car pollution
Can Obama’s EPA Save Us From TCEQ’s “Clean Air Plans”?
 It's only a proposal, but the Obama Administration's plan to cut sulfur in gasoline is aimed primarily at drastically reducing smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide, Volatile Organic compounds and Particulate Matter, the major pollutants that causes DFW to have such bad "ozone seasons." Would it reduce it enough to finally put the region in compliance with the Clean Air Act? Good question.
It's only a proposal, but the Obama Administration's plan to cut sulfur in gasoline is aimed primarily at drastically reducing smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide, Volatile Organic compounds and Particulate Matter, the major pollutants that causes DFW to have such bad "ozone seasons." Would it reduce it enough to finally put the region in compliance with the Clean Air Act? Good question.
Sulfur content in gasoline would drop from the current standard of 30 ppm to 10 ppm by 2017 – one year before the compliance deadline for the tougher 75 parts per billion national ambient air ozone standard. That's not a coincidence. The EPA hopes that this initiative is going to drive urban ozone clean-up throughout the country, even in stubborn dirty air hot spots like DFW, which hasn't been in compliance with a smog standard since it was created over 20 years ago.
Along with new stricter emission standards for cars that have already been implemented, the pollution from cars will be coming down over the next decade to historic-per-vehicle lows. Since forever, the state of Texas and local officials have put almost all the blame for DFW's poor air quality on cars. So does this mean that we might actually have a chance to breathe safe and cleaner air, by say, 2020?
Maybe.
First, there's the question of continued growth. If per-car emissions go down, but you're importing 120,000 more cars every year into North Texas, the decreases in emissions are being canceled out to some degree. In this respect, DFW has been its own worst clean air enemy. By attracting new residents year after year and, for the most part, not creating successful transportation options other than private vehicles, the Metromess dooms itself to more total car pollution.
Then there's the climate. Everyone knows how unbearably hot it can get in DFW during July, August and September. That heat and sunlight is one reason we have a smog problem – it chemically transforms the Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) into ozone. What if it gets hotter, and drier? When the ground can't cool off at night and you start out with high morning temperatures that will only get worse by 5 pm, you know it's going to be a bad air day. The more days like that, the harder it's going to be to have safe and legal air despite the changes in engine design and fuel specs. So climate change could rob us of some of those automobile reductions.
If the last couple of years are any indication, you also have to wonder how much of those vehicle changes will be lost on DFW because we live in the Barnett Shale. 16,000 gas wells that are relatively short-term air polluters are being supplemented with more processing infrastructure like compressors, refineries, and pipelines that are year round polluters. Last year's Houston Advanced Research Consortium study estimated the impact of even a single compressor or flare to be as much as 3-10 ppm within five to ten miles, something it would take thousands of cars to accomplish. Even if those cars aren't there anymore, or their emissions make them less of a clean air threat, you have these decentralized major sources taking up the slack. This is one reason why the state itself told EPA that last year there was more VOC air pollution coming from oil an gas sources in North Texas than all the area's on-road cars and trucks, and a large contributing cause to why air quality has been getting worse in DFW over the last two years.
It's not just the number of these facilities but their physical location as well. The more the gas industry moves eastward, the more of the DFW core urban area is "downwind" of these sources, the more the pollution from these facilities combines with car emissions and other urban sources, and the longer they take to leave the now 10-county "non-attainment area," meaning they linger, exposed to sunlight and heat, and have more opportunity to create high levels of ozone. If you have more flares and compressors within 1 to 3 miles of one of 18 or so state air monitors – you will probably begin to see higher ozone readings as a result of their operation – as you have the last couple of years. Most of these pipelines and processing facilities have come online only since 2006.
And that's just in the North Texas area. There's evidence to suggest that the gas industry's building-out to the southeast – or upwind – of DFW is also affecting our air quality. In the same way that Houston's air pollution is said to make our initial "background" ozone levels higher, so too the 60-100 compressors in Freestone County, about 90 miles southeast of Dallas also feed their under-regulated "Standard Permit" pollution into the DFW urban mix. As does the Haynesville Shale gas play itself, as do the remaining east and central Texas coal plants and so forth. If sources to the south and east continue to increase their emissions, it means DFW starts from further and further behind, so that even if cars get cleaner, they might not get so clean so fast as to compensate for this imbalance.
Then there's the "fire hose" effect of the three Midlothian cement plants sitting so close to one another as to create one large super plume that's usually pointed toward the DFW urban core most of "ozone season." Because of citizen efforts, those cement kilns are substantially cleaner in 2013 than they were as recently as 2008. All but one wet kiln is closed, and that one is due to shut down next year. None are burning hazardous waste. But they're still the largest stationary sources of pollution in North Texas – including emitting copious amounts of NOx and VOCs – and they can still impact monitor readings miles and miles away. It's unclear what impact the burning of newly-permitted "non-hazardous" industrial wastes like car parts and plastics in the Midlothian kilns will have on the formation of smog-forming pollution.
EPA estimates an 80% drop in VOC and NOX pollution from cars as a result of its new low-sulfur fuel rule. That's steep. Remove that amount of pollution from all DFW's cars and trucks, and you'd expect to see a substantial improvement in air quality. That's what you'd expect. But, depending on a lot of other variables the state and federal government may or may not be interested in fixing, it could take more than this proposal to bring DFW into compliance with the new 75 ppb ozone standard that is now the federal definition of safe and legal air.
Study: Car Traffic As Bad As Second Hand Smoke in Causing Asthma
 A large new European study released this week found that as much as 14% of chronic children's asthma in the Continent's urban areas could be due to traffic pollution. That would put it on par with the effects of second-hand smoke, linked to anywhere from 4 to 18% of all childhood asthma.
A large new European study released this week found that as much as 14% of chronic children's asthma in the Continent's urban areas could be due to traffic pollution. That would put it on par with the effects of second-hand smoke, linked to anywhere from 4 to 18% of all childhood asthma.
"Air pollution has previously been seen to trigger symptoms but this is the first time we have estimated the percentage of cases that might not have occurred if Europeans had not been exposed to road traffic pollution," lead author Dr. Laura Perez, at the Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute, said in a press release. "In light of all the existing epidemiological studies showing that road-traffic contributes to the onset of the disease in children, we must consider these results to improve policy making and urban planning."
Although the idea of getting cars off the road as a benefit of mass transit isn't new, this study and others that have been published recently flesh out a new public health concern about the immediate impacts of such reductions in the neighborhoods adjacent to highways. Often these neighborhoods are already low and moderate income, and/or minority-majority with higher-than-average asthma rates already institutionalized because of lack to access to care, poverty or other factors. Highway plannning has yet to take this kind of localized impact into account, especially in Texas and DFW, where regional highway builders are still salivating to build the Trinity Toll Road straight through the middle of Dallas or criss-cross Ft. Worth neighborhoods with the new "Chisholm Freeway."
Asthma affects one in 12 people, or 8 percent of the U.S. population, according to 2009 data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The number has increased since 2001, when one in 14 people were affected.
State Budget Writers Vote to Keep Raiding Anti-Smog Funds
 Today brings news of the first skirmish in this year's state Legislative session over using anti-smog funds collected in DFW and other EPA "non-attainment" areas to ease budget gaps in general revenue.
Today brings news of the first skirmish in this year's state Legislative session over using anti-smog funds collected in DFW and other EPA "non-attainment" areas to ease budget gaps in general revenue.
The Dallas Morning News has an account of local Dallas State Representative Helen Giddings teaming up with Houston Rep. Turner Sylvester during a House Appropriations Committeee meeting on Tuesday to make the case that the funds are desperately needed to help reduce air pollution in Texas' largest cities where unhealthy air is still the norm during "ozone season."
Everyone who gets their car inspected in North Texas pays an extra $6 that goes to the "Low-Income Repair and Replacement Assistance Program," (LIRAP). The money is supposed to be used to help low-income car owners upgrade their vehicles so they'll run cleaner. Because they can't afford to buy new vehicles as often, low income owners usually drive older cars. Older cars are dirtier cars. Fix them or upgrade them to newer cars and you reduce air pollution.
According to the folks that wear the green shades, the LIRAP fund will have approximately $77 million in unspent money at the end of August. Another $80 million is expected to be collected in the state's "non-attainment areas" over the next two years. That's a lot of car repair money. But as it turns out, state budget writers are proposing to only spend a little over $11 million in the next two years to be split up between Houston, DFW, Austin and San Antonio.
The size of the diversion has publicly angered elected officials in DFW and the other urban areas who are facing compliance with a new, stricter EPA smog standard by 2018 even as they annually fail to meet the old standard. In DFW and Houston LIRAP funding is traditionally used to build the clean air plans that must get approved by EPA. Without sufficient funds, local officials are telling the state that its next plan, due in 2015, might not get approved by EPA. You can imagine the disappointment in Austin of hearing that news.
Austin and San Antonio officials have actually threatened to pull out of the fee system all together unless they get more back of what their residents are putting in. That huffing and puffing paid off a bit Tuesday, as the Republican-led committee voted to approve an additional, but token, $1.4 million to those cities. Still, perhaps that lesson will not be lost on DFW officials, who have a long history of suffering silently as the state increasingly robs the region of its ability to control it's own air quality fate.
This was only the opening round of votes, and the House is more conservative than the Senate. But it's probably not a good sign that Rep. Giddings was the only one of at least five DFW-based members of the House Appropriations Committee quoted in News as leading the charge. Missing in Action was former Arlington City Council member and previous sometime-clean air supporter Diane Patrick, and oh yeah, the Chair of the Committee that hails from non-attainment Ellis County, Representative Jim Pitts. If the local North Texas clean air establishment can't get more help from its own players in the Lege, they're unlikely to see more money flowing their way.
Traffic Pollution Linked to Autism
 Along with a higher risk of asthma, children who are born and live their first year closer to major freeways also suffer a significantly elevated risk of autism. That's the conclusion of a new study by the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles.
Along with a higher risk of asthma, children who are born and live their first year closer to major freeways also suffer a significantly elevated risk of autism. That's the conclusion of a new study by the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California in Los Angeles.
"Compared to 245 California children who were not autistic, the researchers found that 279 autistic children were almost twice as likely to have been exposed to the highest levels of pollution while in the womb, and about three times as likely to have been exposed to that level during their first year of life.
They found that children exposed to the highest amount of "particulate matter' – a mixture of acids, metals, soil and dust – had about a two-fold increase in autism risk. That type of regional pollution is tracked by the Environmental Protection Agency.
Volk and her colleagues also saw a similar link between autism and nitrogen dioxide, which is in car, truck and other vehicle emissions.
'This is a risk factor that we can modify and potentially reduce the risk for autism,' wrote Dawson in an email to Reuters Health."
It's been estimated by the Centers for Disease Control that autism affects one in every 88 children born in the United States.
A new federal Particulate Matter standard is under consideration by the EPA and could be announced this year. It's been linked to other neurological diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimers.
2nd TCEQ Clean Air Plan in Four Years Fails, Leaves Air Dirtier
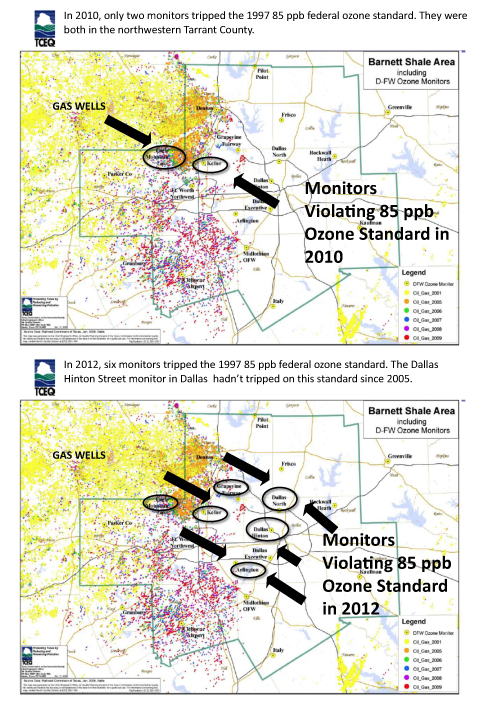 For the second time in four years a state-designed clean air plan to bring safe and legal air to DFW residents has failed, missing its goal by an even wider margin than on its first try, and leaving local air quality worse than when it started.
For the second time in four years a state-designed clean air plan to bring safe and legal air to DFW residents has failed, missing its goal by an even wider margin than on its first try, and leaving local air quality worse than when it started.
November 1st marked the official end of the eight-month 2012 ozone season. According to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, or TCEQ, its plan was supposed to deliver record-breaking clean air to DFW this summer on its way to bringing the region into compliance with the Clean Air Act for the first time in two decades.
Study: Green Spaces Make Pregnancy Easier
 Coming under "Confirming Things You Probably Already Knew," is this study via the folks at Environmental Health News:
Coming under "Confirming Things You Probably Already Knew," is this study via the folks at Environmental Health News:
"Living in homes surrounded by grass and trees can reduce pregnant women's exposures to traffic-related air pollution, according to a study in Barcelona, Spain. As green space around their homes increased, their exposure to fine particles and nitric oxides decreased. Particles and gases in vehicle exhaust can affect the development and health of fetuses, so this study suggests that green space in urban neighborhoods has a health benefit."
Over the last five years, study after study has provided proof that living near roadways increases your likelihood of having respiratory problems and other health problems. And yet, just like the regulations surrounding lead smelting or waste-burning haven't caught up to the most recent science, so traditional highway risk assessments don't yet acknowledge most of this new scholarship.
The design of the CF Hawn/SM Wright freeway redo that will help shape South Dallas for a generation or more is in its final stages of planning. There may be as little as 2-4 months until approval will be given by the Federal Highway Administration to proceed with a 6-lane thoroughfare instead of a more community-friendly four land boulevard that residents have voiced support for time and again.
Now is the time to call attention to a factor that may not have been examined very thoroughly, if at all, by TXDOT or local officials in designing the redo – before another wrong is inflicted on South Dallas by the city.
Risks from Freeway Air Pollution “Very Important” to Consider. Will Dallas?
 Over the past five years, there's been a significant increase in the amount of scholarship devoted to chronicling what kind of risks are posed by running freeways through communities and exposing adjacent residents to the cumulative air pollution of thousands of tailpipes. For the first time, urban planners are having to consider the public health consequences of transportation choices that still rely on the internal combustion engine.
Over the past five years, there's been a significant increase in the amount of scholarship devoted to chronicling what kind of risks are posed by running freeways through communities and exposing adjacent residents to the cumulative air pollution of thousands of tailpipes. For the first time, urban planners are having to consider the public health consequences of transportation choices that still rely on the internal combustion engine.
"Researchers who affirm that children living near freeways are more likely to suffer from asthma are alerting urban planners about the importance of keeping homes away from busy roads.
The asthma-pollution link is especially vital as planners look at clustering jobs, transportation and homes as a way of limiting sprawl, the researchers said in the study published Monday, Sept. 24."
The study in question is from the University of Southern California's Keck School of Medicine. It found that higher air pollution levels less than 100 yards from freeways caused an estimated 27,000 additional cases of childhood asthma in Los Angeles County in 2007, almost 8% of the County's total that year.
Sarah Katz, a research associate at UC Irvine’s Institute of Transportation Planning, said clustering homes near transit, services and jobs is a newer trend in urban planning.
In view of that, Katz said, the USC report is essential reading for planners. The science on the health effects of roadway pollution is relatively new, and not all planners are familiar with it, she said.
“I hope this report gets a lot attention, because it is very important,” Katz said
Indeed. But is anybody at TXDOT reading these studies and paying attention? If so, why does Austin insist on turning the new CF Hawn freeway project in South Dallas, you know, the fixing of the "deadman's curve," into a 6-lane Carmageddon running straight up the middle of the community instead of the less frantic boulevard concept the neighborhood is requesting?
Because of studies like the one from USC, there's now plainly environmental justice and public health litmus tests that can be applied to every new freeway project. Environmental impact statements should have to take this new evidence of air pollution harm into account. But if government won't do that kind of accounting, then the people who are affected need to do it themselves. South Dallas shouldn't have to settle for a 1960's style concrete conduit that's going to act as one big funnel for air pollution when the trend is away from building such dinosaurs.
“How your great grandmother’s chemical exposures may affect you”
 In a study published this week, "rats exposed in the womb to five common environmental pollutants passed on DNA-changing attributes that persisted in causing ovarian cancer three generation removed from the original exposure."
In a study published this week, "rats exposed in the womb to five common environmental pollutants passed on DNA-changing attributes that persisted in causing ovarian cancer three generation removed from the original exposure."
It's another example of "epigenetics" – when harmful environmental exposures to one generation can skip a generation or two and show up as health effects decades later.
According to the new study, the five pollutants reprogram how DNA is expressed in the developing fetus' eggs, setting the stage for ovarian disease later in their life.
If you're a Vet, the news is worse. The U.S. Department of Defense helped select the pollutants based on potential exposures in military personnel. They included vinclozolin, a fungicide that's used in the wine industry; a pesticide mixture including permethrin and DEET; a plastic mixture including bisphenol A (BPA) and two widely used phthalates (DEHP and DBP); the industrial byproduct dioxin; and a hydrocarbon mixture called "jet fuel," which is used to control dust on road surfaces.
Researchers at Washington State University exposed pregnant rats to one of five different chemicals alone or in mixtures during a critical time of pregnancy when their daughter pups' eggs were developing. The pups were then mated with males from the same treatment group, and the resulting pups were bred yet again. Only the original generation of pregnant rats had been exposed to the chemicals. The adult daughters and great granddaughters of the dosed animals (called the F1 and F3 generations) were examined for ovarian disease.
In all exposure groups, both the daughter (F1) and great-granddaughter (F3) mice had fewer egg follicles in their ovaries compared to controls, indicating a reduced pool of available eggs. Both generations – but particularly the F3 animals – also had an increased number of ovarian cysts compared to controls.These findings are characteristic of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) and Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI), which are believed to affect 18% of all women.
Other diseases, including allergies and asthma; liver, gastric, prostate and colorectal cancer; and psychiatric disorders are thought to have an epigenetic component. This is the first time that epigenetic changes have been shown in association with ovarian disease. This proof-of-concept study used higher doses of chemicals than what people would typically encounter. Future work is needed to investigate whether lower, more environmentally relevant chemical levels also affect ovarian disease across generations of the rodents.
Locally, we're surrounded by sources of one or more of these pollutants, especially phthalates, BPA, dioxin, and hydrocarbons. BPA is the subject of a lot of media attention and just yesterday, the FDA banned its use in sippy cups for infants. Frisco's Exide lead smelter has been a top ten dioxin polluter in Texas over the last decade. The cement plants in Midlothian are also large industrial sources of dioxin, and new permits to burn more "non-hazardous" wastes that turn into hazardous emissions only ensure that will remain the case. On the ground, internal combustion engines from cars and the natural gas industry facilities in the Barnett Shale soak us in hydrocarbons.
Despite the documentation of the epigenetic effect of certain pollutants in recent years, this impact has not yet been incorporated into any risk assessment of a polluting facility by any environmental or public health agency in the U.S. We may be planting the seeds for epidemics of all kinds in the next 20-50 or more years, and it's all perfectly legal now. Once again, the science is way out in front of the regulations. That's why citizens must arm themselves with the latest research. You won't be getting updates on this stuff from EPA or TCEQ. That's also why it's ridiculous for anyone to speak about the "over-regulation" of polluters in this country. We're nowhere close to understanding what the long term consequences are of our actions in allowing so many chemicals into the environment to mix and match with our own biology. In this larger public health sense, pollution is still very much under-regulated in the United States.
“Moderate” PM Pollution in DFW Kills and Maims
It’s behind the paywall, but the Morning News and Randy Lee Loftis commit real journalism today in the form of anarticle on the dangers of Particulate Matter pollution, even at so-called “moderate” levels. It’s based on two recent studies, inlcuding one we profiled here last week, but then does the right thing by localizing what the results of those studies mean for DFW air quality. The answer isn’t pretty. It turns out there were an average of 41 days a year from 2007 to 2011when PM readings at one of two monitoring stations in Dallas were in the range that’s associated with increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. By comparison, DFW experienced 38 days last summer when the new 75 parts per billion ozone standard was exceeded. Considering that there are about three times as many ozone monitors as PM monitors in DFW, you can see where some folks might think we have a problem: for more than a month every year, we breathe air that can make us sick or kill us. Unfortunately for future victims, it appears it will take some kind of threat from the federal government, or the courts, or both to make PM pollution as much of a target for control as ozone pollution, even thought the scientific evidence continues to mount that particulates cause much more widespread public health damage. That’s because state and local governments risk losing federal highway dollars if they don’t try and reduce ozone pollution, or smog. There is no such threat driving public policy regarding any other air pollutant. There are almost 40 posts on PM pollution listed in our category directory for this blog. Many of these summarize recent studies showing how pervasive PM pollution is and how insidious its health effects are. It damages you by being both a piece of dirty soot that can make it hard to breathe, and as a carrier of any number of toxic chemicals that attach themselves when the piece of soot is created. PM can have lead or mercury on it. It can have benzene or formaldehyde. It’s a microscopic suitcase for toxins. PM can cross the lung/blood vessel barrier and travel throughout your body, affecting your brain, your reproductive health or your immune system. It’s the most underestimated, and under-regulated pollution. Federal standards for PM pollution are stuck way behind the times and need to be updated, but the Obama Administration decided not to go forward with trying to write a new standard in its first term – probably because of projections about how far-reaching the solutions to PM pollution will have to be – taking in everything from cars to power plants to diesel trucks, to cement plants. You’ve seen the howling from industry over new ozone standards and power plant mercury rules. Imagine the reaction to a tougher PM standard. Yet that is the direction the science is sending us. We’ve often been critical of the dearth of local environmental reporting in DFW, but this piece today is an excellent example of he kind of work a major metropolitan daily needs to be churning out on a regular basis. Kudos to the News and Loftis.
First they Come for the Peanut Shells
Here's a story from Florida about the Brooksville Cemex cement plant's new permit that displays the quintessential spin from the cement industry about their transformation into garbage burners. 1)The headline uses the preferred industry term of "alternative fuels" instead of garbage. 2) It leads with all the feel-good fuzzy bio-garbage like peanut shells and wood chips. Only further down do they let you see the rest of the list – "including plastics, carpet, roofing materials and wood treated with creosote. Included, too, are so-called engineered fuels such as cleanup debris from natural disasters, processed municipal solid waste, dried and sanitized sewage bio-solids, noninfectious hospital materials, expired pharmaceuticals and confiscated narcotics." 3) It makes sure you know that this new garbage burning will shrink the plant’s carbon footprint and lower emissions of toxic chemicals like Mercury – but the plant will not be amending its operating permit to reflect those proposed decreases. 4) for all the talk of "alternative fuels," the plant is mainly still burning coal and tires, both of which it's been burning for a long time. The largest expense of running a cement plant is fuel costs. The industry is always finding a way to cut those costs. In the 1980's and 90's it tried turning cement kilns into hazardous waste incinerators by getting paid by polluters to burn their crap for less money than the pros. That met with quite a bit of public resistance and new regulations that made it harder to keep doing that. So now the industry is pivoting toward a laundry list of "non-hazardous" wastes – municipal garbage, sewage, medical waste, plastics, car interiors – garbage. Except that anyone who's ever studied the the history of American garbage incineration – and there's quite a history – knows there's nothing non-hazardous about the practice. Just because a waste isn't classified by EPA as a "hazardous" waste coming in the front door doesn't mean it doesn't emit hazardous air pollution when it's burned or carted off as ash out the back door. And even thought there's a lot of boasting about emission decreases, the industry isn't backing up that talk with real cuts in their permits. Places like Midlothian, home of three huge cement plants, and a concentration of cement manufacturing unmatched anywhere else in the US, are looked upon as nothing but large "landfills in the sky" to both waste producers and the cement plant operators themselves. TXI's Midlothian plant, directly south and upwind of DFW, just received a new permit "amendment" last June that allows them to burn the same kind of long list of garbage as the Florida kiln. They got this without any public notice or hearing or anything. None required as long as TXI promises, cross their heart, that the emissions won't increase above what they are now. And if they do? We won't even be able to know for sure until a test burn that will occur after they start burning garbage – they can wait up to a year to do the testing. This is why public participation is an over-arching issue in Texas now.Without it, there are no checks and balances. Only more experiments taking place in your lungs.
