Smog
Stay Inside. Plant Trees. An Annotated Guide to City of Dallas Air Quality Monitoring

Over the last couple of weeks, the staff responsible for the Air Quality Department at Dallas City Hall’s Office of Environmental Quality have been making the rounds giving presentations about their official air quality monitoring efforts. You can find their complete PowerPoints here as PDFs on the agenda: https://cityofdallas.legistar.com/MeetingDetail.aspx?ID=903849&GUID=B69AEEB6-D5DA-4AE2-B8A4-5BB13C3FD4BE&Options=info|&Search=
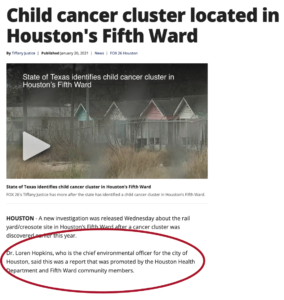
The presentations are divided into two parts. The first deals with the monitors placed in Dallas as part of the State and federal enforcement to monitor DFW’s status as a “non-attainment area” for ozone, or smog. The second is about the “non-regulatory” (i.e not EPA-certified) air monitoring staff has been doing that has up to now has been going on under the “Breathe Easy” banner with a fleet of 12 monitors due to expire this year.
New federal grants have made it possible for the City to buy 35 new “non-regulatory” air monitors of various sizes and capabilities that are aimed at “community monitoring.” By the terms of the grants, five of these have to be placed in two West Dallas zip codes. The other 30 include six larger, more sophisticated air monitors that also come with their own metrological towers and will be placed at the City’s discretion.
This is quite an upgrade for a Department that only a short time ago was dismissing the idea of community monitoring and is in their fourth year of rejecting Joppa residents’ pleas for an air monitor in their neighborhood. That’s the good news.
What’s unclear is how all this new monitoring capability will be used to move the needle of air pollution exposure in Dallas.
Houston has a staff toxicologist that identifies AND advocates for environmental health. Why doesn’t Dallas?
Is the City collecting air quality data so residents can brace themselves on “bad air days”, or are they collecting it to shape City Hall policy that could reduce air pollution and its impacts?
When the goals of all this City air monitoring come up in the new presentations, there’s no mention mention of impacting Dallas City Hall policy. Instead, there are boasts about gathering ““high quality data,” “contributing to local and regional databases,” and “better understanding the performance of low cost sensors” for “public health measures” and “understanding the role air pollution may play in pediatric asthma” (Really? there’s lots of studies already proving this link)
No suggestion for any pro-active City policy to reduce air pollution. No talking point about using the data to address environmental racism or increase City Hall’s much-valued “Equity” in air quality. There’s a lot of emphasis on collecting data but not much attention paid at all to what will be done with that data.
During the Question and Answer session that followed the presentations in front of the Dallas City Council’s Environmental Committee, staff suggested the results of the monitoring could be used to further the City’s air quality goals like…..staying indoors when pollution is bad, and planting trees to mitigate it. Honest.
Dallas City Council Member Jaynie Schultz:
“What are we going to do to reduce air pollution as a result of this data, this incredible trove of information we’re gathering? ….Will you be proposing to Council different things we can do to reduce that asthma so we can actually affect those numbers?
Office of Environmental Quality and Sustainability Assistant Director Susan Alvarez:
“We are currently working with our Office of Data Analytics to get that data added to the big data website so it will be publicly available. This is one piece of our grant for the West Dallas project; is to also develop appropriate messaging and to work with a non-profit on that to get that message into some of those schools where we have higher than average pediatric asthma rates….
CM Schutlz: But what’s the message? I’m sorry to interrupt.
Alvarez: The message is related to how to, um, best avoid, um, outside, outdoor activities. The other thing that we’re doing is working with the Texas Trees Foundation on, ah, piloting some interventions using nature based solutions, AKA, trees, and they’re working on that right now. They’re already working on planting vegetative screens”
It’s these kind of circa-1990’s answers that reveal why modern public health expertise is so needed at OEQS and City Hall. And not just included in the mix, buy actually driving City Hall environmental thinking. Data collection without application to policy is the Status Quo.
No OEQS staff holds a public health degree, has done research on the public health effects of air pollution, or is charged with evaluating air pollution levels from a public health perspective. When very high levels of air pollution are picked up by any of these new monitors, OEQS won’t have anyone on staff who’ll have the expertise to tell residents what that means.
Instead, the City will still be making residents do all the heavy lifting of solving problems the City helped create. You’re not only assigning them the task of linking pollution levels to impacts but also making it their responsibility to come up with the answer to cutting that linkage. This is what happened at Shingle Mountain. This is what’s happening in Joppa. This is what’s happening in West Dallas. Despite a fleet of new monitors, the City’s stance seems to be that we’re just collecting the numbers. What people do with them isn’t up to us.
Imagine that being the City’s response to finding levels of toxins in tap water faucets in Dallas neighborhoods. City Hall wouldn’t just publish the information in hopes of residents avoiding drinking the water. City Hall would take action to provide fresh water and eliminate the harm. But for some reason the City feels under no obligation to address toxic air quality in homes the same way.
There are a total of 20 slides in the two presentations. Here’s a brief annotated guide to the four slides that provide the crux of the City’s information:



The City of Dallas’ approach to air pollution in its city limits is reminiscent of the old Community Organizing story about the village that finds abandoned babies floating downstream along its river banks and decides to organize to do something about it. At first there’s only a few, but after a couple of weeks there’s hundreds. Adoption bureaucracies are established. Seal Teams of Baby rescuers are on call 24/7. Special baby dams are built.
Until one day some smartass villager asks: “Why don’t we go upstream to see why the babies are ending up in the river?”
Dallas is always responding after the fact to air pollution problems in a downstream way when residents want them to go upstream and solve the real problems. Problems its often responsible for creating in the first place.
Instrumentation without context and action is pointless. “Neighborhood monitoring” without neighborhood oversight is worthless.
If the City of Dallas wants to maximize the potential of so many new air monitors, it needs real public health expertise to tell residents not just to avoid the danger, but how the danger can be eliminated. And neighborhoods must be driving its monitoring deployment process, not just informed after the fact or consulted on a token basis.
But right now there’s absolutely no process in place at Dallas City Hall to ensure either.
Update: A 21st Century Regional Air Monitoring Network for DFW is On Its Way
 me technical and bureaucratic hitches, momentum is starting to build toward the 2020 operation of a true 21st Century DFW regional air quality monitoring network.
me technical and bureaucratic hitches, momentum is starting to build toward the 2020 operation of a true 21st Century DFW regional air quality monitoring network.
A small army of University of Texas at Dallas graduate students are assembling over 100 solar-powered wireless air monitoring units to be dispersed throughout the metro area. A third of those have been purchased by Downwinders for placement in Joppa, West Dallas, and Midlothian. 40 or more or going to Plano. Three Dallas County Community College campuses are receiving one, along with the Fort Worth and Richardson school districts.
And now news has come that Paul Quinn College has received an EPA grant to purchase 11 of these monitors for placement around its Southern Dallas campus. Downwinders is working to coordinate the location of its Joppa area monitors with Paul Quinn to provide Southern Dallas with its own mini-network of monitors.
Meanwhile another group of UTD students are working on the mapping software and app residents will be able to use to access the data in real time. They’re being led in this effort by Robert “The Map” Mundinger, who Downwinders hired for the job. All in all, Downwinders has now invested almost $50,000 in this network, which we hope will become a model for the rest of Texas and the nation.
LafargeHolcim is a “Conscientious Corporate Citizen” Everywhere But Texas

In Europe, LafargeHolcim is a multinational cement manufacturer based in Switzerland and France – two countries on the cutting edge of climate crisis planning and members of the progressive European Union. The Company portrays itself as a climate-conscientious corporate citizen, to the point of its Swiss CEO declaring the reduction of CO2 emissions as his first, most important priority.
In Midlothian Texas, LafargeHolcim runs the most conventionally dirty cement plant in Texas and is seeking a permit that could make it one of the most climate-hostile one as well. In fact, there’s some reason to believe the Holcim plant in North Texas is preparing to burn by-products from either the Canadian Tar Sands, the Permian Oil Field, or both, as fuel.
Baking rock to make cement takes a lot of heat. Regardless of how new or old a cement kiln is, regardless of the pollution controls a kiln has, every cement maker in the world still has to employ the same age-old process of applying a 2000 degree open flame to a mix of limestone and other ingredients. A third or more of the cost of running a cement plant is keeping that open flame consistently hot enough to do the job.
This is the reason cement kilns will always try to find cheap, free, even profitable sources of fuel for that flame. Hazardous and industrial wastes that c an be diverted from incinerators or landfills can be burned in cement kilns for slightly less money because they don’t have to meet the same standards. Used tires and oil. Lottery tickets. Dashboards from cars. Even municipal waste is now being burned in kilns.
an be diverted from incinerators or landfills can be burned in cement kilns for slightly less money because they don’t have to meet the same standards. Used tires and oil. Lottery tickets. Dashboards from cars. Even municipal waste is now being burned in kilns.
Burning anything causes air pollution. Burning wastes causes lots of conventional and exotic air pollution, including CO2. But just baking limestone rock also releases a lot of stored CO2. Even if there was some was to make cement without a flame, the heat needed would still release tons of CO2.
Worldwide the cement industry is estimated to be responsible for 5 to 7% of the planet’s CO2 emissions – larger then the airline industry. If the industry were a country, it would be the third largest emitter on earth, behind the United States and China.
Companies like LafargeHolcim are facing both public and financial pressures to reduce that number. In July European funds managing $2 trillion in assets called on cement companies to slash their greenhouse gas emissions, warning that a failure to do so could put their business models at risk. The mangers specifically mentioned LafargeHolcim and urged it to adopt the goal of net zero carbon emissions by 2050 and align itself with the Paris Climate Accords.
LaFarge Holcim has responded by initiating a series of technical innovations and pilot projects under the banner of “The Plant of Tomorrow” to prove its forward thinking.
Almost 300 facilities around the globe are targeted for inclusion in one or more of these “Plant of Tomorrow” projects, including a Canadian kiln installing a carbon-capture pilot project, an Ohio kiln building three wind turbines to secure its electrical needs, and kilns burning industrial waste as “low carbon” (if not low toxic) fuel.
Left out of this mix so far is Holcim’s woe-be-gone Midlothian plant. You might call it Holcim’s “Plant of Yesterday.” Despite having lots of stiff competition, Holcim not only operates the dirtiest cement plant out of the three doing business in Midlothian, but it’s the dirtiest in the entire state.
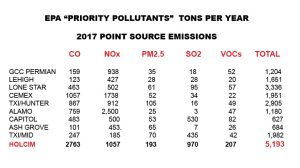
Holcim’s Midlothian plant is the largest Carbon Monoxide (CO) polluter among all 10 Texas cement plants – a sign of poor combustion. It’s the second largest Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) polluter among the bunch, emitting almost twice as much smog pollution as the other two Midlothian cement plants combined. It’s the largest PM 2.5 (Particulate Matter) polluter by far – almost 100 tons a year separate it from second place. It’s the largest Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) polluter by a large margin and releases four times as much Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) than the next highest plant. Almost all 2017 pollution numbers for Holcim have gone up over the last five years. A plant that was already bad is getting worse.
Now add Holcim’s request for a new permit to burn 100% Petroleum Coke in one of its two kilns.
Pet Coke is a byproduct of oil refining. It’s a concentrated carbon solid residue that is left behind after the refining process has converted the bulk of the oil into liquid fuels such as gasoline and diesel.
Pet Coke is like coal, but dirtier. Pet Coke looks and acts like coal, but it has even higher carbon emissions than coal. On a per-unit of energy basis Pet Coke emits 5 to 10 percent more carbon dioxide than coal. A ton of Pet Coke yields on average 53.6 percent more co2 than a ton of coal.
As well as significantly higher co2 emissions, Pet Coke also has high sulfur and toxic metals content than coal.
Because its a waste product, Pet Coke is cheap for Holcim to buy or it could even be free if a refinery wanted to get rid of its supply. And now, thanks to the exploitation of the Tar Sands and the oil boom in the Permian the US has lots and lots of Pet Coke. The heavy oil refining capacity in America is now the largest in the world, with over 40 percent of the global market. Much of that production takes place on the Texas Gulf Coast in huge new expanded refinery complexes like Motiva and Total in Port Arthur. The capacity to produce Pet Coke in U.S. refineries has doubled since 1999. In fact, the annual production of Pet Coke is so large these days, it’s outstripped most of the usual uses for it and is “priced to move.”
Because Holcim wants to burn 100% Pet Coke, and it must have a reliable source to burn it 24/7, there’s reason to believe the company has signed a sweetheart deal with one or more refineries to supply it. Probably from the Gulf Coast, and probably from one of the refineries dealing in Canadian Tar Sands oil or Permian Basin product. Both are poster boys for irresponsible fossil fuel development with the Tar Sands and the Keystone Pipeline igniting modern Climate Crisis activism and the Permian becoming one the planet’s largest sources of Methane as tons of unused natural gas are burned off from thousands of rigs.
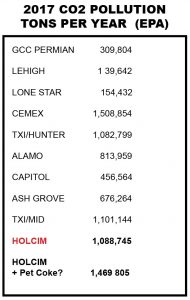 Currently, Holcim is “only” the third largest CO2 polluter among all ten cement plants in Texas, and fourth among all of Holcim’s U.S. plants. But burning 100% Pet Coke in its Kiln #2 could change that rapidly by adding a whopping 400,000 tons more of CO2 to its annual totals. That would send it to #2 in Texas and #2 in the entire US Holcim fleet of cement plants. Not very climate conscientious. And probably not a number you want to tout in trying to sell your “Plant of Tomorrow.”
Currently, Holcim is “only” the third largest CO2 polluter among all ten cement plants in Texas, and fourth among all of Holcim’s U.S. plants. But burning 100% Pet Coke in its Kiln #2 could change that rapidly by adding a whopping 400,000 tons more of CO2 to its annual totals. That would send it to #2 in Texas and #2 in the entire US Holcim fleet of cement plants. Not very climate conscientious. And probably not a number you want to tout in trying to sell your “Plant of Tomorrow.”
At the same time Holcim is trying to project an image of a concerned 21st Century corporate entity to the rest of the world, it’s doing business in Texas like its still 1999.
Officially, the State of Texas doesn’t care about CO2 pollution. Heck, officially it doesn’t even believe there’s a climate crisis. There is no regulatory system for controlling its releases and only the EPA bothers to track CO2 releases at all. So this increase in planet-melting pollution will go completely unaddressed in the permit proceedings themselves.
Also officially, despite the evidence, the State and Holcim both say no other kinds of pollution will increase when 100% Pet Coke is burned at Holcim. No increase in PM 2. 5. No increase in SO2. No increase in metals. Citizens don’t believe them. A group calling itself “Midlothian Breathes” has formed to fight the new permit and has already caught regulators off guard asking tough questions about new emissions.
But trying to get the State of Texas to do the right thing about air pollution is an uphill fight. Instead, perhaps citizens should take these embarrassing numbers directly to LafargeHolcim, who’s claims of new fund corporate responsibility are belied by them. Contrasting its Texas operations with those of the rest of its facilities may be a way to shame the company in its own European backyard. Officially the company may still be able to be embarrassed. Texas state government left that possibility behind years ago.
DFW Smog Gets Worse for First Time Since 2015. Government: ¯\_(ツ)_/¯

2019’s “ozone season” came in like a lamb but is headed out as big, wheezy lion.
A three-day stretch from Thursday September 5th to Saturday the 7th that combined triple digit temperatures with lots of air pollution was enough to push Dallas-Fort Worth smog numbers for the year over 2018’s annual average. It was the first year-to-year increase in ozone levels since 2015, and more than enough to insure DFW will be in violation of the Clean Air Act for the 28th year in a row.
Because the formula for arriving at these averages is so convoluted, discounts the highest three numbers, and is stretched out over 8-hour periods, it takes a lot ozone to make them go up even incrementally. Raising the annual average by even one part per billion (ppb), from 76 to 77, as occurred by Saturday evening, hides a lot of Really Bad Air. Smog levels were in the 90’s and even close to 100 parts per billion at monitoring sites in the northern part of the Metromess. EPA’s national standard for 8-hour exposure to ozone is a 70 ppb average.
Three sites saw their 2019 highs set during this 72 hour period. Frisco had an eight hour average of 88ppb on Saturday, Keller 84 ppb and North Dallas 83ppb. There were four hours on the afternoon of the 6th when smog was over 90 ppb in Frisco.
That’s reminiscent of the bad ‘ol days from the Turn of the Century when levels in the upper 90’s and even topping 100 ppb were routine. Since 2000, there’s been a more or less steady fall in smog in DFW thanks to better controls on combustion-powered vehicles, and the citizen-induced decreases in pollution from Midlothian cement plants and the retiring of East Texas coal-fired power plants. In 2000 DFW’s annual ozone average was 102 ppb. It’s taken 20 years to lower that number to the high-to-mid 70’s. For the last three years we’ve seen decreases of 3, 1 and 3 ppb. 2019 halts that downward trend.
Beside the human health toll these numbers represent – an increase in asthma attacks, ER visits, strokes and heart attacks. – they also represent a challenge to government. This increase comes as the usual planning process to reduce dirty air in DFW sits in tatters. In fact, there really is no process anymore.
In the past, the North Central Texas Council of Governments (NTCOG) would bring the Chambers of Commerce, elected officials and some environmentalists together to cobble out a list of proposed strategies to reduce smog, then submit it to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality in Austin where it would get watered down by corporate lobbying. Nevertheless, those past plans did have an influence on tightening emissions for ancient cement kilns and other industrial sources and they can take some credit for the two-decade decrease in smog.

But that process hasn’t taken place since even before the current administration took office. The last plan submitted by the region to the state was in 2013. Because Austin kept ignoring most of the region’s recommendations, NTCOG just gave up trying after that. It’s Clean Air Steering Committee was disbanded and hasn’t met for six years now. Despite approaching our fourth decade of illegally bad air there’s no official body in DFW working on a regional clean air plan. Everything is being run by Greg Abbott’s state agency – one that doesn’t believe there’s a climate crisis, wants to increase permissible exposure for dangerous pollutants, and whose former Toxicologist in now leading the Trump administration’s efforts to roll back federal pollution standards.
It’s doubtful a single part per billion rise in the regional average will prompt reconsideration of this laissez-faire approach. But it should.
Before the 2016 election, Downwinders was trying to pave a path for the federal government to take away the power of Austin to determine DFW’s clean air progress. We had hoped to have EPA delegated as the “final cut” author of a new clean air plan. Trump’s election made that impossible. But should this administration be gone by 2021, that strategy is still one local residents would be wise to pursue. As long as the State’s environmental agency is in the hands of anti-science flunkies and fanatics, there will be no concern about DFW smog in Austin.
DFW Holcim Cement Plant Seeks to Burn 100% Petroleum Coke
Increases Predicted in Air Pollution, including 100 more tons of PM a Year
Holcim Cement’s Midlothian cement plant has requested a permit application to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to release an additional 2700 tons per year of Carbon Monoxide and burn 100% Petroleum Coke in its Kiln #2. Holcim estimates these change will set of federally-mandated reviews for increases in emissions of Particulate Matter (PM), Nitrogen Oxide (NOx), Sulfur Dioxide (SOx), and Carbon Monoxide (CO).
Notice of the company’s permit amendment was published in the Midlothian Mirror earlier in the  month.
month.
Holcim is one of three very large cement plants doing business just south of I-20 in Midlothian in what is the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. The other two are TXI and Ash Grove. These are not batch plants. These are where the batch plants get their product. With annual air pollution emissions in the thousands of tons, any one of these kilns would easily be the largest “stationary” industrial source of air pollution in North Texas. Combined, they represent a mega source of air pollution for DFW.
Review of the numbers in the permit application show the company wants to scrap its current limit of a little over 4000 tons a year for Carbon Monoxide and replace it with a higher 7112 ton per year ceiling. In addition, the difference between actual emissions and proposed changes could result in 100 tons more of Particulate Matter, 260 more tons of smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide, and 1700 additional tons of Sulfur Dioxide.
 Missing from the permit analysis is the impact of the changes on CO2 climate crisis pollution. Petroleum Coke is nothing but carbon. It releases a lot of CO2 when burned. Burning 100% Petroleum Coke at Holcim will significantly increase this kind of air pollution. Cement plants are already a huge source of CO2 worldwide and Texas leads the country in CO2 pollution.
Missing from the permit analysis is the impact of the changes on CO2 climate crisis pollution. Petroleum Coke is nothing but carbon. It releases a lot of CO2 when burned. Burning 100% Petroleum Coke at Holcim will significantly increase this kind of air pollution. Cement plants are already a huge source of CO2 worldwide and Texas leads the country in CO2 pollution.
Overall, it’s the largest requested air pollution increase from any of the three Midlothian kilns in a very long time. And it reveals how badly the snake-bit 20th Century Holcim plant is aging.
Holcim’s current air pollution levels are already way out of sync with the other two, newer cement plants in Midlothian, and the Holcim facility has had a long troubled history with what its owners claim is a problem with the area limestone – the same patch of limestone the other two plants use. Holcim is already releasing 14 times the amount of four major air pollutants compared to Ash Grove’s 2014 renovated plant, and three times the amount of those same pollutants as TXI. This permit amendment would make the difference even starker.
Clearly Holcim has a problem child cement plant. Since Kiln #1 opened in 1999 it’s never performed to expectation. Because it would otherwise have set off a national non-attainment area for Sulfur Dioxide, Holcim had to add scrubbers to the plant before it even opened. When Kiln #2 was added in 2000, Holcim predicted it would cut pollution in half. Instead it doubled air pollution and by EPA decree the company had to add new pollution controls and buy Downwinders at Risk an independent scientist to monitor their operations. Now Holcim is saying their longstanding plan to reduce Carbon Monoxide pollution at that second kiln just didn’t work out and they need to increase their CO “permit allowables” by over 2700 tons a year.
Even for a very large cement plant, that’s a significant increase in pollution. CO pollution is a red flag for poor combustion, which is always worrisome when you’re looking at a facility of Holcim’s size that’s burning a flame at 2400 degree flame 24/7/365. Poor combustion at a cement plant burning tires and industrial waste, as Holcim does, or even coal and Petroleum Coke, means the creation of more “Products of Incomplete Combustion,” or “PICs.”
PICs are bad news. Dioxin – the poison in Agent Orange – is a PIC but there are thousands more. Some are extremely toxic. Holcim is already releasing 168 times more CO than the newer Ash Grove plant – located just across Highway 67, and nine times more than former Bad Boy TXI. That’s a lot of potential PICs. Something isn’t right in the basic design of the plant to make it so inefficient, but instead of investing in a new plant, Holcim just wants to increase its pollution levels.
There’s a second part of Holcim’s request that’s even more disturbing. Besides the increase in CO pollution, Holcim is seeking approval from the State to burn 100% Petroleum Coke as a fuel for its Kiln #2.
Cement kilns need a cheap source of fuel. Since 1960 the Midlothian kilns have burned gas, coal, hazardous waste, tires, used oil, car inards, plastic packaging, and other “industrial wastes” to keep a flame at 2400 degrees F or hotter. But never 100% Petroleum Coke.
Pet Coke is a refinery waste high in BTU value and sulfur content. It’s very dirty. It’s basically solid carbon. In the application submitted by Holcim, the company says Particulate Matter pollution could go up by 100 tons per year. There’s also a very good chance of increases in smog-forming Nitrogen Oxides and Sulfur Dioxide pollution. Separately there’s also a significant but undocumented increase in CO2 that will occur because of Pet Coke’s composition, so this is a very bad Climate Crisis move as well.
Holcim says not to worry – most of these increases are on paper only and they’re not really changing the emissions, just “refining them.” But with the plant’s history, it’s more likely air pollution will increase, and not by a little bit.
TCEQ’s permit engineer assigned to the Holcim case says this is only a preliminary application and that the company will have to answer more questions about pollution increases, and more importantly will have to stage a “test burn” to see what the impact of burning 100% Pet Coke will actually be (under ideal conditions when everyone is looking over their shoulder). Many long time observers of the modern TCEQ under Governor Greg Abbott are skeptical any of this will happen before Holcim gets their permit however.
Because of the increased volumes of pollutants, this application will be generating an official response from Downwinders requesting at least one public meeting for a briefing on the permit and objecting to any increase in PM and NOX, insisting on test burns using 100% Pet Coke before the permit is approved, and protesting any increase in Climate Crisis pollution.
There’s two responses you can take right now to oppose Holcim’s permit amendment:
1) You can request a public meeting in Midlothian to have the TCEQ and company brief the public on the permit amendment and have the opportunity to ask questions
CLICK HERE TO SEND AN EMAIL NOW TO THE TCEQ
AND ALL LOCAL STATE REPRESENTATIVES AND SENATORS
Requests should be addressed to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality as well as local State Representatives and Senators – not just those representing Midlothian.
TCEQ:
By email:
https://www14.tceq.texas.gov/epic/eComment/
bbohac@tceq.state.tx.us
By mail:
TCEQ, Office of the Chief Clerk, MC-105, P.O. Box 13087 Austin, Texas 78711-3087
Texas State Senators
St. Senator Brian Birdwell/Midlothian: Brian.Birwell@senate.texas.gov, 512-463-0122
St. Senator Royce West/Southern Dallas County: royce.west@senate.texas.gov 512-463-0123
St. Senator Beverly Powell/ Southern Tarrant County: beverly.powell@senate.texas.gov 512-463-0110
Texas State Representatives
Rep. John Wray/Midlothian: john.wray@house.texas.gov 972-938-9392
Rep Yvonne Davis/ Southern Dallas County: yvonne.davis@house.texas.gov 512-463-0598
Rep. Carl Sherman/Southern Dallas County: carl.sherman@house.texas.gov 512-463-0953
Rep. Chris Turner/ Southern Tarrant County/Arlington: Chris.Turner@house.texas.gov 512-463-0574
Contact all of these folks individually, or you can send them and the TCEQ the same email requesting a public meeting on Holcim’s permt via Downwinders’ ClickNSend feature. Leave your own personal message too.
2) Request a Contested Case Hearing
If you feel you’ll be affected by Holcim’s new air pollution, you have a right to ask for a contested case hearing – a formal legal proceeding that sets a higher bar for Holcim to get a permit. In order to request a Contested Case hearing, you must send the TCEQ Chief Clerk:
1) YOUR NAME, or GROUP NAME
2) MAILING ADDRESS AND TEL #
3) APPLICANT’S NAME AND PERMIT #: Holcim, Air Quality Permit 8996 and PSDTX454M5
4) THIS EXACT STATEMENT: ” I/We request a contested case hearing.”
5) A DESCRIPTION OF HOW YOU WILL BE HARMED BY HOLCIM’S AIR POLLUTION
6) THE LOCATION OF YOUR HOME OR BUSINESS AND THE APPROXIMATE DISTANCE TO THE HOLCIM CEMENT PLANT TO THEM.
7) A DESCRIPTION OF HOW YOU USE THE PROPERTY AFFECTED BY HOLCIM’S AIR POLLUTION (HOME OR BUSINESS OR RECREATIONAL)
8) A LIST OF DISPUTED ISSUES
Example: 1. Any increase in PM Pollution from Holcim will be harmful to my health and enjoyment of my property, 2. There has been no evaluation of the PM, NOx, SOx, or CO emissions of burning 100% Petroleum Coke in Kiln #2, 3. There has been no evaluation of the burning 100% Petroleum Coke in Kiln #2 on increase in CO2 4. Holcim’s cement plant isn’t applying Best Practices and Best Available Control Technology for emission reductions of PM, CO, NOx, and SOx.
Send your request to the TCEQ’s Chief Clerk:
By email:
https://www14.tceq.texas.gov/epic/eComment/
bbohac@tceq.state.tx.us
By mail:
TCEQ, Office of the Chief Clerk, MC-105, P.O. Box 13087 Austin, Texas 78711-3087
Electric Buses: A Big Climate Change and EJ “Something You Can Do Now”

Register for the Electric Glide Bus Pub Crawl here.
Thursday, December 6th
Catch the bus at 6:30 or 7:00 pm
at the Green Door in the Farmers Market District
600 South Harwood Dallas 75201
Plug In. Get Lit. Stay Current.
How did we get from cement plants burning hazardous waste in Midlothian to transit or and school buses making runs in inner city Dallas?
The answer is PM, Particulate Matter. The two-decade fight against the cement plants was one long primer on PM pollution. They were, and remain the largest industrial sources of the pollution in North Texas. We learned firsthand about the toxicity, reach, and insidious health effects of PM pollution. Not just strokes and asthma, but IQ loss, Autism, Dementia, Diabetes, low-weight births. PM is the new lead.
Every boiler, furnace, fire, flame and combustion engine produce PM. Diesel engines emit an exceptionally toxic form of PM called Black Carbon.

Because they’re on the road so much, are diesel or natural gas-powered, and make people wait by the side of traffic-heavy roads to ride, bus systems turn out to be a major source of PM pollution. And climate change gases. And smog. A rough estimate shows DART’s bus fleet would be the 10th largest PM source in Dallas County if it were all parked in one spot. But of course its the dispersed nature of a bus fleet’s pollution that often makes it more of a widespread threat to public health than a stationary “point source” a.k.a. an industrial facility.

What’s missing is a constituency for electrification of school district bus fleets and transit agencies like DART and Trinity Metro. Because of the potential impacts and benefits, this could be a wide-ranging and powerful alliance – PTAs, transit riders, physicians, environmentalists, environmental justice advocates, and even the utilities that could buy the power from bus batteries. But until we get the ball, er wheel rolling, its all just that – potential.
One of the reasons we’re sponsoring the December 6th “Electric Glide bus pub crawl” as part of this year’s Root and Branch is that we wanted to start that rolling. And real, wheels-on-the-bus-go-round-and-round rolling discussions and presentations on the advantages of electric buses are part of the evening, but so is just showing your support for the goal of electrification as something local officials could accomplish right now, especially if they combine their collective purchasing power.
The more people that show-up on the 6th, the more DART and local school boards – whose memberships we’re inviting as well – will get the impression someone gives a damn and the more we’re a force to be reckoned with. We need a people’s lobby for 21st Century electric buses in DFW.
 In exchange for coming out and forking over $25, we give you three custom drinks, Graham Dodds’ food, a presentation by Dale Hill, the co-founder of the Proterra electric bus manufacturer, and maybe, just maybe some food for thought about what we all can do right now to advance a bunch of causes in one campaign that’s winnable at the local level in the Trump era.
In exchange for coming out and forking over $25, we give you three custom drinks, Graham Dodds’ food, a presentation by Dale Hill, the co-founder of the Proterra electric bus manufacturer, and maybe, just maybe some food for thought about what we all can do right now to advance a bunch of causes in one campaign that’s winnable at the local level in the Trump era.
Register for the Electric Glide Bus Pub Crawl here.
Thursday, December 6th
Catch the bus at 6:30 or 7:00 pm
at the Green Door in the Farmers Market District
600 South Harwood Dallas 75201
Plug In. Get Lit. Stay Current.
End of Year Report: DFW Smog Goes Up While Going Down; PM is Worst Since ’03

Only in the nonsensical world of EPA air quality regulation could the official regional average for DFW smog actually decrease despite the worst levels of DFW Ozone pollution in five years.
In 2018 a quarter of all North Texas official monitor sites recorded smog levels in the 90-95 ppb range for more than an hour. 2018 was the first time in two years that any DFW monitors have had 8-hour averages of 80 ppb or above, and the first time since 2013 since there been at least six. In fact, this year’s total number of 80-or-above monitors is almost equal to the total number from the last five years combined.
Nevertheless, the regional average for smog pollution that determines government action actually went down from 81 to 76 parts per billion.
How does that happen? Not without a lot of numerical manipulation. EPA’s formula for smog pollution classification is a two part affair. First EPA only counts the highest 4th highest annual reading from each monitor in DFW. That means every monitor gets three “Mulligans” or “do-overs” before the results are eligible for regulatory use. Then EPA combines the last three year’s worth of those highest 4th highest readings to produce a rolling average. So that 2018 average is actually the results of the highest 4th highest reading from 2016, 2017, and 2018.
High readings from the summer of 2015 are rolling out of that three-year rolling average, while lower readings in ’16 and ’17 remain. While this year’s smog levels were higher, but not so extraordinarily high as to be able to counter the lower numbers making up the rest of the average.
But our smog was bad enough last year and this to once again make sure DFW is in “non-attainment” of the clean Air Act for the pollutant. For the umpteenth time in a row, we missed a deadline for meeting a Clean Air Act smog standard – this time it’s the 2008 75 ppb standard. If EPA follows its own protocol, that means DFW will be go from being “moderately” out of compliance to being in “Serious” non-compliance.
And please remember all of these numbers are based on only 20 smog monitors, half of which are located well-outside the DFW urban core, and none of which are located in Wise County, where Downwinders is doing the job of monitoring ozone pollution that the State and EPA refuse to do.
 What are the consequences of this continuing violation of the Clean Air Act that imperils public health? Nada probably. At least while the Trump Administration holds office. In the past such classifications would have triggered a process leading up to some kind of official plan of action that, at least rhetorically, is aimed at correcting the 30-year old problem. But no one expects the State of Texas, or now the EPA, to take that responsibility seriously.
What are the consequences of this continuing violation of the Clean Air Act that imperils public health? Nada probably. At least while the Trump Administration holds office. In the past such classifications would have triggered a process leading up to some kind of official plan of action that, at least rhetorically, is aimed at correcting the 30-year old problem. But no one expects the State of Texas, or now the EPA, to take that responsibility seriously.
What you can expect is some official TCEQ spin about how it’s been successful in bringing down smog pollution levels. In fact, it was the wettest September on record that brought an abrupt end to what was shaping up to be an even worse smog year than it already was at the end of August. Historically, September is when DFW sees some of its worst bad air days. But not this year.
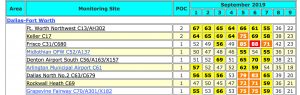
Accompanying the rise in smog pollution in 2018 was also a dramatic rise in the regional numbers for Particulate Matter (PM) pollution – the highest North Texas has seen since 2003.
After a long spell of annual peaks of between 24 and 28 migrograms per cubic meter of air, the 2018 average for highest daily readings among all sites has risen dramatically as of this month – to almost 40 µg/m3
Before this year, they’d only been four daily peaks above 40 µg/m3 over the last 15 years. In 2018 four out of 6 PM monitoring sties had registered daily readings averaging between 41 an 43 ppb as of October.
The EPA annual standard for PM pollution is 12 µg/m3. The 24 hour standard is 35 µg/m3.
As with smog, these readings are coming from a very small pool of monitors – in this case just six PM monitors scattered over an area only slightly smaller than Rhode Island.
Some of this might be blamed on the drought we we experiencing during the summer and increased dust circulation, but comparing it to 2011 when similar if not worse conditions were in play shows no similar bump then. Fewer coal plants blowing their plumes into DFW this year might lead you to think we were even due for a drop. Instead it’s as if someone turned the key on a couple more. There’s no obvious reason why PM levels would have jumped so much in a single year.
What’s clear is that local governments are the last refuge for effective and new air pollution control measures. Until political leadership changes in Austin and/or Washington, there’s no expectation of any relief. In fact, every day sees new proposals from the State or EPA that will actually increase smog and PM pollution in DFW. This is why local city and county elections are just as important as state and national ones.
 We’ll have to wait until the end of 2019 to see if this rise in pollution averages is a trend or blip, but there’s no question that smog and PM are taking their toll on public health in DFW. Study after study shows harms at levels of exposure well below these annual and daily averages that determine EPA regulations. In the real world, your lungs, heart, brain and immune system don’t seem to be able to distinguish between “safe” and “unsafe” levels of poison as defined by the government.
We’ll have to wait until the end of 2019 to see if this rise in pollution averages is a trend or blip, but there’s no question that smog and PM are taking their toll on public health in DFW. Study after study shows harms at levels of exposure well below these annual and daily averages that determine EPA regulations. In the real world, your lungs, heart, brain and immune system don’t seem to be able to distinguish between “safe” and “unsafe” levels of poison as defined by the government.
2018: Worst Smog in Five Years…and Ozone Season Isn’t Over
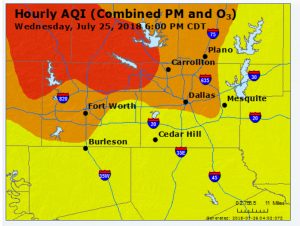
With months of “ozone season” still to come, 2018 is already one of the worst years of DFW smog pollution this decade.
As of August 9th, six out of the 20 North Texas ozone pollution monitors have registered at least four days when the average concentrations of smog were 80 parts per billion or higher over any eight-hour period. The current EPA ozone standard is 70 ppb over eight hours. Most scientists who study ozone pollution recommend between 60 and 65 ppb.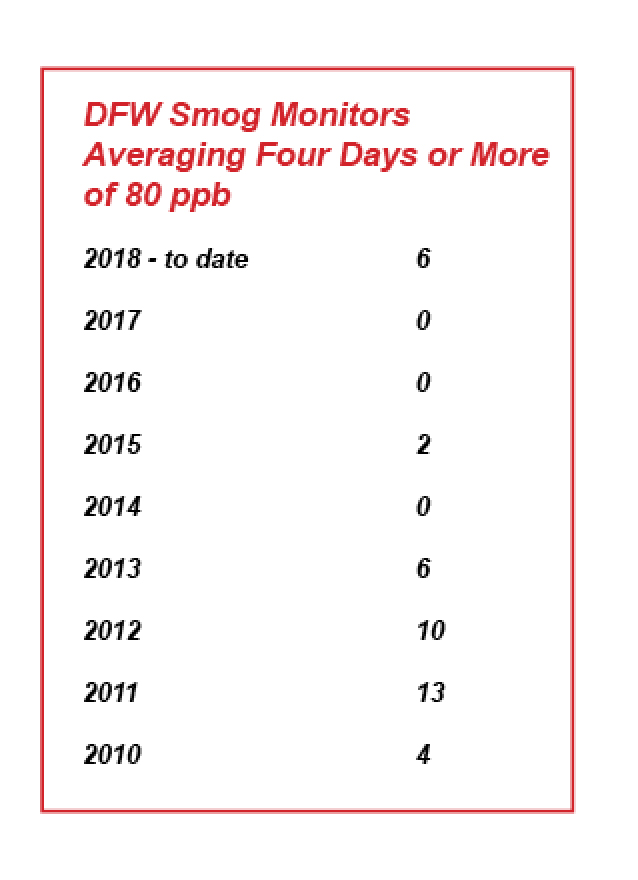
Unfortunately our lungs don’t breathe averages. Regulatory accounting smooths out the highs and lows. This summer has seen at least five sites record smog in the 90-95 ppb range for more than an hour. That’s very hazardous breathing.
There’s no question there were public health consequences to those extreme air pollution levels. Asthma attacks were triggered, COPD patients were gasping, but also strokes and heart attacks. We just don’t know how many…until after the fact.
It’s the first time in two years that any DFW monitors have had 8-hour averages of 80 ppb or above, and the first time since 2013 since there been at least six. In fact, this year’s total number of 80-or-above monitors is almost equal to the total number from the last five years combined.
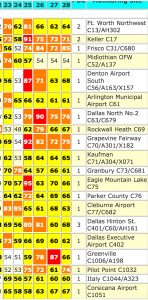
The last week of July was a bad one for DFW breathers.
Besides the number of high smog readings, the location of the monitors recording them should be of concern. Five out of the six registering the highest numbers this year have long histories of being among those registering the highest numbers in past years – Grapevine, Eagle Mountain Lake, Dallas Hinton, Dallas North and Frisco. Only Cleburne might be considered an outlier. The fact the same sites keep popping up over and over again means the strategies for reducing smog pollution aren’t working when put to the test like this July’s heat wave.
But of course that assumes there are any strategies for reducing smog in DFW. And technically there are. But they aren’t being vetted for their effectiveness, and they aren’t being enforced, and some are even being rolled back. After 27 years of continually violating the Clean Air Act for smog pollution, there’s nobody in any level of government working on a cogent plan to get DFW into compliance. Law and order rhetoric from Austin and Washington not withstanding.
What made July smog worse than usual was the heat. Climate scientists are telling us we’re going to be having more summers like 2018, not fewer. So this year’s levels are probably a precursor, not an aberration. But that’s a hard sell to elected officials whose campaign accounts depend on denying the science.
The punch line to this year’s sudden and dramatic spike in higher smog levels? It might still result in officials taking the Orwellian stand that the air in DFW is getting better. How is such a thing possible? Through the wonders of regulatory math.
EPA’s classification of how bad or good air quality is in any region is done by taking the 4th highest annual reading from each monitor and then keeping a rolling average of three years’ of those annual 4th highest numbers for each monitor. For this year, only the 4th highest numbers for 2016, 2017 and 2018 are included in the rolling average. Denton did see high numbers in 2015, but those are all now rolling off and not being counted.

Up to now those 2015 numbers have kept the regional smog average in Denton at 81 ppb despite relatively light ozone seasons in 2016 and 2017. Now that that 2015 high number is rolling off, it would take the Denton site having 4 separate days of 90+ ppb smog in the next 90 days to make the average rise back up to 81 ppb. If that doesn’t occur, then the Denton average could drop to somewhere in the mid-to-upper 70 ppb range.
Should that happen, expect to see lots of regional back-slapping among officialdom for bringing down that Denton number and “continuing to make air quality progress.” Even as more monitor sites see higher smog numbers, officials will declare their anti-pollution measures are working splendidly. But that will not be the case, and you should not be misled.
While there might be a bit of specific progress made at the Denton monitor site, the increase in the number of other sites registering higher levels of smog they haven’t seen in years negates it. If all it takes is a heat wave to send two years of lower numbers down the drain, and the future is full of heat waves, then that’s not really progress, is it? We’re forced to put our fate in the hands of the weather instead of our own planning. Not very proactive, but that’s the state of air pollution control in DFW in 2018: “Please Dear God, keep it cool this summer.”
Even before the Trump Administration came into office the EPA wasn’t enforcing provisions of the Clean Air Act that DFW blew by ages ago – not correctly classifying its non-compliance, not requiring controls on major polluters, providing one extension after another. Now of course, there’s total abdication of even the pretense of striving toward cleaner air for its own sake.
Which is why if any progress is going to be made over the next 2-3 years, it must be made at the local level. No one else gives a damn. Officially.
THE CLEAN AIR FUND THAT TIME FORGOT
Over a decade ago $500,000 was collected from North Texas local governments to protect Texas air.
It’s been sitting in a bank account ever since. Until recently, not too many people even knew it existed.
Now, citizens want to use a part of it to build a world-class 21st-Century air monitoring network for DFW.
__________________________________________
In 2006, then-Dallas Mayor Laura Miller teamed up with Houston Mayor Bill White and organized a coalition of Texas local governments to oppose the “fast-track” permitting of a dozen new coal plants Governor Rick Perry was pushing.
15 North Texas cities, Houston, and McLennan County (Waco) established the “Texas Clean Air Cities Coalition” to fund a legal team and the technical expertise needed to take on not only the big utility companies, but Perry and the State of Texas as well.
But before the battles could begin, a settlement was reached that cancelled all but one of the coal plants. The approximately $500,000 raised by the Coalition to wage clean air war was not needed now. Instead of reimbursing the separate contributors, it was kept in total by the Coalition, possibly because it had already been budgeted to “protect Texas air.”

And there it’s sat ever since. With each new election cycle, the number of local elected officials who knew about the fund got smaller and smaller, until there was hardly any institutional memory of the Coalition or its half-million dollar fund left at all.
Downwinders only recently found about the money in the course of discussing funding of the new regional air quality monitoring network we’re working to establish with local policymakers.
While visiting with Dallas Council Member Scott Griggs about Dallas establishing such a network in partnership with Plano and Dallas County, CM Griggs mentioned the Texas Clean Air Cities Coalition and the $500,000 it had accrued, and asked us how our Network idea was different than the TCACC mission. We consider ourselves the premiere clean air watchdog group in DFW but we had no idea the Coalition or its fund was still around.
And, as it turns out, Griggs is the “Principal Officer” of the fund.
Needless to say, we were gobsmacked.
After reviewing some paperwork on the Coalition in Griggs’ office, we answered his question by suggesting that while the original goal of TCACC was to actively oppose those “fast-tracked” coal plant permits, the mission of the monitor network was to gather air quality information for public health purposes.
But on closer examination, we did notice similarities. Many of the municipalities that contributed to the Coalition fund are the same ones that are now interested in participating in the new monitor network, which like the Coalition, is a regional effort. The Mission of the Coalition is “to protect Texas air” primarily, but not exclusively through permit opposition. The spirit, if not the mechanics of the Coalition and Network are originating out of the same concern for public health.
That being said, extracting the money from the fund for modern use could be a convoluted affair. Despite the broad executive  powers given to the Principal Officer in the Coalition’s by-laws, including the authority to commence litigation and intervene in permit proceedings, they don’t address air quality monitoring directly per se. It would appear to take a vote of the remaining Coalition members to ratify a new expenditure for the regional monitoring network, but it’s not clear who they are.
powers given to the Principal Officer in the Coalition’s by-laws, including the authority to commence litigation and intervene in permit proceedings, they don’t address air quality monitoring directly per se. It would appear to take a vote of the remaining Coalition members to ratify a new expenditure for the regional monitoring network, but it’s not clear who they are.
Of the five Coalition officer positions listed in the paperwork Downwinders received from Griggs, three would appear to be vacant, with no one representing Houston, Waco, or Irving due to retirements or elections. Only Griggs and Arlington City Council member Kathryn Wilemon, who both term out in May 2019, remain in elected office.
The discovery of the Coalition fund in 2018 raises all sorts of questions about why it didn’t get used over the last decade of air quality problems. Although there hasn’t been another tsunami of coal plants proposed, there’s still cement plant plants burning industrial waste, still oil and gas facilities still releasing way too much methane, still battles over batch plants in places like West Dallas and Joppa that the money could have gone to…but didn’t. Advocates like Downwinders didn’t even know about it to be able to make the case for its use. It’s a large policy failure on all fronts, that perhaps can be partially redeemed now by spending some of the the collected monies on another regional clean air initiative.
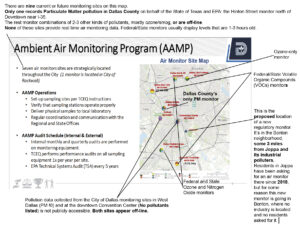
After learning of the Coalition fund, Downwinders asked Dr. David Lary of the University of Texas at Dallas Engineering Department to outline what kind of North Texas air monitoring network could be built with approximately HALF of the fund’s $530,000.
Dr. Lary is the author of the National Science Foundation grant that originally proposed the idea of grid air monitoring in DFW. He’s an expert in the field of high-tech low cost sensors and just got a large US Army contract for testing sensor equipment for the nation’s armed forces.
What he suggested was a 200 + sensor network, operating mostly on solar power and using wifi to bring real time air quality information to the regions seven million residents..for a low, low price of $280,000. This is his itemization:
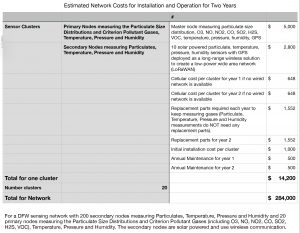
All previous plans had any regional monitoring network growing slowly by charging affordable fees for purchase and installation of sensors. If there’s a large clean air fund that could pay for the immediate build-out, it would propel DFW into the front ranks of “smart cities” and provide public health benefits much sooner.
Now that a City Council Quality of Life Committee hearing has been set for Dallas to decide whether to join the monitor network, the opportunities the fund could provide deserve overdue attention. The question of what role the fund can or should play in paying for a new regional clean air network will be important. Having squandered the ability to provide the kind of assistance it was created for over a decade ago, let’s hope current officials don’t make the same mistake and ignore public health…again.
Historic: Texas’ First Citizens’ Smog Monitor Begins Operation in Wise County

After a few technological hiccups, the state’s first permanent smog monitor built and operated by a citizens’ group is up and running in rural Southeast Wise County. And by the looks of this summer’s ozone season, just in the nick of time.

Conceived, designed, and supervised entirely by environmental scientist and UNT doctoral candidate Kari Northeim on behalf of Downwinders, the Atlas Monitoring Station is a first-of-its-kind adaptation of smaller, less expensive technology to perform the job of monitors many times its size and cost. It instantly becomes a huge milestone in our efforts to build a better system of air quality monitoring in North Texas.
The Atlas Station is a product of Downwinders’ Wise County Ozone Project, financed by a grant from Patagonia and an EarthTank prize won by Downwinders at EarthDay Texas in 2016. It’s objective is to collect continuous readings of Ozone, otherwise known as smog, in Wise County – until this week the only one of ten DFW “non-attainment” counties with no ozone monitors.
 Besides being downwind of much of DFW’s smog, Wise County is the birthplace of modern “fracking” and blistered with gas patch facilities that produce significant amounts of smog-causing air pollution. However, the nearest official smog monitors are approximately 30 miles to the east in Denton County and 20 miles south in Tarrant County. Despite past state and private computer modeling predicting smog to be worse in Wise County than the rest of North Texas when “ozone season” winds are out of the south-southeast, there’s been no monitor there to test that hypothesis. Until now.
Besides being downwind of much of DFW’s smog, Wise County is the birthplace of modern “fracking” and blistered with gas patch facilities that produce significant amounts of smog-causing air pollution. However, the nearest official smog monitors are approximately 30 miles to the east in Denton County and 20 miles south in Tarrant County. Despite past state and private computer modeling predicting smog to be worse in Wise County than the rest of North Texas when “ozone season” winds are out of the south-southeast, there’s been no monitor there to test that hypothesis. Until now. 
Accurate regional ozone readings are important to DFW because they determine how much in or out of compliance with the Clean Air Act we are. If smog levels being recorded by EPA monitors in their current locations aren’t reflective of higher smog levels actually being breathed in North Texas, then we need to know that and add more protective air pollution measures.
Last spring Downwinders bought two portable smog monitors the size of cable boxes from Colorado’s 2B Technologies at $5000 each. That’s a huge drop in price and size. Traditional EPA monitors doing the same job can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars and take up a quarter acre.
 2B factory-calibrates the monitors and they’re already certified by EPA, but from from June 2017 to March 2018, they were subject to additional testing by Kari at the University of North Texas (UNT) Engineering Lab.
2B factory-calibrates the monitors and they’re already certified by EPA, but from from June 2017 to March 2018, they were subject to additional testing by Kari at the University of North Texas (UNT) Engineering Lab.
Although small, these are incredibly reliable machines with an accuracy of greater than 1.5 parts per billion by volume, or 2% of the total reading. They measure ozone every ten seconds and can automatically average over a minute, 10 minute, or hour interval (like the state monitors do so we can compare apples to apples).
Small, portable, cheaper, but the monitors still need electricity. In order to have more siting options in a mostly rural county, the Atlas uses a 100 W solar panel to connect the monitors to the juice they need to take readings. Batteries provide back-up. This makes is a completely stand alone, self-sufficient monitoring station that we can put anywhere with a good south view.
Air is collected through a funnel and shuttled down a pipe that brings it into a weather-protected box where the monitor itself sits. 
During the Wise County Ozone Project, one monitor at a time will be deployed for a period of 3-6 months. Unfortunately, there’s not a way yet to get real time access to the monitor via the internet, so instead data will be downloaded by Kari every month and compared to readings at those Denton and Tarrant County monitors. Not perfect, but better than no monitor at all.
According to Northeim, who expects to be able to mine several scientific papers with the data she collects, “This research is critically important to develop an understanding of the true ozone exposure in Wise County. It’s very exciting.”
____________________________________________
Putting a Smog Monitor
Where No Smog Monitor Has Gone Before
EPA has 20 ozone, or smog, monitors in North Texas. Approximately half of those are considered “background” monitors on the edge of the denser urban areas. Originally the DFW “non-attainment area” for smog was only Dallas and Tarrant Counties. As the area’s populations grew, so did its air pollution problem and Denton, and Collin Counties were added, then Johnson, Parker, Rockwall, and Kaufman. Citizens petitioned and sued to bring Ellis And Wise Counties into the fold. All of these counties except Wise have an EPA smog monitor, despite Wise County being included in the non-attainment area since 2012, and despite state and private computer air modeling showing the County could have some of the region’s worst smog.



