see major industrial sources of pollution better controlled, and why you want these anti-smog plans to do more. Be there or keep breathing bad air.
