Asthma
The North Texas Clean Air Network Gets an Unanimous Vote in its First Dallas City Hall Test…But Staff is Still Resisting
 Rebuking its own staff’s misinformation campaign, the Dallas City Council’s seven-member Quality of Life Committee voted unanimously at its Monday morning meeting to recommend joining the North Texas Clean Air Network.
Rebuking its own staff’s misinformation campaign, the Dallas City Council’s seven-member Quality of Life Committee voted unanimously at its Monday morning meeting to recommend joining the North Texas Clean Air Network.
But in an unusual move, staff requested and received an almost three-month delay in scheduling a full city council vote on endorsing the new local air monitoring system. It won’t be until December 5th when the entire council gets briefed on the Network, and December 12th when they actually vote on whether to join. That’s a very long gestation period for a measure that just passed in Committee 7-0.
Staff claimed they wanted the long pause because of what they said were questions about how the city would participate in the Network and what provisions were necessary to get access to monitor locations like….utility poles. Citizens might be forgiven for suspecting the real reason for the three-month delay is to give staff time to find some new “fatal flaw” in the network and scuttle the whole thing before it ever comes up for a vote. If one listened hard enough, you could hear the startled disbelief in staff’s comments when the yes vote came down, despite every outward sign pointing to that outcome.
 When one considers there was a Dallas city staffer at just about every meeting that led up to the creation of the Network, that these meetings began over a year ago, and that this specific presentation and vote has been scheduled for the Council’s review since August, it’s really quite incredible that staff admits they’ve spent no time thinking about how to implement this proposed policy within the city limits. Maybe because they’ve spent so much time trying to shoot it down.
When one considers there was a Dallas city staffer at just about every meeting that led up to the creation of the Network, that these meetings began over a year ago, and that this specific presentation and vote has been scheduled for the Council’s review since August, it’s really quite incredible that staff admits they’ve spent no time thinking about how to implement this proposed policy within the city limits. Maybe because they’ve spent so much time trying to shoot it down.
As late as the Friday before Monday’s vote staff was still at it, sending out a memo to Committee members downplaying the need for any regional network, conveying regulatory-correct but scientifically-misleading language about local Particulate Matter pollution levels, and writing one of the oddest sentences we’ve ever seen associated with air quality monitoring. In dismissing the formidable capabilities of the kind of low-cost high tech sensors the Clean Air Network will be using, Dallas Assistant City Manager Joey Zapata concluded, “These low-cost air sensors present new opportunities for uses beyond regulatory monitoring but are not yet able to provide direct measurements of real-time health impacts.“
That’s because that’s not what air pollution sensors or monitors do. None of them. Nada. Zero. Not even the really big and expensive ones the City currently operates for the State and EPA. They can only measure what levels of PM pollution are in the air you’re breathing, not what cancers, birth defects, strokes, heart attacks, diabetes problems, IQ loss, dementia or other illnesses that PM Pollution are causing “in real time” in your body as you breathe it in. No such Star-Trek-like technology exists.
In the real world researchers take the PM measurements recorded by sensors and correlate them to rates of illness. It’s a branch of science called epidemiology. The staff memo manages to completely confuse two wildly different scientific methods in a stunning, head-shaking way. It’d be flat-earth funny if it wasn’t, you know, the official position of Dallas City staff on the subject. Then it just becomes embarrassing.
 But whatever doubts about the Network staff tried to infect the council members with, they seemed to vanish once UTD Physics Professor Dr. David Lary and Downwinders’ Jim Schermbeck, representing the DFW Air Research Consortium, gave their 35-minute presentation on the Network.
But whatever doubts about the Network staff tried to infect the council members with, they seemed to vanish once UTD Physics Professor Dr. David Lary and Downwinders’ Jim Schermbeck, representing the DFW Air Research Consortium, gave their 35-minute presentation on the Network.
A roomful of “Clean Air Now” button-wearing supporters also helped the cause considerably. Thanks to everyone who came on an early Monday morning to make sure the Committee did the right thing. Thanks also to everyone who sent in emails to the Committee via our prepared Citizen Action website feature.
That combination of grassroots support plus technical expertise is one of the things that’s so impressive about this bottom-up approach, and it paid off again in the Committee meeting. Schermbeck made the case for change, Lary gave the details of how to build that change, monitor by monitor.
D Magazine published an online piece Monday morning that provides a point-by-point rationale for why this Network is A Big Idea Whose Time Has Come. Basically Big, Expensive and Slow has been replaced with Small, Cheap and Fast and it’s democratizing air quality information. All of that was included in the Committee presentation, plus examples of how it could have made a difference in the real world during a past crisis like the Sunshine Recycling Fire of December last year in West Dallas.
Both Plano and Dallas County officials have already said they’re onboard with the Network and may act to ratify the founding documents in their jurisdiction before the scheduled December Dallas vote. By the end of the year a new 21st Century regional air monitoring system, driven by local expertise, controlled by local governments, and designed to promote public health could become a reality.
But citizens may still have to fight to see it happen. In an ironic twist, the same staff that has been opposing the idea of Dallas joining the Network is now in charge of writing the briefing paper for the Council to explain why it’s a good idea. Bets are already being taken on how well they succeed.
ARC’s Network presentation was only half of an interesting compare and contrast exercise looking at two local projects using air sensors in two very different ways that Chair Sandy Greyson had arranged for the Committee.
The other half was a presentation by the Texas Nature Conservancy outlining their city staff-supported “resiliency” (i.e. Rockefeller) project, the “Breathe Easy” study proposing to place a PM and ozone monitor for two years at nine DISD schools that already see high student asthma and absenteeism rates, all below Interstate 30. Breathe Easy has already started spending money and needed no vote…although it was the first time any Council Committee had been briefed on it.
The study was supposed to get started back in August with the beginning of the school year but the nine schools haven’t been announced yet and so no monitors have been installed. Since the 2018-19 academic year is designed to provide a “baseline” of student asthma health, the study has already missed its chance of getting any data during the worst summer for ozone pollution in five years. It could take another month or longer to name the schools and wire-up the monitors. It’s uncertain how much this gap of missing information diminishes the value or definition of a baseline to which three specific intervention efforts are to be measured against beginning in the 2019-20 academic year.
Those intervention efforts include vehicle idling policies at or near schools, screens of vegetation between the  street and school, and in-school asthma therapies. The question being posed by the study is whether these intervention efforts have any impact on school-site pollution levels and therefore student asthma or absenteeism rates that can be measured.
street and school, and in-school asthma therapies. The question being posed by the study is whether these intervention efforts have any impact on school-site pollution levels and therefore student asthma or absenteeism rates that can be measured.
There’s certainly no harm in doing this study, but… its about ten years behind the times and spends a lot of money to tell us what we already know.
For example, we know DFW children’s asthma levels are higher than the national average. In their presentation, the TNC uses the 2009 Cook’s Children’s Hospital study made infamous by Downwinders almost a decade ago. That study contains the map showing a huge diagonal swath of childhood asthma running the length of Tarrant County that almost exactly syncs-up with the prevailing pollution plumes from the three Midlothian cement plants. Downwinders used that map time and again to prove the impact of the cement plants on downwind health during our Green Cement Campaign.
We know asthma is worse in minority communities. Many green groups were speaking out about this fact during the first wave of Environmental Justice activism during the 1990’s and have never stopped. What’s interesting is that TNC and the staff never ever talk about WHY this is a fact. It’s like they consider it an inherent genetic defect.
 One reason might be that the Dallas City Hall staff now feigning concern for sick black kids is the same crew responsible for actively pressing racist zoning and land use planning in black and brown neighborhoods, like their predecessors before them.
One reason might be that the Dallas City Hall staff now feigning concern for sick black kids is the same crew responsible for actively pressing racist zoning and land use planning in black and brown neighborhoods, like their predecessors before them.
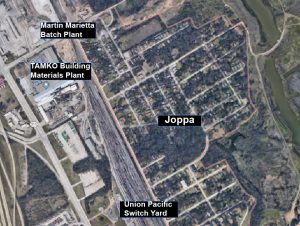
It was only last March when they were recommending approval for those two new batch plants in Joppa. Only last February when they recommended the Ash Grove Cement Silo in West Dallas. Before that they approved the move of the Argos batch plant from trendy Trinity Groves to a location next to a school in West Dallas.
Why do black kids have higher asthma rates in Dallas? Perhaps because the City of Dallas has designed it that way for over a century.
There is not a single note of contrition about this contradiction in the TNC or staff’s presentation on its Breathe Easy project. No “we’re sorry for putting people and polluters way too close in minority neighborhoods.” No “we’re going to do better from here on out – not just with these studies, but with actual policy.” No change in behavior, or even why there might need to be one, is ever discussed.
Those supporting the Breathe Easy study – or any other collaboration with the the Office of Environmental Quality and Rockefeller Sustainability – should understand they’re aligning themselves with a bureaucracy that’s been at the forefront of making the pollution problems in Joppa and West Dallas worse. And now the same bureaucracy wants to “study” the problem they helped make by testing out three piecemeal approaches to reducing exposure, rather than looking at how institutional changes could bring more fundamental and lasting solutions.
In the end, a year of intervention strategies at your school does little lasting good if you walk home through a polluted  neighborhood whose industries have been given a blank check by city staff.
neighborhood whose industries have been given a blank check by city staff.
We know reducing exposure to PM pollution improves your health. Lots and lots of studies show that.
We know which specific strategies work to reduce PM pollution. Buffer zones, vegetation screens, inside air filters, pollution controls, electrification of vehicles – all of these have been examined by researchers and found to reduce PM pollution levels. Even the Nature Conservancy cites the empirical success of tree planting in reducing pollution based on a past study. We don’t need a new study to tell us these strategies are effective. We need more money to implement them.
What the Breath Easy study seems to want to acquire is a new number – A, B and C intervention strategies reduce student asthma attacks/absenteeism by X, Y and Z amounts.
But can that be a meaningful, scientifically-robust number now that you only have an abbreviated baseline that excludes summer? Can it be meaningful if you only spend a year testing intervention strategies, including growing vegetation screens? Even applying copious amounts of Miracle Gro, your trees are not going to get that tall in 12 months.
Using all of TNC’s own data, a convincing case can be made that the $300,000 + being spent on this study could have been better spent on buying trees for those nine schools and installing them as PM screens. But that would have just reduced PM pollution. It wouldn’t have produced a study for the Rockefeller Foundation.
 A dense regional Network of air monitors will begin to expose the deep disparities in pollution burdens in Dallas and elsewhere. It’ll provide a map to black and brown neighborhoods they don’t have now, providing further evidence that what you breathe in Dallas depends on where you live in Dallas. There’s plenty of indications this is the real disparity that Dallas City Hall staff are concerned with – even more than higher rates of black childhood asthma.
A dense regional Network of air monitors will begin to expose the deep disparities in pollution burdens in Dallas and elsewhere. It’ll provide a map to black and brown neighborhoods they don’t have now, providing further evidence that what you breathe in Dallas depends on where you live in Dallas. There’s plenty of indications this is the real disparity that Dallas City Hall staff are concerned with – even more than higher rates of black childhood asthma.
The curtains are about to part and provide a much clearer picture of how Dallas’ institutional racism has poisoned its own residents. It behooves everyone who calls themselves an environmentalist in Dallas in 2018 to commit to changing that picture, not just studying it.
Transformational National Science Foundation Grant for 21st-Century Air Monitoring Gets a Call Back
 In a milestone for the local consortium Downwinders At Risk is working with to bring DFW air quality monitoring into the high-tech era, its $3 million request to the National Science Foundation for funding two pilot projects got a call-back last week.
In a milestone for the local consortium Downwinders At Risk is working with to bring DFW air quality monitoring into the high-tech era, its $3 million request to the National Science Foundation for funding two pilot projects got a call-back last week.
Led by University of Texas at Dallas high tech guru Dr. David Lary, the group includes scientists and researchers from the University of North Texas and UNT’s Health Science Center, Texas Christian University, the cities of Dallas, Fort Worth Plano and Richardson, the Fort Worth Independent School System, the Dallas County Community College District, the Fort Worth League of Neighborhoods, Livable Arlington, Mansfield Gas Well Awareness, and Downwinders at Risk.
There were said to be over 200 applicants applying for the NSF’s “Smart and Connected Cities” grant when the deadline passed about a month and a half ago. The NSF isn’t revealing how many of them got a follow-up “Virtual Site Tour” of the proposal, but the number isn’t believed to be very large. Rumor has it that one of the main competitors to the DFW proposal is Argonne National Laboratories, a 70-year old gigantic research industrial complex born out the Manhattan Project.
 That a group that wasn’t even in business a year ago is now in the running with such a Colossus in a very competitive nationwide talent contest for valuable and scarce research dollars is pretty remarkable on its own. What makes it even more remarkable is that staff at the NSF itself actively discouraged the DFW project from even applying, because they didn’t think the proposal could compete with the scientific heavies already in the race.
That a group that wasn’t even in business a year ago is now in the running with such a Colossus in a very competitive nationwide talent contest for valuable and scarce research dollars is pretty remarkable on its own. What makes it even more remarkable is that staff at the NSF itself actively discouraged the DFW project from even applying, because they didn’t think the proposal could compete with the scientific heavies already in the race.
But what the NSF staff underestimated was how much the DFW project challenges and changes the status quo from the bottom up. It’s hard to imagine a proposal that has the potential to deliver more benefits to more people. 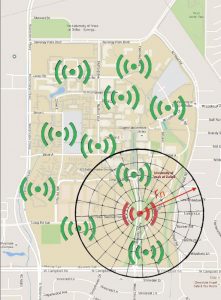
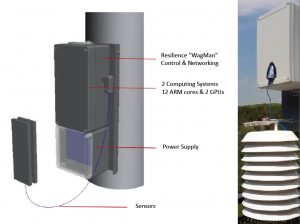
At the heart of the vision for the DFW grant proposal is the idea of an independent network of hundreds, then thousand of small e-sensors placed in a thought-out grid across the entire urban core of the Metromess. These sensors would be located every kilometer or even half-kilometer, block by block, down major thoroughfares, by schools and parks and daycare centers, by facilities that pollute.
So instead of relying on a handful of clunky large official EPA/TCEQ monitors scattered over an area the size of a couple of New England states, you know have data from just outside your own door.
Moreover these sensors would be able to deliver information about air quality in real time to an app on your phone or computer. Contrast this with the two-and-a-half hour wait between sampling and result you see on the official monitor websites now.
But wait, there’s more. As part of the app, you’re made aware of local conditions via an avatar or virtual human, who you can design yourself from a number of attributes. It will present you a list of health symptoms the poor air quality might trigger. But this avatar is also interactive through the network “portal.” You can upload your own symptoms when you’re having a bad air day. The software will look for correlations – wind direction and speed, concentrations of pollutants and allergens in the air, etc. and alert you when days are shaping up to be like the ones that give you trouble.
In the same way many of us now check the weather forecasts, pollen counts, and ozone alerts to know if we need to take extra care with our lungs, you can use this network and software to fine tune that investigation to a degree never before possible.
 Want to be a neighborhood air pollution watch cop? Use the software to track down hotspots you didn’t even know existed, or enforce the permits issued to local facilities. The network of sensors allows you to track plumes in real time as they cross county and city boundaries.
Want to be a neighborhood air pollution watch cop? Use the software to track down hotspots you didn’t even know existed, or enforce the permits issued to local facilities. The network of sensors allows you to track plumes in real time as they cross county and city boundaries.
This is all administered by an independent group of researchers, colleges, scientists, municipalities, and public health specialists, not the State of Texas or EPA. And it’s all made possible by the same leaps in technology behind smart phones, smart cars, and even smart refrigerators: the ability to cram larger and larger tech capacities into smaller microchips and sell them for less money.
While the aim is to grow a huge network of sensors, the submitted NSF grant proposal calls for establishing two separate smaller pilot project grids of 40 sensors a piece – one grid in Southeast Fort Worth and one in Central Plano.
As the proposal explained, the differences in these two communities represent different ways to use the sensor network.
SE Fort Worth is a predominantly African-American and Latino neighborhood with documented high childhood asthma rates, high absentee rates in its schools, and for much of the year lies downwind from the Midlothian cement plants.
There the network can demonstrate how it can become a household health consulting tool, as well as empower neighborhood groups to address micro and macro-level air quality problems. Downwinders at Risk’s role in SE Fort Worth is yoking the high tech sensor network with traditional community organizing. In effect, we’re creating a new citizens tool for cleaner air and a brand new guide on to how to use it to get results.
 In Plano, city officials want to use the sensor network to help traffic flow and minimize vehicular air pollution. Smart technology is already being installed in the city’s infrastructure, so it’s not a huge leap to imagine installing their 40 sensors on a major roadway for 40 blocks in a row to see how traffic light timing and other variables can be adjusted to minimize internal combustion transportation pollution.
In Plano, city officials want to use the sensor network to help traffic flow and minimize vehicular air pollution. Smart technology is already being installed in the city’s infrastructure, so it’s not a huge leap to imagine installing their 40 sensors on a major roadway for 40 blocks in a row to see how traffic light timing and other variables can be adjusted to minimize internal combustion transportation pollution.
When you begin to realize that the system can not only report conditions, but learn from them and apply that learning to being able to guide not only your own personal health, but the public health policy for millions, you realize how transformational this technology can become. It has the potential to be the most important tool in fighting for cleaner air that we’ve ever seen – because it works from the bottom up and puts the power to change things in the hands of individuals instead of agencies.
We don’t always have to fight the bad guys head on – we can go around them. We can replace them. That’s what makes this network so sublimely subversive. It just leap frogs over an obsolete, regressive status quo.
We should know by the end of next month whether the participants in last week’s call were persuasive enough to convince the NSF to fund the DFW project. Regardless of that decision, the same consortium of colleges, cities and citizens groups is committed to building-out their own 21st-Century air quality monitoring network.
Summer Isn’t Coming, It’s Here. Ozone Season Arrives with a Vengeance.
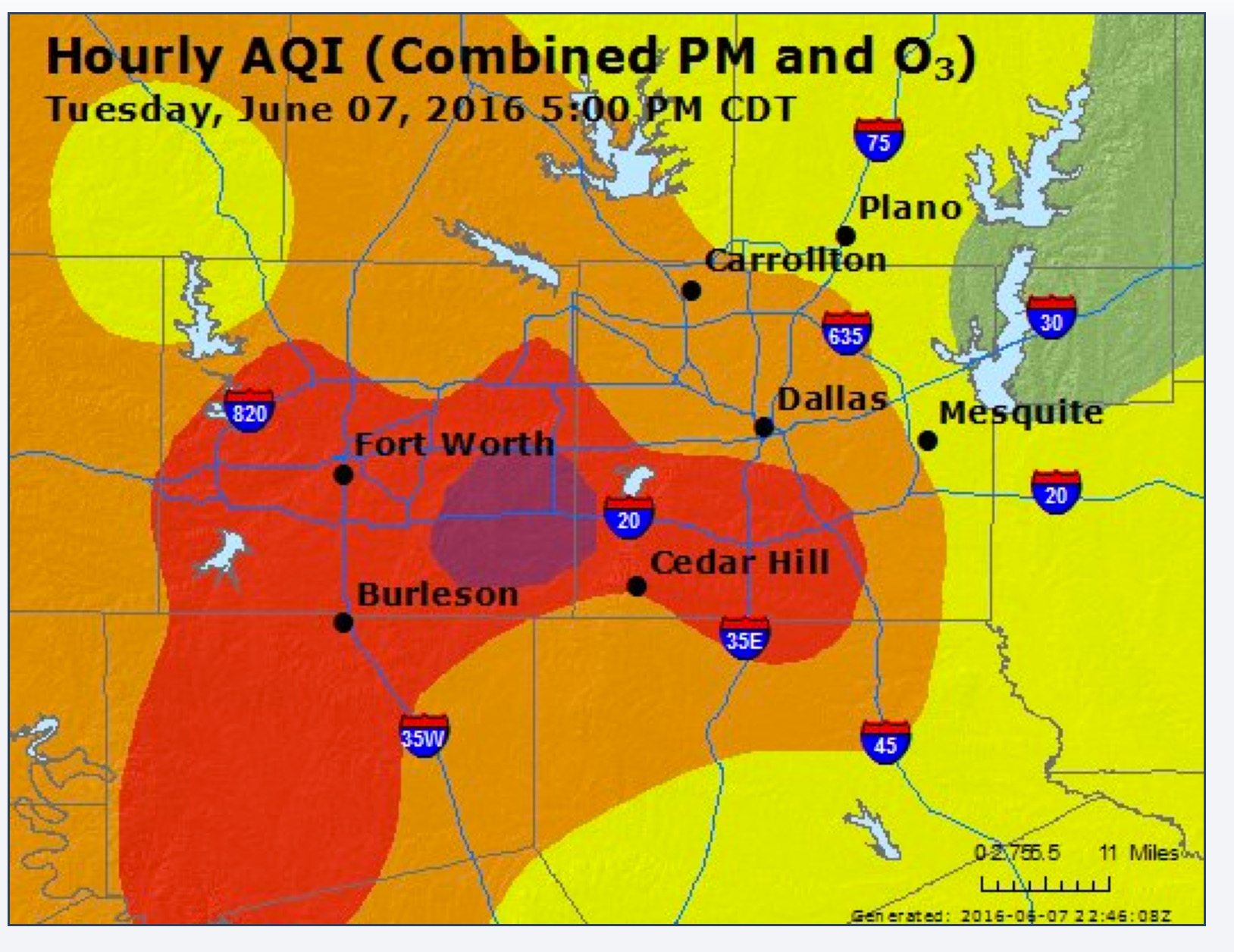
 Yesterday was the single worst day for DFW smog in the last three years.
Yesterday was the single worst day for DFW smog in the last three years.
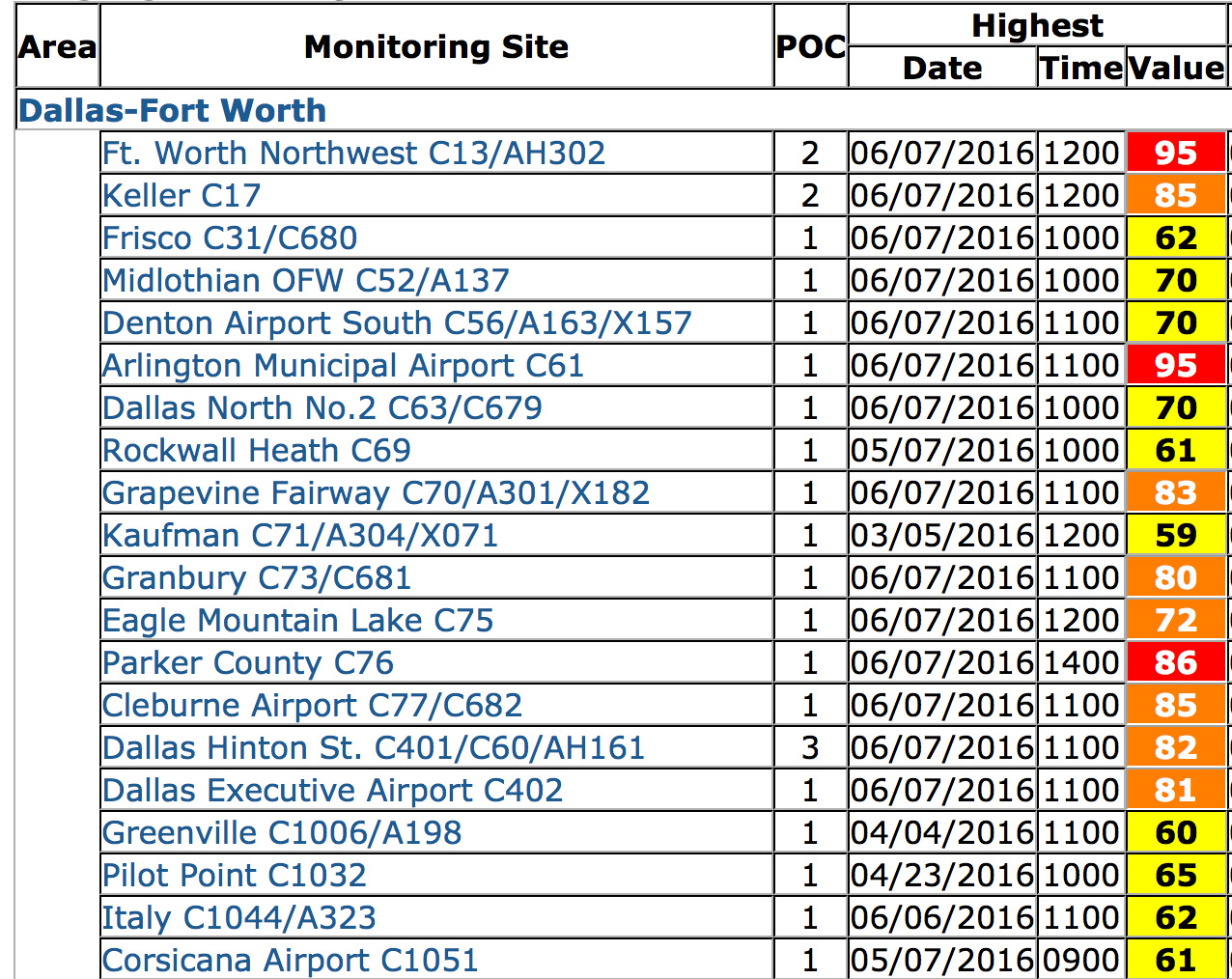
Seven monitoring sites stretching from central Dallas to Weatherford saw hourly averages of 90+ parts per billion. Three sites in Arlington, Northwest Fort Worth and Keller saw levels reach 100 + ppb. Two of those sites saw hourly levels climb to 113 ppb. To give you some idea of how bad that is, the original dreadful, obsolete standard during the 1980's and early 90's was 125 ppb in a single hour. We probably came within an hour or two of reaching a level of air pollution at not one, but two sites yesterday that would have exceeded a 40-year old smog standard.
14 out of the 20 DFW monitors recorded average ozone "exceedences" that violated the current 75 ppb 8-hour standard (what you see above). Two sites saw 8-hour averages of 95 ppb, the worst showing since September 2013.
It became a hazard to breathe for hundreds of thousands, maybe millions of DFW residents, yesterday afternoon. South Arlington residents experienced unhealthy levels of air pollution from 12 noon to 7 pm. In Keller it was 2 to 7 pm.
The good news? It could have been worse. The only thing preventing even higher numbers was the changing wind direction in mid-day. Monitors located in Dallas were recording high smog levels in the morning and lunchtime from northerly winds, but then they turned east and the pollution headed west, raising smog levels across broad swaths of Tarrant, Johnson, and Parker Counties. Had the wind been coming from the east all day, you would have seen the numbers those monitors reached at 2 -5 pm happen sooner, with more room to grow.
Wednesday also looks to be a bad day, as does the rest of the week of full-bore summer sunshine. Bad as they were, none of yesterday's exceedences actually count as a Clean Air Act violation…yet. It takes four bad days where the 8-hour average exceeds the 75 ppb standard over the course of the ozone season to make a violation. Regulators only use the fourth highest smog level recorded at each site to determine the annual average and whether an area is meeting the Clean Air Act standard (you can keep track of those here). Yesterday, nine monitors recorded their first exeedence of the year. Only three more to go.
However, the region's current reigning bad air champ, the Denton airport monitor, uncharacteristically remained out of harm's way and saw levels barely above the 75 ppb standard in mid-afternoon. It'll have it's chance. Summer is only beginning.
 Tuesday's smog attack put an exclamation point in front of next Wednesday's Dallas City Council scheduled vote on Councilwoman Sandy Greyson's air quality resolution rejecting the current state plan – ain't it working out swell!? – in favor of a plan to eliminate days like yesterday.
Tuesday's smog attack put an exclamation point in front of next Wednesday's Dallas City Council scheduled vote on Councilwoman Sandy Greyson's air quality resolution rejecting the current state plan – ain't it working out swell!? – in favor of a plan to eliminate days like yesterday.
Greyson's resolution requesting a new and better clean air plan, as well as the staff presentation that provided background information, can be reviewed here. It's similar in content to one passed earlier in May by Dallas County.
Supporters can sign-up to speak for 3 minutes each when it comes up on the agenda and as always, we'll have plenty of lapel pins with the DFW Clean Air Network logo on them so you can non-verbally support the resolution as well.
If you want to speak at the Council meeting in favor of clean air, please contact the City Secretary beginning at 8:15 am tomorrow, Thursday, June 9th at (214) 670-3738 to reserve a 3-minute speaking slot or Item #12 on the "consent agenda."
Consent agendas are tricky things. They require complete unanimity among all 15 council members and are usually reserved for the most benign, non-controversial subjects. So at first glance, it's a good thing our resolution is on the list because it implies support from all 15 members.
But, and it's a big but….any member who doesn't agree it should be on the consent agenda can ask that it be taken off and placed in the "Items for Individual Consideration" bin – kind of like going to the back of the line and waiting for all the other business to get done before re-visiting the matter.
If there's industry opposition, or any opposition for that matter, it would give a council member an excuse to take it off the consent agenda and send it to the back of the line in hopes us cooling our heels and losing speakers as the day wears on. And it only takes one council member disagreeing to do so. This is why we need you to send emails to ALL 15 council members.
Since it's on the consent agenda, at least for now, it'll be among the first orders of business next Wednesday. Supporters need to show up at 9 am sharp.
Dallas passing this resolution would mean that the most populous city in the DFW "non-attainment area" for smog is rejecting the anti-science "do-nothing" approach of the State and demanding a better strategy to actually clean up chronic air pollution.
That's exactly the kind of statement local governments have to send EPA in order for the federal agency to screw-up enough courage and reject the current state proposal in favor of something better.
And after yesterday, is there anyone outside of Austin who believes we don't need something better?
Dallas City Council Clean Air Vote
Wed. June 15th 9am
Dallas City Hall 1500 Marilla
Dallas County Votes to Reject State Air Plan, Asks EPA for Help
 By a vote of 3 to 2 this morning Dallas County became the first local government in DFW to take a stance rejecting the state-sponsored anti-smog plan for the area, and ask EPA for help in writing a new one that might actually produce cleaner air.
By a vote of 3 to 2 this morning Dallas County became the first local government in DFW to take a stance rejecting the state-sponsored anti-smog plan for the area, and ask EPA for help in writing a new one that might actually produce cleaner air.
At stake is the last comprehensive chance to address chronic smog in North Texas until the next decade.
Pct 1 Commissioner Dr. Theresa Daniel introduced the resolution. It garnered support from Dallas County Judge Clay Jenkins and Pct 4 Commissioner Elba Garcia.
One-by-one Judge Jenkins cited, and then shot down, arguments he said he'd heard from industry about East Texas jobs, electric grid reliability, and the "premature" nature of the vote, given that the state's plan doesn't officially arrive at the EPA's doorstep until July. He said he found none of these persuasive in light of the impact to public health and lost productivity from dirty air days in Dallas County cited in Dr. Robert Haley's landmark 2015 study on the costs of smog in DFW. And he saw no indication the state was planning to change anything in the plan prior to July's official submission.
Garcia was hopeful that the measure, although without the weight of law, would still be effective in getting the EPA to provide a more effective clean air plan.
Daniel cited the fact the area has continually been out of compliance with the Clean Air Act since 1991 despite five previous state air plans as evidence of something more being needed this time around. She also reminded the Court of the conclusions of the UNT's ozone study, based on the state's own computer air modeling, showing the East Texas coal plants to be the single biggest influence on DFW smog.
Commissioner John Wiley Price, facing federal corruption charges, gave perhaps the most puzzling and incoherent defense of dirty air ever heard inside a local governmental chamber. He seemed to be adopting the TCEQ party line in arguing that the coal plants weren't impacting DFW air and the Court's actions were "premature" – he latched on to Jenkins phrase like a drowning man to a floating log. But honestly, there weren't a lot of complete sentences to his explanation. Which is a shame, because when you talk about who pays the price for dirty air in Dallas County, a disproportional number of those casualties are Commissioner Price's constituents – people of color who make less than the median income. They need a strong advocate for clean air, not a rambling echo chamber for the failed status quo.
Commissioner Mike Cantrell, the lone Republican on the court, did not speak at all. Such is the state of the Texas Republican Party.
Dallas County's resolution now goes to EPA, will it will join a letter sent two weeks ago by Dallas area congressional representatives Eddie Bernice Johnson and Marc Veasey, which also requested EPA reject the state's plan and write one of its own if it has to.
Meanwhile, clean air advocates are fanning out and seeking appointments with representatives from other North Texas counties and cities to attempt to get as many similar resolutions as they can between now and the end of the year, when a final decision could be made by EPA to accept or reject the plan. They say the more local governments that pass them, the more likely it is EPA will feel it has the political support to intervene.
Because Dallas District 12 Councilwoman Sandy Greyson served with Commissioner Daniel on the same committee overseeing the UNT and Haley studies, it's probable Dallas City Hall will be one of the next front lines in this fight. Stay tuned.
New Comments from EPA on DFW Air Plan: It Won’t Work
 This plan won't work.
This plan won't work.
That's the simple message from the three pages of new comments Region 6 EPA staff submitted to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality last month concerning its anti-smog plan for DFW.
That message begins with the cover letter, written by Mary Stanton, Chief of the State Implementation Plan Section for Region 6. "… additional local and regional ozone precursor emission reductions will be necessary to reach attainment by 2017."
How much in reductions? EPA estimates an additional 100-200 tons per day more in cuts of smog-forming pollution will be necessary to achieve compliance with the current 75 parts per billion ozone standard. "Without emission reductions on this scale, it is unlikely that the area will attain by the attainment date.”
To give you some idea of how large a number that is, TCEQ calculates that all gas and oil air pollution in DFW equals 78 tons per day, the Midlothian cement plants belch out over 18 tons per day, and all the power plants in the immediate DFW area, 21 tons per day. Totaled, those three sources add up to 117 tons of pollution a year.
All the cars and trucks on DFW roads are said to add up to 180 tons per day of pollution.
So the decrease in pollution EPA is saying is necessary to get down to the current ozone standard is huge.

But take a look at those obsolete East Texas coal plants outside the boundaries the DFW nonattainment area. TCEQ says they account for a total of 146 tons per day. Add Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) which can get you up to 90% reductions in coal plant emissions, or close them down completely, add decreases from new controls on the cement kilns and oil and gas sources, and you're well on your way to amassing 200 tons a day of cuts in pollution.
Which do you think is more attractive to most DFW residents: permanently parking their cars, or putting new controls on the coal plants? Even though the coal plants harm the whole DFW airshed more than any other major source, they're not held accountable to the same regulatory requirements as sources closer to the center of the urban core, but which have less impact. Our cars must have special gasoline formulas in summer, we have to have HOV lanes, and we still go through Ozone Action Days, but the coal plants party like it's 1979. TCEQ is taking a hands-off approach to the plants and as a result the DFW region will continue to be in violation of the smog standard or huge cuts from other sources will be necessary.
TCEQ could have added new controls to the coal plants to the plan, but it chose not to. In fact, there are no new controls in the state's plan on any major sources of air pollution affecting DFW. EPA's new comments go to the heart of that choice. "Without additional emission reduction measures, we don’t see how the area will meet the standard of 75 ppb by the end of the 2017 ozone season," writes EPA staff.
EPA goes on to say TCEQ's computer modeling supporting it's do-nothing plan is "unrealistic," severely underestimating future smog levels, and delivering projections of decreases "that seem unlikely to be reached."
 With this stance, EPA seems poised to reject this "attainment demonstration" part of the air plan as being insufficient. But it must wait to see how TCEQ responds to EPA comments about its modeling shortcomings and need for new cuts when the state officially submits its plan this July. Then, and ony then can the Agency approve or disapprove. We're going out on a limb here and predicting TCEQ won't change a thing, thus inviting EPA disapproval.
With this stance, EPA seems poised to reject this "attainment demonstration" part of the air plan as being insufficient. But it must wait to see how TCEQ responds to EPA comments about its modeling shortcomings and need for new cuts when the state officially submits its plan this July. Then, and ony then can the Agency approve or disapprove. We're going out on a limb here and predicting TCEQ won't change a thing, thus inviting EPA disapproval.
That's the pattern TCEQ has already established with its "screw you" response to the EPA's comments about the part of the plan dealing with "Reasonably Available Control Technology," or RACT, last February. This second part decides what new controls should be required of major sources of air pollution within the 10-County DFW "non-attainment" area – like the Midlothian cement plants and the thousands of oil and gas facilities checkerboarding the western half of the Metromess.
TCEQ says nothing new is required. EPA disagrees. EPA told TCEQ last year it had to do a new RACT review and lower the kiln's emission limits to account for a new generation of technology or it would have to reject the state's plan. TCEQ ignored the request, daring the EPA to disapprove. EPA seems more than willing to take them up on the offer.
And so while you're waiting for the state's computer modeling and suspect math to be rejected by EPA in July, you can probably expect to see EPA officially rejecting the RACT part of the state's plan sooner – maybe as soon as the next 60-90 days.
Despite the TCEQ going out of its way to submit an unacceptable plan to EPA, if the Agency pulls the trigger and begins a federal takeover of the DFW air plan, the Commission and the whole of Texas State Government will cry bloody murder about the usurpation of the state's authority and once again proclaim how "out of control" the EPA is on their way to filing suit.
 This is why the rowdy eruption of public sentiment for an EPA plan at the hearing in Arlington two weeks ago was so critical (Thank you again). It's also why we now have to be about the business of getting DFW local governments, hospitals and school districts to pass resolutions in favor of an EPA takeover. The Agency will need this kind of public support to counter all the criticism it will take from the Usual Suspects in Austin and DC. If you're interested in helping us pass one of these resolutions in your county, city, school or hospital district, please let us know at: downwindersatrisk@gmail.com
This is why the rowdy eruption of public sentiment for an EPA plan at the hearing in Arlington two weeks ago was so critical (Thank you again). It's also why we now have to be about the business of getting DFW local governments, hospitals and school districts to pass resolutions in favor of an EPA takeover. The Agency will need this kind of public support to counter all the criticism it will take from the Usual Suspects in Austin and DC. If you're interested in helping us pass one of these resolutions in your county, city, school or hospital district, please let us know at: downwindersatrisk@gmail.com
And as always, it's why you, and people you know should:
The Politics of Smog, in the US and Texas
 One of things about basing your health or exposure standards on science is that as research gets more sophisticated, the standards tend to get revised, usually downward. The more you know about how a substance affects the human body, the more subtle the health effects you discover. This has happned most spectacularly with substances like lead and benzene, but it's also happened routinely with smog, or as it's know in government regulations lingo, ozone.
One of things about basing your health or exposure standards on science is that as research gets more sophisticated, the standards tend to get revised, usually downward. The more you know about how a substance affects the human body, the more subtle the health effects you discover. This has happned most spectacularly with substances like lead and benzene, but it's also happened routinely with smog, or as it's know in government regulations lingo, ozone.
Unlike those other chemicals and substances however, the Clean AIr Act says standards for ozone exposure must be reviewed every five years to see if they're keeping up with the science. Standards must be protective fo public health. If new research discovers they're not, then they must get lowered. It's one of the most progressive and pro-active enforcement mechanisms that was included in the Act in a series of 1991 amendments.
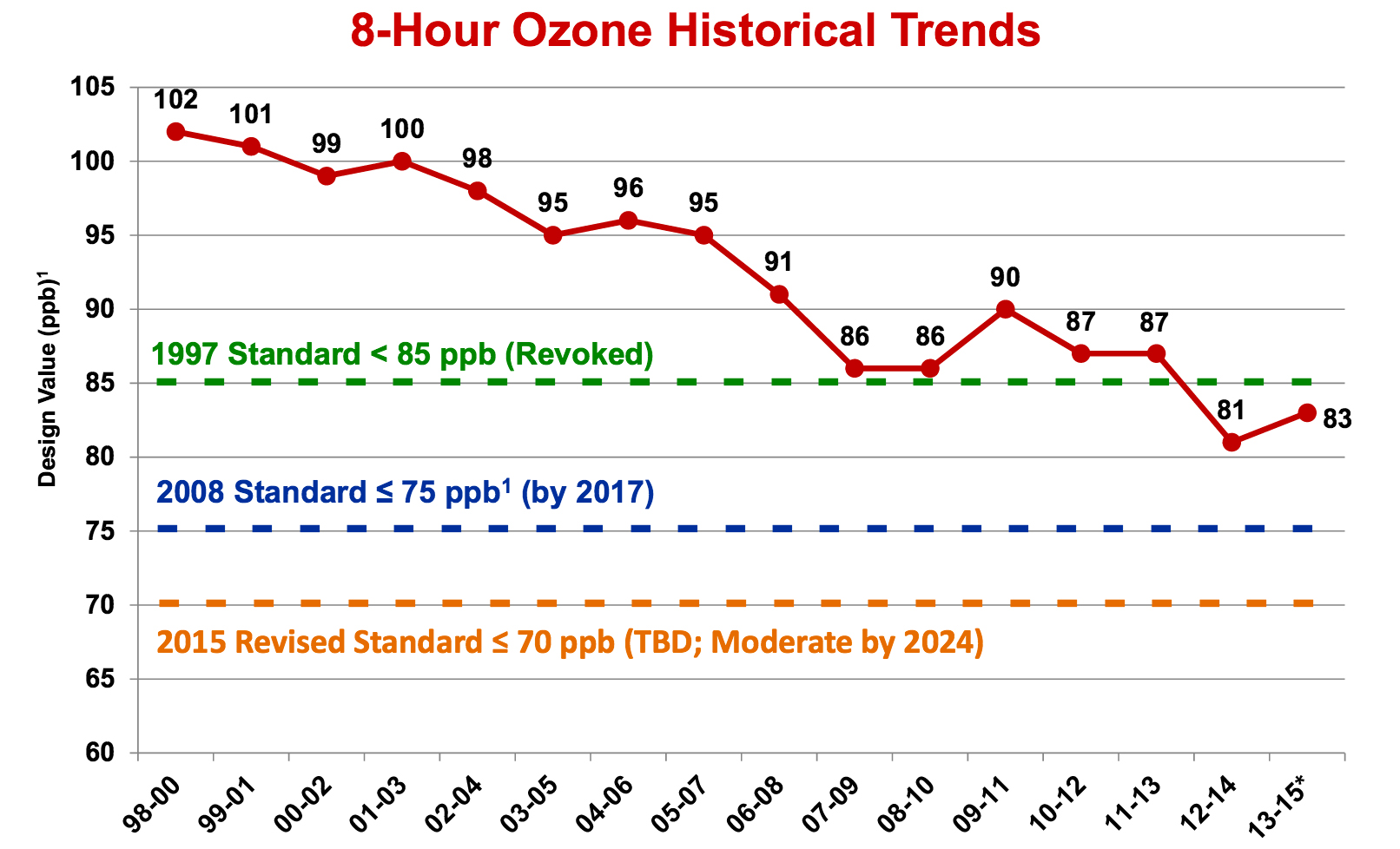
As a result, in the past 20 years, the levels of ozone that were believed to be "safe" have come down dramatically as the science has gotten better. In the mid-1990's, an area wasn't out of violation unless it had over 125 parts per billion (ppb) of ozone as a one hour average. Dallas-Fort Worth more than matched that level, sometimes seeing one-hour readings as high as 135 ppb an hour. North Texas was out of compliance with the standard the moment it was passed.
As more research was published, scientists saw health effects at lower levels of smog exposure and so the standard was changed, as well as how it got measured. in 1998, the one-hour standard was tossed out and an eight-hour average began being used to reflect more realistic exposure patterns. And instead of 125 ppb, the number came down to 85 ppb.
Since 2006, the EPA panel of independent scientists in charge of those five year reviews mandated by the Clean Air Act have been concluding that the standard needed to come down to an eight-hour average of 60 to 70 ppb. But politics has interfered twice in trying to reach that goal. During the last Bush Administration it was brought down to only 75 ppb, where it stands now, and immediately before the 2012 elections, the Obama administration delayed another review that might have brought a lower number.
Now the process is cycling back and once again the EPA's own panel of researchers has recommended an ozone standard of 60 to 70 ppb. The EPA is said its looking at a range fo 65 to 70 ppb. Because the regulations haven't caught up with the science yet, it means, according to a new series of articles published by the Center for Public Integrity that,
"… people in a wide swath of the country breathe air that doesn’t violate any rules — and thus doesn’t trigger any warnings — and yet, according to research, is unhealthy."
There's no better example than DFW to demonstrate this behind-the-curve approach. Even while the state is in the final stages of submitting a new clean air plan for the region aimed at reaching the Bush Administration-era 75 ppb standard (by doing nothing but waiting for cleaner federal gasoline mandates to kick-in) the EPA acknowledges that number is obsolete and should come down to protect human health. Yet the state isn't penalized for not aiming lower, and isn't rewarded for reaching a lower number sooner than the deadline of 2018. The two tracks of regulation never intertwine, as if they were regulating two different kind of air pollution. In effect, government is blessing another half decade of unhealthy air in DFW.
Despite this lenient strategy it will come as no surprise that the State of Texas is fighting the current proposed revision downward in the ozone standard. It's at least consistent. Texas has always fought the lowering of the smog standard. Had it been up to Austin, we'd be living with the 125 ppb levels of 20 years ago – the smog equivalent of smoking two packs a day. As part of its look at the politics of ozone, the Center for Public Integrity's journalists spotlight the the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality's efforts to use industry researchers to make its case the standard is just fine where it is. One of the few pieces of good news is the involvement of local physicians with the Dallas County Medical Society stepping up and taking on Austin over its stance. Dr. Robert Haley of UT-Southwestern has become a well-known opponent of the TCEQ in his and the Medical Society's battle over the East Texas coal plants.
As the Center's articles indicate, court battles are an inherent part of the fight for better standards. Often environmental groups have had to sue the EPA to get the agency to implement the standards recommended by its own panel of scientists. Often, the EPA like it that way, because then it can say it was forced to lower standard by the courts instead of on its own. In Texas, with the submission of a state plan for DFW smog that many feel doesn't meet the Clean Air Act requirements for new controls, a court challenge could be facing the the EPA for the first time in a long time if it approves Austin's lax approach to providing safe and legal air to over six million residents.
The Center's articles are required reading for anyone trying to understand how the machinery of government works both to advance and retard the protection fo public health from a very basic threat. For DFW citizens, they could be a primer for an upcoming fight.
Study: Less Smog Means Healthier Kids
 Up to this point almost all studies about air pollution have tracked increasing levels of air pollution with decreasing levels of health. Respiratory problems, strokes, heart disease, Autism, Parkinson's-like symptoms – they've all been linked to exposure to high levels of air pollution vs exposure to less severe air pollution.
Up to this point almost all studies about air pollution have tracked increasing levels of air pollution with decreasing levels of health. Respiratory problems, strokes, heart disease, Autism, Parkinson's-like symptoms – they've all been linked to exposure to high levels of air pollution vs exposure to less severe air pollution.
Now, comes a new study that approaches the problem from the opposite end of things. It associates healthier kids, specifically, increased lung capacity, with cleaner air over time in Southern California. It provides much needed evidence that pollution controls mandated by the Clean Air Act over the last 40 years have had their intended effect and improved public health.
On Wednesday, the results of the effort were published in the New England Journal of Medicine by researchers from the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California (USC).
Over two decades, researchers at USC studied air pollution levels as they declined in five smog-plagued local communities, while also measuring breathing capacity in 2,120 school children from those same communities during three separate time periods: 1994-1998, 1997-2001 and 2007-2011.
The last group of kids tested showed improved lung growth of about 10% between the ages of 11 and 15, compared with children at the same age in 1996. Overall, the percentage of children with abnormally low lung function at age 15 dropped from nearly 8% in 1994-98, to 6.3% in 1997-2001, to just 3.6% in 2007-11. The positive effects were observed in boys and girls, and regardless of race and ethnicity.
This increase in lung function tracks with improvements in air quality in the LA Basin. According to the ALA, despite a higher population and more cars, Los Angeles had 68 fewer high-ozone days last year than in 1996, and 75 fewer high-particulate-matter days than in 2000. By the study’s conclusion in 2011, fine particulates had fallen by 50 percent and nitrogen dioxide levels by 35 percent in the communities being studied.
Those communities had fewer bad air days because of the pollution controls introduced by government beginning in the mid 1970's with the introduction of the automobile catalytic converter, and continuing to this day with emissions restrictions on everything from shipyards to power plants to lawn mowers.
According to the USC study, those controls and the decrease in smog they produced, have led to fewer stunted lungs and fewer children susceptible to asthma and a host of other respiratory disorders.
According to USC's James Gauderman,
“Improved air quality over the past 20 years has helped reduce the gap in lung health for kids inside, versus outside, the LA basin.”
Consensus in the scientific community (outside TCEQ) seems to suggest that this kind of study wil be important in proving the efficacy of new pollution controls across the country.
Morton Lippmann, a professor of environmental medicine at New York University School of Medicine, said the research would be influential and predicted that within the next few years, when federal emission standards are due for review, “this kind of information will play a major role.”
“It provides confirmation that the work we’ve done to improve air pollution has made a difference in kids’ health,” said Dr. Joel Kaufman, a physician and epidemiologist at the University of Washington, who was not involved in the research. “There are more kids comfortable running around.”
The caveat here is that while new controls benefited public health, it was not necessarily the controls on ozone pollution alone that caused the benefits. During the two decades of study, ozone levels declined only modestly. Ozone has been associated with acute health problems, such as asthma attacks, but the researchers concluded that its reduction does not have the long-term effects on overall lung function that reductions in fine particulates and nitrogen dioxide do.
Pollution controls for ozone, or smog, often have the side effect of reducing particulate matter (PM) and NO2 (one of the forms of Nitrogen Oxide that form ozone), as well. It may well be that these side effects have more impact on public health than previously believed. Certainly the accumulating evidence about the variety of insidious harms caused by even low levels of particulate matter exposure give credence to this idea. Based on the scientific literature, many local downwinders have believed that the single most dangerous kind of pollution being emitted by the cement plants in Midlothian are their voluminous amounts of PM pollution.
One of the reasons Downwinders at Risk has been so insistent on getting Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) on the kilns is that, besides being able to reduce NOX pollution by 80-90 % or more, the equipment is also able to make sizable dents in Dioxins, Volatile Organic Compounds, and yes, Particulate Matter pollution.
EPA Scientists Say Current Smog Standard Not Protective Of Public Heath Even While TCEQ Blows Off Current One
 It's been a pretty nice summer in DFW so far hasn't it? Wetter and cooler than usual. More wind. According to the stats, this past month was the first June without any 100 degree days in seven years or so. Consequently, it's also the first June in forever that hasn't seen any "Orange" or "Red" ozone alert days. If this keeps up, DFW may actually come into compliance with the 1997 ozone standard of 85 parts per billion (ppb) over an 8-hour time period – a first as well.
It's been a pretty nice summer in DFW so far hasn't it? Wetter and cooler than usual. More wind. According to the stats, this past month was the first June without any 100 degree days in seven years or so. Consequently, it's also the first June in forever that hasn't seen any "Orange" or "Red" ozone alert days. If this keeps up, DFW may actually come into compliance with the 1997 ozone standard of 85 parts per billion (ppb) over an 8-hour time period – a first as well.
But unless you think "global weirding" is going to produce these kinds of summers routinely from here on out, there's little cause for comfort. This year's cleaner air is a direct result of cooler weather. Substitute the hellish summer of 2011 for this mild one and you'd be seeing ozone alerts filling up your e-mail box. As a result, it's not out of the question we could meet the standard this year, but flunk it in 2015 if the weather reverts back to "normal."
In addition, while we may come in under the 1987 smog standard for the first time, the public health goal posts have moved with better science. In 2008, the Bush Administration lowered the acceptable level of smog to 75 ppb. That's the goal of the clean air plan that Downwinders and other groups are fighting the state over right now, saying it's not adequate to even get to that 75 ppb level.
Texas Commission on Environmental Quality staff say we don't need to implement any major pollution control measures on cement kilns, power plants, or natural gas facilities to reach this 75 ppb goal by the deadline in 2018. All we have to do is sit back and let a new federal gasoline standard hit the market in 2017 and we'll all be fine – well, except for those millions of residents who'll be breathing-in smog greater than 75 ppb on the north and western side of the Metromess. But the TCEQ staff say we'll be "close enough." No harm, no foul say the folks from the agency where smog is not considered bad for you.
But close enough should only count in horseshoes and hand grenades, not what people breathe into their lungs. And while some of us are trying to make sure the new TCEQ plan is serious about reaching an air quality goal that's now six years old, the level of ozone considered "safe" by experts is once again going down.
In a letter to EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy last week, the Agency's own Clean Air Scientific Advisory Committee (CASAC) recommended a new smog standard of between 60 and 70 ppb, saying that there's a boatload of evidence showing that the 75 ppb level is not protective of human health, and even at 70 ppb there's significant public health harm done by bad air.
"At 70 ppb, there is substantial scientific evidence of adverse effects….including decrease in lung function, increase in respiratory symptoms, and increase in airway inflammation. Although a level of 70 ppb is more protective of public health than the current standard, it may not meet the statutory requirement to protect public health with an adequate margin of safety….our policy advice is to set the level of the standard lower than 70 ppb within a range down to 60 ppb…"
This recommendation was not unexpected. Every five years, the CASAC is legally obligated to review the scientific literature to make sure the federal ozone standard is giving adequate protection to public health. The last time it did so in 2008, the panel came to a similar conclusion to lower it somewhere between 65 and 70 ppb, but the Bush Administration ignored its own scientists and chose the higher standard instead. An Obama EPA was supposed to correct that mistake when it came into office, but then-EPA head Lisa Jackson got mugged on her way to the White House by the President's re-election campaign. Any changes were put on hold until that five year review clock began ticking again. And now the official alarm has gone off on that clock. The result is a re-affirmation of the earlier findings, this time with even more science to back up the changes.
As a result, EPA will have to decide whether or not to adopt the tougher recommendations of its scientists by December 1st of this year. If they do, a new standard will be officially adopted by 2015 and we'll have to write a new clean air plan in a couple of years to achieve that goal by the end of the decade. If it doesn't, they'll be sued, with the CASAC letter as exhibit #1, and they'll lose and have to set a new standard anyway.
Why is that important to the current debate over TCEQ's plan to meet the 75 standard? Because the TCEQ plan leaves at least four monitors, spread out from Denton, to Keller, to Eagle Mountain Lake above 75 ppb – a standard that EPA scientists now say conclusively is not protecting public health.
"Close enough" to that 75 ppb level turns out to be too far away from real protection in light of the new recommendations for a standard below 70 ppb from the Science Advisory Committee. And that assumes you believe the computer modeling TCEQ has done to support its plan. To date, the state is 0 for 5 going back to 1991 in being able to accurately predict these things. If history is any indication, the state's plan will fail to reach its goal of 75 ppb at just about every one of the 20 monitors in DFW, not just four.
If you know your target of 75 ppb of smog over an 8-hour period is no longer a safe standard, and your current plan condones levels above that, it's not really a clean air plan.
December is not only when EPA must decide if it's going to pursue a lower smog standard. It's also when the state is scheduled to take public comment on its current DFW anti-smog plan. So you have the surreal possibility of holding public hearings over the merits of an already obsolete plan that isn't even serious about reaching its obsolete goal.
This is why DFW residents must demand a plan from Austin that aims lower, not higher. It's why they must demand the EPA not allow TCEQ to get away with being "close enough" to a standard that's not protecting their health. A real clean air plan would be shooting for an average of 65-70 ppb knowing that that standard will be coming down the road sooner or later. A real clean air plan wouldn't allow any monitor to exceed the current 75 standard. A real clean air plan would try to do its best to protect public health by implementing pollution control measures on the sources of smog that are the cheapest and most effective to target – Midlothian's cement plants, east and central Texas coal plants, and the natural gas industry.
And that's exactly what Downwinders and other members of the new DFW Clean Air Network are trying to do. We're pushing for stricter EPA enforcement of the 75 ppb standard, and we're pushing for adoption of "Reasonably Available Control Measures" on the cement plants and gas compressors – now, not later. Because the only way DFW breathers are going to get a better clean air plan out of Austin and Washington is by organizing for one themselves.
Study: Climate Change Will Likely Increase DFW Smog
 Just last week at the June regional air quality planning meeting the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality was bemoaning the fact that the weather too often determines how bad an "ozone season" DFW will have. And it's true. When we have really hot, dry, and windless summers, ozone levels soar as they did as recently as 2011-2012 when the recent drought seemed to reach its most awful heights in DFW. Conversely, when we have relatively cool, wet and windy summers, ozone levels abate, as they seem to be doing this year – at least so far.
Just last week at the June regional air quality planning meeting the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality was bemoaning the fact that the weather too often determines how bad an "ozone season" DFW will have. And it's true. When we have really hot, dry, and windless summers, ozone levels soar as they did as recently as 2011-2012 when the recent drought seemed to reach its most awful heights in DFW. Conversely, when we have relatively cool, wet and windy summers, ozone levels abate, as they seem to be doing this year – at least so far.
Of course, the TCEQ spokesperson was using weather as an excuse why DFW hadn't yet achieved compliance with the 1997 ozone standard after two tries that fell short. Completely overlooked was the fact that the last state air plan for DFW in 2011 promised historically low ozone levels by 2013 without any new pollution controls on major sources of pollution. Combine that lack of action with a really hot, dry summer like we saw in 2011, and you get the first clean air plan ever to leave ozone levels higher after it ended than when it started.
That's why it's important to think about the weather when you're trying to build new clean air plans for DFW that stretch years into the future. Air quality planners have to ask themselves if between now and the next federal clean air plan deadline of 2018, will there be more summers like this seemingly anomalous one, or will they more like the summer of 2011 when we had a constant barrage of 100 degree plus days as early as March?
Currently, the TCEQ is using a stretch of bad air days from 2006 to predict ozone levels between now and 2018 in their computer model for the DFW air plan to comply with the new, tougher 2008 ozone standard. But 2006 was pre-drought. Although they say they're "adjusting" the meteorology to compensate for weather changes since then, do you really trust TCEQ to assume worst-case weather scenarios when they're still trying to hide the smog impacts of gas pollution from the public? Us either.
So it's with more than a little self-interest that we note a new Stanford study with the too-sexy title of "Occurrence and Persistence of Future Atmospheric Stagnation Events" concluding that the Western US, including Texas, should expect hotter and therefore smoggier summers thanks to climate change. Why? Because hotter temperatures will slow the flow of air around the globe. That means less wind, and less wind means more time for smog-forming chemicals to sit and bake in the hot sun and form harmful levels of ozone. Historically, most of our worst ozone days are when winds are blowing less than 5 mph – stagnate air.
DFW isn't like Denver or LA where mountains form bowls around the urban areas and trap pollution in inversions. But the new study concludes the impact from global warming could have the same effect on the Texas prairie by stagnating air currents:
"Our analysis projects increases in stagnation occurrence that cover 55% of the current global population, with areas of increase affecting ten times more people than areas of decrease. By the late twenty-first century, robust increases of up to 40 days per year are projected throughout the majority of the tropics and subtropics, as well as within isolated mid-latitude regions. Potential impacts over India, Mexico and the western US are particularly acute owing to the intersection of large populations and increases in the persistence of stagnation events, including those of extreme duration. These results indicate that anthropogenic climate change is likely to alter the level of pollutant management required to meet future air quality targets."
And who's more prepared to deal with the "pollution management required to meet future (re: tougher) air quality targets than the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality? Almost any one, including your 13-year old niece who's done so well in 8th grade science this year. Because not only is it the TCEQ's official position that smog isn't all that bad for you, but that there's really no such thing as climate change. It's why you should bring a boatload of skepticism to the computer model that's driving the currently proposed DFW clean air plan. To plug hotter and hotter temps into the DFW smog model for coming years would be admitting to a phenomena that the Rick Perry administration in Austin just can't bring itself to concede. One more example of how the DFW plan is being driven by politics, not science.
As the TCEQ's own staff admitted last week, DFW's ozone levels are often hostage to the weather. If you're model isn't correctly estimating the weather during future ozone seasons, chances are your estimates of future ozone levels will be off as well. But of course, since smog isn't really bad for you there's no downside to being wrong about these things at TCEQ HQ, and only an upside in GOP primaries.
For the rest of us who believe what the science tells us, the consequences are more dire. As the VICE magazine take on the Stanford study said:
"….one reason this study is so important to the climate change conversation—it underlines the public health threat posed by climbing temps. When Obama was touting the EPA's new carbon regulations, he emphasized the public health benefits of drawing down emissions: It would reduce asthma and respiratory illness, he pointed out. But that's largely because shuttering dirty power plants cuts both carbon and particulate pollutants simultaneously; fighting climate change also means fighting asthma.
Now, scientists have demonstrated there's an additional layer of concern to grapple with on the pollution front; climate change is going to begin blocking cities' toxic release valves. If we don't work to slow carbon emissions, these steamier cities will find their streets clogged with stagnant smog. Scrubbing that pollution and finding novel ways to clear the air, too, then, will prove to be a pressing concern in the not-so-distant future.
Between Now and Friday: Tell Them What They Can Do With Their Smog
 Frustrated that Rick Perry's Texas Commission on Environmental Quality isn't doing enough to end DFW's chronic smog problem, the local "Council Of Governments" has issued a "Request for Information" asking for the public's help in suggesting ways to reduce ozone pollution in North Texas.
Frustrated that Rick Perry's Texas Commission on Environmental Quality isn't doing enough to end DFW's chronic smog problem, the local "Council Of Governments" has issued a "Request for Information" asking for the public's help in suggesting ways to reduce ozone pollution in North Texas.
Please use our Click N' Send E-mail form to make sure they get the message that the public wants:
1) State-of-the-Art pollution controls on huge "point sources" of pollution like the Midlothian cement kilns and East Texas power plants.
2) New pollution control equipment and strategies to reduce the air pollution from the thousands of natural gas facilities mining the Barnett Shale.
3) Inclusion of all trucks and off-road vehicles in the state's vehicle maintenance and inspection program.
You can also add strategies or ideas of your own as well. Just click here, fill out the e-mail and send it in to be counted.
It takes as little as 30 seconds.
BUT YOU ONLY HAVE UNTIL 5 pm FRIDAY, VALENTINE'S DAY.
______________________________________________________________
Rick Perry's TCEQ is so discredited on the matter of DFW smog, local officials usually working in concert with the state agency are now looking elsewhere for help.
Ever since DFW was required to write and submit new clean air plans, The North Central Texas Council of Governments has been the local vehicle used by the state to funnel information, concern, and ideas back and forth.
It was never easy to get Austin's attention or convince the Powers That Be of the need to take bigger clean air measures. It took a decade for Downwinders to get the State to admit that the Midlothian cement plants had a huge impact on local air quality before they were the targets of new controls.
But ever since Rick Perry began running for President in 2010, it's been impossible for Austin toget serious about any DFW clean air plan. For the past four years, TCEQ has claimed that it can reduce air pollution enough by doing nothing.
That strategy has been a dismal failure. New car buying in the middle of the worst economic downturn since the 1930's was the TCEQ clean air plan in 2011. Austin promised that if we just sat back, we'd have the lowest smog levels ever recorded. Instead we had worse air pollution levels than we did five years ago.
This time round, TCEQ is saying a new EPA-mandated low-sulfur gasoline mix in 2017 will be the region's savior for the new clean air plan that's supposed to be successful in reaching the new federal ozone standard of 75 parts per billion in 2018. We're at 87 ppm now – still in violation of the old 1997 standard.
Just watch this new fuel being added to cars and see the ozone numbers drop, TCEQ is saying. No need to put controls on gas facilities, or cement kilns, or power plants. Nothing that would give Rick Perry's opponents on the Right any opportunity to claim he was "anti-bidness."
Even the Council of Governments isn't buying it.
That's why, in their own bureaucratic fashion, this Request for Information that the COG has issued is it's own middle-of-the-road middle finger to TCEQ.
Usually, it would be the state facilitating a discussion of new air pollution control strategies, but since it's obviously not interested, the COG has decided to go its own way. That's how bad things have gotten in Austin – even their most reliable allies in DFW can no longer take them seriously.
It's not clear what will happen to the list of control measures that the Council of Governments is assembling. Some might receive some more official attention, but locals have no authority to write or override Austin's decisions. TCEQ is the only entity that's authorized to submit a new clean air plan to EPA by the June 2015 deadline.
But there are ways to use the useless clean air plans that Austin is submitting. Downwinders' own green cement campaign is a great example.
In 2007, we successfully inserted a voluntary air pollution control strategy into the TCEQ plan revolving around the purchasing of cement from newer cleaner "dry" kilns by local North Texas governments. We then took that "green cement" procurement option and went to Dallas to pass the nation's first green cement ordinance. Then Fort Worth passed it. Then Plano. Then Arlington. Then Denton. Then Dallas County. Then Tarrant County.
Within two years, we had established a de facto moratorium on dirtier "wet kiln" cement within at least a dozen municipal and counties. Combined with federal rule changes, we were able to get all Midlothian wet kilns closed. The last one is being be converted to a dry kiln this year. All while Rick Perry was governor.
The same thing could happen with a good "off-sets" policy for gas facilities if a local city of county could pass a template ordinance showing the way. Currently, most of the gas industry is exempt from being required to "off-set" their air pollution in smoggy "non-attainment" areas like other large industries in DFW. Take away this exemption and you'll see a swift decrease in gas industry air pollution.
It's these kinds of strategies that don't depend on action from Austin that offer the greatest potential for progress this time around.
TCEQ has never written a successful clean air plan for North Texas, and it's not going to start now. But citizens themselves can take their lungs' fate into their own hands and begin to build a system of local measures that can make breathing easier.
______________________________________________________________
CALENDAR AND STATUS REPORT OF DFW'S NEWEST CLEAN AIR PLAN
Reach a 3-year rolling average of no more than 75 ppm of ozone at all 18 DFW area air monitors.
