Air Quality
US Cement Plant Using SCR Pollution Control Device Achieves 80% Reduction. Texas Says It’s Still Not Feasible.
 EPA has released the results of the first test of a full-scale Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit on a US cement plant and the numbers look good.
EPA has released the results of the first test of a full-scale Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit on a US cement plant and the numbers look good.
As many of you know, SCR is just an industrial-sized version of the catalytic converter in your car. It can capture up to 90% or more of the smog-forming pollution from a cement plant. In use on cement kilns since 2001, there are at least a half a dozen cement plants in Europe that use SCR successfully, but the technology has been slow to arrive in the US because of regulatory laziness and industry resistance.
But after 15 years, that's finally changing.
in 2013, LaFarge Cement entered into a consent decree with the EPA and the US Justice Department as part of a settlement over a string of environmental violations, including excessive smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide (NOX) emissions. As part of that settlement, Lafarge was to retrofit its Joppa, Illinois "dry process" cement kiln with an SCR unit, record its effectiveness during stack testing, and report on the results of those tests by 2015.
This last week, those results were finally made available by EPA and they show SCR was able to reduce NOx by 80%.
That's approximately twice as effective as SNCR technology, (Selective NON-Catalytic Reduction), the current pollution control device for NOx most often used in U.S. cement plants.
Moreover, according to LaFarge, "the SCR control technology performed well and no operational problem was encountered."
In fact, the control technology worked so well, LaFarge is now getting a permit from the Illinois state environmental agency to operate SCR past the EPA-mandated settlement period.
But while LaFarge is getting its SCR permit, Holcim's Midlothian cement plant has already applied and been granted one by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality for construction and operation of its own SCR unit. It should be up and running by this time next year.
So that makes two U.S. cement plants with permits to run full-scale SCR units. One that was forced into the choice by EPA and now wants to keep using it, and another voluntarily adding it.
But according to the TCEQ, even though it gave a permit to Holcim to install SCR, and even though Holcim's SCR unit will be operational in a year, and even though the LaFarge test was a success, and even though SCR has been used for 15 years by European cement companies – SCR is "not economically or technically feasible." That's exactly what the Commission said in response to comments from both citizens and the EPA in its new clean air plan for DFW a couple of months ago.
That's right. One the one hand the Commission has granted a permit to Holcim to build an SCR unit in its own backyard, and on the other it's still calling the technology infeasible. It's the stuff of Monty Python sketches.
And that's not all. There is no mention of the Holcim Cement SCR permit in the TCEQ's own official arguments against SCR in its DFW clean air plan. Not one. Since Holcim's building of an SCR unit would tend to empirically disprove TCEQ's contention that the technology wasn't practical, the state just pretends it's not happening. As with climate change and smog, any facts that conflict with the pre-determined ideologically-correct premise must be ignored.
Presumably, Holcim is building the SCR unit because it's made the business judgment that the technology is not only both economically and technologically feasible, but beneficial to the company's bottom line. Presumably LaFarge is pursuing a permit for its SCR unit because it has made the same practical decision. Yet, in a strange role reversal, a Texas state government agency is now telling business it's making the wrong choices. It's overruling the industry's decision to reduce pollution through SCR use by saying "not so fast."
This is how bad its gotten: the Texas approach to clean air is now so backwards that the cement industry is more aggressive about reducing pollution than Austin.
So how many U.S. cement plants have to be operating with SCR before the State of Texas concludes it's a feasible technology? Two? Four? A Dozen?
Fortunately, the TCEQ isn't the last word on this. The Clean Air Act says any and all reasonably available technology must be used on major pollution sources like the Midlothian cement plants when a clean air plan is being drafted. TCEQ hasn't done that. We think they're breaking the law. There are signs that EPA thinks so as well.
EPA is ultimately in charge of enforcing the Clean Air Act, and if it doesn't do it correctly, then the courts step in.
The best hope for safe and legal air in DFW is for EPA to rigorously enforce the law. The State of Texas will not do so. If you agree then please take a minute to:
1) sign this petition to EPA
2) Send this e-mail to EPA
Thanks.
Going Backwards: DFW’s Annual Smog Average Went Up Twice in Two Days Last Week
 State officials and industry PR types thought they'd caught a break last summer when two things produced a much lower annual smog average, called a "Design Value."
State officials and industry PR types thought they'd caught a break last summer when two things produced a much lower annual smog average, called a "Design Value."
Since it's a three-year rolling average of smog numbers, past years roll off as new ones come on. Smog numbers from 2011 that had been so high they'd sent the average soaring, were finally rolling off and wouldn't be included in the average.
Second, unusually cooler temperatures and rain kept a new round of numbers lower. Combined, these factors resulted in a significant decrease in the smog average for 2014.
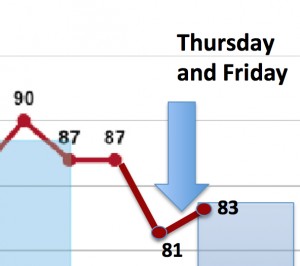
But in 2015, a more typical summer, or at least August, is bringing the average back up (Over 60% of the 100 highest recorded levels of smog this summer occurred in the last 30 days). Smog levels are higher across the board this year than last. There are more monitors recording more "exceedences" of the national smog standard. Leading them all is the Denton monitor, which saw ozone levels rise on Thursday and then skyrocket on Friday. The numbers were so high on both days they moved the needle of the annual smog average, the DFW Design Value, up from 81 to 82 parts per billion (ppb) on Thursday and up to 83 ppb on Friday. The standard is 75 ppb.
Even though Houston has recorded higher smog numbers than DFW this year, 2014's lower smog numbers was even more anomalous for that city than for North Texas. Last year's much lower numbers in the Bayou City are canceling out this year's much higher numbers. So that in 2015, DFW's Denton monitor's annual average of 83 ppb is the highest in the State of Texas.
And that means that according to the official accounting of the Clean Air Act, DFW has dirtier air than Houston. And not for the first time.
It also means we're rolling backwards in terms of air quality progress. With at least a whole month of "ozone season" to go, DFW's smog average is now only a little lower than it was in 2009. It would only take one or two more bad days to raise the average again.
This is the second time in four years that DFW's smog average has increased during the implementation of a state clean air plan for the area. Neither plan required new controls on large industrial polluters significantly contributing to the problem, like the gas industry, East Texas coal plants, and Midlothian cement kilns. There may be some connection there.
Given the state's stellar two decade-old track record of never meeting a clean air plan deadline, its latest plan was always likely to fail. But a federal court roll back of the deadline to get to the 75 ppb standard at all DFW monitors, from 2018 to 2017, plus these new 2015 smog numbers, make it DOA in the real world.
However, in the regulatory world governing these things officially, the plan is still being reviewed by the EPA and, believe it or not, could get approved if citizens don't make a big stink.
That's why you need to sign our Change.org petition to EPA to reject the state's plan and send an email to EPA officials requesting they write a new clean air plan instead of the state of Texas.
Many clean air advocates cautioned that 2014 should be seen as a outlier, and this summer is justifying that caution. If the experts are right, climate change will mean future summers will be more like 2011 than 2014. We've got to have a more realistic approach to the goal of safe and legal air. The State of Texas will not provide that. EPA can.
Sept 23rd: Dallas is Site to One of Three National Public Hearings on EPA’s New Methane Rules – Speak Up to Include Them in Current Air Plan
 Hot off the presses, the EPA published notice in this morning's Federal Register that Dallas will be the site of one of only three national public hearings the Agency is hosting concerning its proposed rules designed to reduce methane emissions at new oil and gas indusry facilities.
Hot off the presses, the EPA published notice in this morning's Federal Register that Dallas will be the site of one of only three national public hearings the Agency is hosting concerning its proposed rules designed to reduce methane emissions at new oil and gas indusry facilities.
On September 23rd, from 9 am until 8 pm in the Dallas City Council Chambers, the EPA will be accepting testimony from the public, in five-minute increments. You can register for your five minute slot online at www.epa.gov/airquality/oilandgas/ between now and September 18th.
Announced to great fanfare only last week, the rules promise to cut future pollution levels as new equipment comes on line, but does nothing about existing faciltiies – with one important exception.
For metropolitan areas like DFW that host large concentrations of gas pollution sources AND are in violation of the Clean Air Act for their smog pollution, EPA has said that states must address new “Control Technique Guidelines” written by the Agency to reduce missions of Volatile Organic Compounds as part of thier smog-figthing plans for those areas. That's good because its smog-forming VOC pollution like Benzene and Toluene that also makes up some of the most toxic air pollution these facilities can emit. The catch is that the rules give the states a two year grace period.
That means that even though the State of Texas and EPA are wrestling over a clean air plan for DFW right now, and even though one of the major smog-polluting industries in DFW are the 17,000 or so wells, almost 700 large compressors and thousands of other oil and gas facilities in North Texas, those new Control Guidelines will not have to be included in that current plan. But they should be.
If you're going to testify, please be sure to make the request that the EPA and Texas go ahead and include these "VOC CTGs" for non-attainment areas in the current DFW air plan. These are anti-smog measures that are no-brainers in a region which has never been in compliance with the Clean Air Act. And they also mean a total reduction in hazardous air pollution.
For more information about the public hearings, contact Ms. Aimee St. Clair, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards (E143–03), U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, byphone at (919) 541–1063, or by email at StClair.Aimee@epa.gov.
The Impact of the EPA’s New Methane Rules on the Barnett Shale? TBD
 Despite all the gnashing of teeth by industry and hallelujah choruses from the Big Green groups, the new methane rules proposed by the Obama Administration this last week have no immediate impact on facts on the ground in the Barnett Shale.
Despite all the gnashing of teeth by industry and hallelujah choruses from the Big Green groups, the new methane rules proposed by the Obama Administration this last week have no immediate impact on facts on the ground in the Barnett Shale.
That’s because, like the recent coal CO2 rules, they regulate future facilities, not the 17,000 or so wells, plus infrastructure, already operating in the Barnett.
They do bring a welcome spotlight to “downstream” facilities like gathering lines and compressors, which is where most of the methane in the gas fuel cycle escapes. They also concede the connection between methane releases and smog (“…reduction of VOC emissions will be very beneficial in areas where ozone levels approach or exceed the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for ozone”), as well as methane and more toxic Volatile Organic Compounds such as Benzene and Toluene (“The measures proposed in this action achieve methane and VOC reductions through direct regulation. The hazardous air pollutant (HAP) reductions from these proposed standards will be meaningful in local communities.”)
EPA’s new rules set a floor for emissions that the industry, over time, will eventually get closer to meeting as a while with the turnover of equipment. But that could take decades. Meanwhile, the agency is only offering “guidelines” to states with smog problems – like Texas – for new pollution controls to reduce methane at existing facilities.
Under this part of the regulation, areas like DFW that host large concentrations of gas pollution sources and are officially categorized as “non-attainment” for smog, or ozone, standards will supposedly be the beneficiaries of new EPA-written “Control Technique Guidelines.”
According to EPA, these CTGs “provide an analysis of the available, cost-effective technologies for controlling VOC emissions from covered oil and gas sources. States would have to address these sources as part of state plans for meeting EPA’s ozone health standards.”
If you live in Texas, you’ve already chortled at that last sentence. Really? The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) would have to use these new technologies on gas sources in their new clean air plans for DFW? Something they’ve refused to do for the last two clean air plan cycles dating back to 2010?
Well, they have to address them at least. And a lawsuit aimed at gutting the new rules is a form of addressing isn’t it?
These are guidelines only, up to the state to enforce – as the EPA admits. “States have some discretion in applying these guidelines to individual sources.” The leverage EPA has is that it still needs to approve these state-generated clean air plans and it can make an official determination that a state didn’t follow the guidelines and send it back to be amended.
This might not be all that important except that the State of Texas is going to have to write a new air plan for DFW in the next year or face the prospect of a federal plan being written in its stead. The one Austin submitted in July is already falling apart on several fronts, and TCEQ has to submit a whole new version or face an EPA-imposed one.
Will the state at least have to acknowledge these guidelines in this current air plan controversy? No. The states have two years to fold the proposed CTGs into their SIPs. So they don’t even have to come into play until this current state plan fails, and Austin or the EPA begin to write a replacement. And why might this plan fail? In part, because it doesn’t apply modern controls to major sources like oil and gas facilities.
You might remember in July, a total of 11 studies were collectively released that concluded the Barnett Shale was leaking 50 percent more methane than previously thought. The day before the EPA made its announcement this week, a national version of those studies estimated US methane pollution from oil and gas was being underestimated by 30%. That’s important because many models of air pollution used by the EPA and the states use those standard emissions estimates that now look obsolete. If you increase the amount of methane, and associated pollutants, by 30-50% in those models, the results might look very different.
So even though the state isn’t officially required to include this new approach to decreasing VOC pollution until 2017 or later, it’d be nice to see it adopted now and have an immediate impact on a region that has a longstanding chronic smog problem. But as long as Texas is in charge of writing DFW’s air plans, that’s just not gong to happen.
Expect Obama’s New CO2 Plan to Close Those Nasty East Texas Coal Plants? Don’t.
 By this point, most of you will have been inundated with opinions and factoids about what President Obama's new "Clean Power Plan" will and won't do about climate change. Bottom Line: while it sets a precedent and an emissions floor for the largest sources of CO2, it does so in a way which turns out to be not so challenging for most states – including Kentucky deep in Coal County.
By this point, most of you will have been inundated with opinions and factoids about what President Obama's new "Clean Power Plan" will and won't do about climate change. Bottom Line: while it sets a precedent and an emissions floor for the largest sources of CO2, it does so in a way which turns out to be not so challenging for most states – including Kentucky deep in Coal County.
That's also true for Texas, where besides being Ground Zero for the fracking boom, we also have plenty of wind power and some solar. According to the EPA, the state must cut an annual average of 51 million tons of carbon to reach its target, a reduction of about 21 percent from 2012 emissions. We're well on our way to achieving most of that reduction with current or planned wind, gas, hydro, and solar. (In what might be a first concession that natural gas shouldn't be a long-term "bridge fuel," some analysts think tweaks performed by EPA prior to the Plan's release give more incentives to adopt real renewables earlier rather than leaning on gas in the interim.)
This is mostly good news. We want the wind and solar economies to grow. The trade-off is that, under Obama's Clean Power Plan, the rise of these technologies and their emissions reductions lets the obsolete East Texas coal plants off the hook because you don't need them to close to meet your CO2-cutting goals.
Five of those obsolete coal-fired power plants surround DFW's eastern side in a half circle (Big Brown, Martin Lake, Monticello, Limestone, and Welsh). They are, without a doubt, the worst examples of fossil fuel-generated pollution in Texas. They're huge emitters of Mercury, Particulate Matter (PM), Sulfur Dioxide (SOx), and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx).
These five East Texas coal plants are projected by the state to still be releasing 150 tons a day of smog-forming NOx pollution in 2018. Because of wind direction and volume, that pollution has a very large impact on DFW air quality – probably more than any other single phenomenon. We need those coal plants to either modernize or close ASAP to help solve our chronic smog problem. But from the initial survey of the policy, the Clean Power Plan is not going to force that outcome.
While the Plan probably signals the end of any new coal plants any time soon, or at least none without CO2 solutions like sequestration or capture, the fate of existing coal plants, especially in a state like Texas, is more ambiguous. More likely, they'll continue to linger on, beneficiaries of friendly state-created policies designed to nullify the requirements of the Clean Air Act, like loosening their PM limits by magnitudes.
Now, you might think that a federal goal that's been mostly accomplished without doing anything new would be a no brainer in Austin, but there are increasingly fewer and fewer brains in Austin. Because the state's environmental agencies are now completely ideologically driven, common sense just isn't a factor anymore. Instead of asking "how can we best solve this problem?" the response is now to deny there's a problem at all and go about ginning up anti-federal hyperbole to better position yourself in the Republican Primary.
Consequently, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality is seriously considering not turning in a required state plan of how to get the reductions needed by the deadline of 2030. If the state doesn't submit one of its own, then the EPA would write one for them. This has the business community in Texas a little nervous, since they have a lot more influence here than in DC. But citizens, which kind of anti-climate change plan would you rather have Texas abide by – one written by a state agency that denies climate change is happening and is doing everything it can to obstruct policies to prevent it, or one written by a federal agency that's actually acknowledging the obvious and doing something about it?
Regardless of whose plan does what by when, the East Texas coal plants look to be able to ride this federal policy out thanks to an almost two-decade homegrown drive to open up the state to renewables. If we want these coal plants to stop causing problems for us, we're probably going to have to find other leverage points.
One of these leverage points is demanding the state of Texas follow the law and require the coal plants install modern Selective Catalytic Reduction controls as part of the new DFW clean air plan it submitted to EPA this summer for approval. SCR could reduce smog pollution from these plants by 90%. So far, Texas has refused to even acknowledge the need to do so. EPA has requested the state change its mind – without success.
If it wants to, EPA can reject the state's plan for not including these new controls on the coal plants. But we have to encourage them to do so – by petition, and by e-mail.
Consider the five East Texas coal plants the energy sector equivalent of the obsolete "wet" kilns in Midlothian that burned hazardous waste for 20 years. They're technological dinosaurs, on their last legs, but still churning out tons and tons of harmful air pollution as they plod their way to the bone yard. The Clean Power Plan insures they'll be the last of their kind, but it's not a silver bullet.
By the End of the Year, DFW Won’t Have Any Environmental Reporters
 News came late last week the venerable Randy Lee Loftis has taken a buy-out and will be leaving the Dallas Morning News sometime in the Fall
News came late last week the venerable Randy Lee Loftis has taken a buy-out and will be leaving the Dallas Morning News sometime in the Fall
When he leaves the newsroom for the last time, he'll be taking the moniker "environmental reporter" with him. Currently, no other DFW media institution funds such a position, and a replacement for him at the News hasn't been announced.
Loftis has been the Morning News' environmental reporter since 1989. He's by far the most experienced journalist still covering the environment in Texas, with his peers in Houston, Austin and Ft. Worth long retired, laid-off or bought out themselves. His career covers most of the modern Texas environmental movement, from the Superfund fight over West Dallas lead smelters, to the epic Midlothian cement kin wars, to current struggles over fracking.
It's hard to believe now, but not so very long ago, it was a seller's market for environmental activists with a good story to tell. Only other newspapers or stations were potential rivals and there was a fierce "Front-Page-like" competition to scoop each other. Because so many pollution problems are linked to corruption, reporters reveled in throwing the spotlight on situations didn't pass the smell tests, toxicologically or politically. Establishment media actually went out on nationwide searches and hired away good environmental beat reporters the same way they would business beat, or cop shop, or city hall reporters. That's how Loftis entered the market in 1989. He came from the Miami Herald, where he'd covered the Everglades extensively.
1989 was a watershed year for the nation's environmental consciousness. The Exxon Valdez catastrophe occurred. A Bush had declared himself "the environmental president." The 20th anniversary of Earth Day was approaching. It was as if the media had woken up and discovered a whole new category of news after a long sleep through the 1980's. Dallas, as well.
There were a host of local issues. Dixico Manufacturing wanted to burn their lead and cadmium ink wastes in an old incinerator in the middle of an Oak Cliff residential neighborhood. West Dallas families were finding high levels of lead in their attic dust and yards from years of smelter operation. And there were rumors that some cement plants south of town were burning hazardous wastes in place of coal.
Loftis' byline in the DMN archives over the last 26 years chronicles these fights and many, many more. Because of that institutionalized history, advocates never had to dumb down their pitches to Loftis. He already knew why the story you wanted him to cover was significant – or not. More than passing knowledge about the subject also gave Loftis the ability to ask the right questions of officials and industry, while also leaving his readers asking the right questions at the end of his articles.
True beat reporters can do that because they have an insider's knowledge of the subjects they're covering. They know the issues, the personalities, and most important of all, the politics. Beat reporters can explain the story behind the story. All of that kind of information, and that style of coverage, walks out the door with Loftis.
It's not just that youngers reporters don't know any history or background in the environmental subjects they're covering for spot news pieces. It's that their employers are insisting they cover the environment as rinse and repeat spot news, and not as a regular beat. You have to start from scratch every time you have a story to tell. You have to explain the context of why it's a good and/or important story. You have to anticipate the opposition's response and suggest skeptical questioning of it, instead of relying on a reporter's experience to do it for you.
It was only a couple of months ago that we last bemoaned the state of local environmental coverage in DFW. Lack of any established media eyes on problems can make the gap between success and failure much wider. Right now, the state and EPA are at loggerheads over DFW air quality policy. This on-going argument affects what amount of poisons millions will take in with every breath over the next three to five years. It could decide the fate of obsolete coal plants, jumpstart national cement plant modernization, and bring new attention to gas industry air pollution. But unless you have some reporters that can make the fight "sexy" and explain why it could impact your child's asthma, it will not be the public policy debate it should be.
In light of Loftis' departure, alternative local sources of news become more critical. And we don't just mean the Observer or the Weekly. This blog and others are now often the only places you can find close to real time information about this or that environmental issue in DFW. That's great for citizen journalism, but it's a sad state of affairs for mainstream media in the nation's fourth largest metropolitan area, which continues to suffer a chronic smog problem, hosts a half dozen Superfund Sites, and is Ground Zero for the fracking boom.
Texas Doctors Tell EPA to “Take on Texas” Over DFW Air Quality. Join Them.
 Texas physicians have told the EPA to reject the State of Texas's "do nothing" air plan for DFW, greatly enhancing support for more real cuts in regional air pollution.
Texas physicians have told the EPA to reject the State of Texas's "do nothing" air plan for DFW, greatly enhancing support for more real cuts in regional air pollution.
STATE CONVENTION RESOLUTION
On May 2nd at its annual state convention, the Texas Medical Association passed Resolution 309 originating with Dallas County doctors, stating,
"That TMA reject the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality's (TCEQ's) 2015 State Implementation Plan (SIP) report and advocate for development of a new SIP report that conforms to the scientific, peer reviewed modeling methods developed by UT Southwestern and University of North Texas experts.
TMA advocates for implementing reasonably available control measures
at the state level capable of meeting national ozone standards, based on the UTSW and UNT validated models.
Although replete with regulatory references, the intent of the resolution is to get the EPA to officially "disapprove" of the current state's anti-smog plan and substitute one that requires "reasonably available" control technologies like advanced air pollution controls on the Midlothian cement plants the East Texas coal plants, and oil and gas facilities. So far, Texas has refused to even consider cuts at these major sources.
Join the Texas Medical Association in urging the EPA to reject the state's air plan. Right now.
1. Send an Email to both the Regional EPA Administrator in Dallas, and the National Administrator in Washington DC, requesting they disapprove the state's air plan because it ignores cuts from major polluters.
2. Add your name to the Change.org petition to EPA to reject the state's air plan for DFW in favor of on of their own.
3. Circulate these links widely.
A new federal air plan for DFW is the fastest way to get big cuts in air pollution from large polluters. That's why these Doctors support it. You should too.
______________________________________________
LOCAL MEDICAL SOCIETY PRESIDENT SPEAKS OUT
Dallas physicians have been leading the fight for cleaner air within their own organizations for years. Their leadership has a sophisticated understanding of the politics surrounding the issue. They had a strong and articulate presence at the Arlington public hearing for the state plan in January.
In his June newsletter column, Dr Jim Walton, the President of the Dallas County Medical Society, writes extensively about air quality:
"Despite two air quality improvement plans (termed State Implementation Plans, or SIPs) written by our state leadership (Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, TCEQ) designed to help DFW meet the 1997 federal ozone standard of 85 parts per billion, neither achieved success by their deadlines.
One key reason for this outcome relates to the State of Texas' 2011 plan for DFW that failed to require new control measures on any major pollution sources, while predicting that the region would see historically low ozone levels. As a result, it became the first state plan for DFW to result in higher ozone levels.
Now the TCEQ has drafted a new plan to try to achieve DFW's compliance with the 2008 ozone standard of 75 ppb. However, once again TCEQ staff has announced that it sees no need to require new control measures on any major pollution sources, even while the Commission's own computer air modeling shows that DFW will remain above the 75 ppb standard by the 2018 deadline.
With action on this issue, we will be presenting our newly sworn-in colleagues – and ourselves – the opportunity to see that a new State Implementation Plan for DFW can produce cleaner air for seven million of our fellow citizens and patients who desperately need relief from more than two decades of noncompliance. We can and should lead in this very practical and real issue that continues to threaten the health of our community."
__________________________________________________
NEW RESEARCH COMING SOON
Dallas docs are also generating original research to aid their advocacy.
Dr. Robert Haley, the staff epidemiologist at UT Southwestern in Dallas, is directing a study on the public health impacts of reducing smog in DFW. It's expected to be released in tandem in August with the results from Downwinders at Risk's own Ozone Modeling Project (these are the studies referenced in the TMA's resolution).
Support from the local medical community is critical for the success of our campaign to convince EPA to replace the state's air plan for DFW with one of its own.
Dallas docs are doing their part. Please do yours and let the EPA know there are DFW residents who want the federal government to enforce the Clean Air Act when the State of Texas won't. Send an email to EPA and add your name to the online petition.
Study: PM Pollution is an “Environmental Neurotoxin” to Brain
 It was just two months ago we featured the results of a study out of Boston that linked exposure to Particulate Matter, or PM pollution to brain aging and increased risk of dementia. Before that, we highlighted studies linking PM to autism and Parkinson-like symptoms. Now comes one more long-term, peer-reviewed report that connects ambient levels of the pollution to accelerated brain aging.
It was just two months ago we featured the results of a study out of Boston that linked exposure to Particulate Matter, or PM pollution to brain aging and increased risk of dementia. Before that, we highlighted studies linking PM to autism and Parkinson-like symptoms. Now comes one more long-term, peer-reviewed report that connects ambient levels of the pollution to accelerated brain aging.
This one is from the University of Southern California and looked at over 1,400 women without dementia who were initially enrolled in a large health study from 1996 to 1998. Researchers measured their brain volume with M.R.I. scans in 2005 and 2006, when the women were 71 to 89 years old.
Using residential histories and air pollution monitoring data, they estimated their exposure to PM air pollution from 1999 to 2006. For each increase of 3.49 micrograms per cubic centimeter (μg/m3) cumulative exposure to PM, there was an associated 6.23 cubic centimeter reduction in the subject's brain white matter, the equivalent of one to two years of brain aging. The current EPA standard for 24 PM exposure is 35 μg/m3, while the annual average standard is 12 μg/m3, although many leading scientists now believe there's no "safe" level of exposure to PM pollution. That is, any amount of exposure is capable of doing some damage.
The association between pollution exposure and brain aging in the USC study remained after adjusting for many variables, including age, smoking, physical activity, blood pressure, body mass index, education and income.
“This tells us that the damage air pollution can impart goes beyond the circulatory system,” said the lead author, Dr. Jiu-Chiuan Chen, an associate professor of preventive medicine at the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California. “Particles in the ambient air are an environmental neurotoxin to the aging brain.”
It's important to note that all of these women were subject to ambient levels of PM pollution, that is, levels that we're all being exposed to on a daily basis living in the modern world. Everyday kinds of exposure to this substance is making our brains age prematurely.
What makes PM pollution dangerous to human health is the fact that its soot particles are so tiny that they can actually cross from the lungs into the blood stream and travel anywhere in the body, including the brain. Soot is a toxic substance on its own, but when its carrying the residues of whatever was burned to produce it – benzene in a combustion engine, mercury from the coal in a power plant, dioxins from "hard to recycle plastic waste" in a cement kiln – it becomes even more dangerous.
While PM pollution remains an important factor in respiratory diseases, heart attacks and strokes, the more insidious effects to the brain it causes are raising its profile among policymakers and activists. They have implications for zoning highways near schools, parks, and residences, as well as pollution control measures at industrial facilities.
PM is one of the best examples of "the closer we look, the more trouble we find" phenomena in environmental health science. Advances in technology and medicine show that subtle changes in exposure to chemicals that went unnoticed before can have profound consequences to our species.
The State’s “Do-Nothing” DFW Air Plan is Falling Apart. Here’s Our Chance to Have a Real One.
 For the second time in five years, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality thought it had gamed the system. It believed it could get away with another DFW "clean air plan" that didn't actually do anything. It looks like it was wrong.
For the second time in five years, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality thought it had gamed the system. It believed it could get away with another DFW "clean air plan" that didn't actually do anything. It looks like it was wrong.
A series of events playing out since December of last year has seemingly laid waste to the state's intent to get approval from EPA for its "State Implementation Plan" (SIP) for DFW smog that didn't touch the major sources of air pollution in North Texas. As a result, citizens have an opportunity for the first time since 2011 to get a real clean air plan – but only if we organize and focus on demanding EPA do its job.
Stick with us here. It's kind of a long trip, full of regulatory jargon and jousting, but the destination is worth it.
Because of what seems like an intractable disagreement between the state and EPA over the content of the state's proposed 2015 air plan for DFW, citizens have a chance to press for the real thing – a federal plan, drafted and implemented by EPA – that could finally bring deep cuts to major sources of pollution like the Midlothian cement kilns, East Texas Coal Plants, and the oil and gas industry.
If that sounds like an attractive option to you, there are two things you can do right now to make it more likely:
1) Sign the petition for a Federal Plan at Change.org
In the last six months the fate of the state's plan has been radically altered. Among the most dramatic changes:
1) Only days before Christmas, a federal court ruling pushed back the deadline for DFW to meet the current 75 parts per billion ozone/smog standard from 2018 to 2017. Despite knowing about the court decision, until very recently the state kept aiming its plan at 2018. It hadn't made changes to its computer modeling to adjust to a 2017 goal. Now there's a real question as to whether it can submit all the data EPA requires by a July 20th deadline to turn it in for review. If the state doesn't get all the information in, EPA must rule that the plan is "incomplete." As of right now, a month before it's due, that's the conclusion EPA would have to reach.
2) Official EPA comments on the state's plan are highly critical of it, echoing many of the same assessments raised by citizens in the January Arlington City Hall hearing, and written comments submitted by Downwinders and the Sierra Club. For example,
– The inadequacy of the state's plan and need for more pollution reductions: "…it is difficult to see how the area would reach attainment in 2018….The fact that the attainment year will likely be 2017 makes the chance of attainment smaller…The recent court decision…makes it less clear that the area will attain the standard by 2017 without additional reductions…we believe it is likely that additional reductions will need to be included to demonstrate attainment.”
– The quality of the state's computer modeling, which drives the entire plan: "The monitor data does not show the large drops in local ozone levels and therefore raises a fundamental question whether the photochemical modeling is working as an accurate tool for assessing attainment in 2018 for DFW”….the episode overall is not fully representative of the most difficult ozone scenarios. In addition, while current ozone trends and the model predictions support that ozone levels will continue to improve, it is not clear to EPA that these trends are sufficient for the area to attain by 2018.”
– More cuts are needed from the Midlothian cement kilns: "…the TCEQ estimates that reducing the source cap for the kilns in Ellis County would not provide significant emission reductions for the DFW area. However, a reduction in the source cap…does appear significant...TCEQ’s rules need to be reevaluated to insure…the emission limits reflect a Reasonably Available Control Technology (RACT) level of control as required by the Clean Air Act….We can no longer conclude the emission limit that is in place reflects a RACT level of control…Failure to conduct a thorough RACT analysis for cement kilns which would include appropriate emission limits would prevent us from approving the RACT portion of the attainment plan submittal.”
– More cuts are needed from the East Texas coal plants: “The TCEQ provided an evaluation of emissions from all of the utility electric generators in east and central Texas. However, the discussion in Appendix D on the formation, background levels, and transport of ozone strongly supports the implementation of controls on NOx sources located to the east and southeast of the DFW nonattainment area."
What is that discussion in TCEQ's Appendix D? It's this incriminating admission: "…efforts focused solely on controlling local emissions may be insufficient to bring the DFW area into ozone attainment …."
– Link between oil and gas sources and higher ozone levels: "These monitors (Eagle Mtn. Lake, Denton, and Parker County) are in areas more impacted by the growth in NOx sources for Oil and Gas Development that seem to be countering the normal reduction in NOx levels seen at other monitors…."
"We have some concern that as well pressure diminishes that natural gas fired engines driving natural gas compressors may be utilized more than the current usage per production amount. This may result in the projected NOx emissions not dropping as much as projected. The same volume of gas being produced with less well head pressure flow could need more overall actual compression to get to market. This situation could result in more NOx emissions than estimated based on the current emissions/production level relationship."
3) EPA requests for information from TCEQ leave no doubt that EPA wants more pollution cuts in the plan and that without those cuts, the plan is in deep trouble. Examples:
– “Please provide the estimated amount of emission reductions (in tons per day) that would reduce ozone values at the monitors by 1 ppb…please include the estimated emissions reductions associated with each of the (control) measures."
– “An evaluation…for cement kilns in Ellis County is needed that reflects the level of control that can reasonably be achieved and new limits to reflect the reasonable level of control.”
– “How would a reduction in emissions from utility electric generators in just the counties closest to the eastern and southern boundaries of the DFW area impact the DFW area?”
– “The updated modeling results provided in early January by TCEQ indicate one monitor at 76 ppb in 2018 using the new DRAFT guidance and existing guidance methods indicate 77 ppb at Denton and 76 ppb at Eagle Mtn. Lake and Grapevine. We note that these numbers will most likely go up some with an attainment demonstration based on 2017. We request that TCEQ supplement their analysis as needed to show that the area will attain by 2017.”
All of those EPA comments and requests were made way back in early February. The state only got around to responding to them on June 3rd. With the July 20th deadline for final submission of a DFW air plan to EPA rapidly approaching, this is TCEQ's June 3rd answer:
"It was not possible to complete all work necessary for this DFW Attainment Demonstration SIP revision to demonstrate attainment in 2017. The DFW AD SIP revision also commits to develop a new Attainment Demonstration SIP revision for the DFW 2008 eight-hour ozone non-attainment area as long as 2017 remains the attainment year. The new DFW Attainment Demonstration SIP revision would include the following analyses to reflect the 2017 attainment year: a modeled Attainment Demonstration, a reasonably available control measures (RACM) analysis….."
Rhetorically, TCEQ seems to be committing to submitting a new plan or parts of a new plan to EPA by July 20th, but it's very unclear how much, if any a "new" TCEQ DFW air plan will differ from the current one. The modeling for 2018 took Austin over a year to finish and there are serious doubts about whether the state can condense that process into less than two months to churn out entirely new results for 2017.
Moreover, the state knows what it will find if it does accomplish that feat: higher ozone levels.
At its most basic, the TCEQ plan for 2018 attainment with the 75 parts per billion standard relied exclusively on federal changes in the chemical make-up of gasoline that will reduce its sulfur content, due to hit the marketplace in January 2017. Before the December court ruling, that meant a whole two summers for that fuel change to reduce the pollution from cars without the state lifting a finger to cut pollution from industrial sources like the cement kilns, coal plants, or gas industry.
Now, however, with the attainment date moved up by a year, it means only one year of impact from that fuel change. It means that instead of averaging the 4th highest ozone readings from 2016, 2017, and 2018 for the required rolling three- year average that determines success or failure, it will be this year, 2016 and 2017. Two out those three years will not see the benefit of that federal fuel change on the marketplace, resulting in a higher number than the state was counting on before. Will the state want to put that new number on paper? Because when/if it does, it's Exhibit A for the need for new pollution cuts the state will have to impose. And it really doesn't want to do that.
TCEQ could ignore the July 20th deadline while it works on updating its modeling for the 2017 deadline. Officially, EPA has up to six months (until January 20th, 2016) to decide the state's plan is "incomplete." It could be that EPA accepts a tardy TCEQ 2017 computer model while the state scrambles to come up with its next ridiculous theory to propose in lieu of real cuts from major polluters.
But just pushing back the computer modeling to 2017 wouldn't solve all of the state's problems. For one thing, the gap between projected ozone levels and the goal of 75 ppb will be wider because we're looking at 2017, not 2018. They'll be more ozone that needs reducing. How do you do that? EPA could also find a new state approach inadequate in the same ways it's shooting down the current "do-nothing plan" if it doesn't analyze the impacts of cuts from major polluters. EPA seems to be boxing-in the TCEQ to either admit the need for more real reductions from major sources, or face being "incomplete."
Secondly, and based on TCEQ's June 3rd response to EPA, seemingly even more awkward, is the EPA's request for the state to perform a new review of control measures and their impacts on DFW smog levels. You can't get any more explicit in EPAese than "Failure to conduct a thorough Reasonably Available Control Technology analysis for cement kilns which would include appropriate emission limits would prevent us from approving the RACT portion of the attainment plan submittal.”
As some of us have been saying from the start, TCEQ ignored the fact that there are off-the-shelf controls to get 90% smog pollution reductions from cement kilns and coal plants, controls being used or implemented on kilns and coal plants right now, as well as a long history of electrification of gas compressors in areas of the US with air quality problems.
In its comments and information requests EPA is very specifically requesting drastic, fundamental revisions in the state's analysis, not just in regard to the cement kilns, but also the East Texas coal plants and any other control measure that can get you a 1 part per billion or better improvement in DFW smog levels.
This is something the state is loathe to do. It hasn't done this kind of "sensitivity" analysis in almost a decade. In it's June 3rd comments, it's very clear that the TCEQ is still not finding any reason to revise its opinion that no new control measures on any major sources are needed, and so no such analysis is warranted. "The TCEQ disagrees that the existing cement kiln rules no longer satisfy RACT….and …"the TCEQ has determined that imposing additional controls on these attainment county EGUs (coal plants) is not justified.”
So even though the state says it will work on submitting a new plan aimed at 2017, it's digging in its heels and also saying it's not going to revisit these potential control measures as ways to reach attainment as EPA is requesting. As a result, it's unlikely the state will provide answers to the EPA's many questions about what impacts different controls have on future DFW smog levels.
(If only there was some way to provide those answers to EPA using the TCEQ's own modeling. If only someone had made a copy of the TCEQ model and then run all those "what if" scenarios that the state won't perform.)
On one side is EPA saying the state needs to dramatically revamp its air plan for DFW. On the other is TCEQ saying that it won't do everything the EPA is asking.
What happens if the state won't give in? TCEQ outlines the possibilities in its June 3rd response:
“TCEQ: What are the consequences if this SIP revision does not go forward? Are there alternatives to this SIP revision? The commission could choose to not comply with requirements to develop and submit this DFW Attainment Demonstration SIP revision to the EPA. If the DFW SIP revision is not submitted by July 20, 2015, the EPA could impose sanctions on the state and promulgate a federal implementation plan (FIP). Sanctions could include transportation funding restrictions, grant withholdings, and 200% emissions offsets requirements for new construction and major modifications of stationary sources in the DFW non-attainment area. The EPA could impose such sanctions and implement a FIP until the state submitted and the EPA approved a replacement DFW 2008 eight-hour ozone AD SIP revision for the area.”
And that folks, is what citizens need – a serious FEDERAL Implementation Plan that puts the responsibility for getting cleaner air in the hands of the adults for a change. That's what we all should be asking the EPA to implement.
Waiting for the state of Texas to draft and implement a sincere clean air plan for DFW is the political equivalent of waiting for Godot. Remember the last time the state drafted a DFW air plan in 2011, also exempting major polluters from cuts, it actually raised ozone levels in DFW. After five attempts over 20 years, the state has never met a federal smog clean-up deadline.
Whether you're concerned about pollution from the cement plants, the coal plants, or gas compressors, or just don't want to see the air you're breathing anymore, this is a strategy that can get you real reductions and cleaner air. This is a campaign that can unite a lot of different local groups and causes under one banner.
It's a two step process. First we have to convince the EPA to find the state's plan "incomplete." As you can tell from the EPA's own language, that might not be that hard. But this judgment needs to happen as quickly as it can after July 20th in order to move on to the second decision EPA must make – to formally reject the TCEQ plan, that is, "disapprove" it. On paper, EPA has up to a year to make that decision. Our job is to convince them to do it asap so we can really get down to business.
A formal disapproval will result in the EPA beginning to write a Federal Implementation Plan of its own. Once this process begins the EPA has more of an upper hand. Even if the state panics and submits a new plan of its own, it will have to follow the outlines of what EPA is already proposing. The state has two choices – do it under their own name, or let the EPA carry it out.
Having suffered almost a decade under unprecedented state neglect, DFW air quality is the best example in the US of the need of a federal takeover.
What Texas is doing to subvert the letter and spirit of the Clean Air Act is no different than what southern states did to subvert civil rights legislation in the 1960's. The response from the federal government should be the same now as it was then. If the state won't enforce the law of the land, citizens need the feds to do it for them.
There are two things you can do right now to help this effort, both from the comfort of your own computer screen:
1) Sign the petition for a Federal Plan at Change.org
We need lots of people to begin doing this. Not dozens. Not hundreds. But thousands.
Think about everyone who uses an inhaler in DFW, who knows a family member or friend who suffers respiratory problems. Send this appeal out far and wide.
This is our chance to finally get some progress. We need your help. Thanks.
That Didn’t Take Long: Fracking Resumes in Denton. Because It Can
 As its way of giving Denton residents an industrial size middle finger, the Denton Record Chronicle is reporting that Vantage Energy is preparing to begin fracking in the city on May 27th. The company's announcement came a day after Governor Abbott signed a new law prohibiting local governments from banning fracking, or, really, doing much of anything to hinder whatever the hell gas companies want to do in a city.
As its way of giving Denton residents an industrial size middle finger, the Denton Record Chronicle is reporting that Vantage Energy is preparing to begin fracking in the city on May 27th. The company's announcement came a day after Governor Abbott signed a new law prohibiting local governments from banning fracking, or, really, doing much of anything to hinder whatever the hell gas companies want to do in a city.
Usually, new laws take effect the following September 1st after a session, but the Governor and industry wanted to make sure they was no summer of doubt holding-up their smack down. Until yesterday, Denton city representatives were sounding prepared to continue defending their ban from industry court challenges, but the new law keeps them from being able to file preliminary injunctions to halt resumption of fracking itself.
Because the Vantage site sit on the edge of town and is more than 1200 feet from a "protected use," like a home, the new activity is not a direct challenge to Denton's off-set regulations, or the ambiguous lynch-pin language of "commercially reasonable" driving the newly-signed legislation. And because the Vantage operation was under way when the city declared a year-long moratorium on new fracking in 2014, it could ask for, or assume it has, a hardship case under that local rule.
So only 200 days or so after it took effect the disassembling of Denton's fracking ban will begin. Because it can.
After it was clear the legislation would become law, most citizen observers expected such a demonstration of political spite by industry, although many were predicting it would be lead by Eagle Ridge's resumption of fracking in the original neighborhood by the UNT stadium that kicked off the entire controversy. This first baby-step back into town isn't quite so in-your-face, but it may be opening the doors.
What is the appropriate response by angry Denton residents to this news in the short term? Is it a picket line outside the site's fence? That would certainly attract media for a day but it wouldn't have much impact on the operators. Is it civil disobedience to stop the trucks from entering or leaving the site? That would get even more attention, but unless you have wave after wave of demonstrators lined-up and organized, this too seems like it's a temporary inconvenience rather than a real threat. On the other hand, if this is not the time and place to register your discontent by risking arrest, what does such a place and time look like?
There are lots of rumors about a court challenge to the new state legislation, but that will take years to play out in the courts, and remember, unless there's a constitutional challenge, they'll be Texas state courts, where the judges are all elected, not appointed.
The choices facing Denton residents are the same facing every other group of concerned fracktivists in the state right now – they're just facing them sooner. No option looks very satisfying. Most cities are cowering at the thought of enacting new off-sets or rules and taking on industry and running up millions in legal bills. Individual nuisance suits against operators offer some hope to the most extreme examples, but not necessarily to victims as a class. Legal challenges to the state law itself offer a very long maze of trials and rulings. Up to now, the way citizens have organized themselves has not been conducive to national relief and even if that weren't true you have an Administration relying on the fracking boom for much of its energy policy and so reluctant to crack down on it. Incrementalism has never seemed so incremental.
New strategies are needed, but right now nobody can't see clearly what those will be. One thing you can count on however. When citizens are frustrated and angry over being shat on involuntarily, and you don't allow them to express that anger and frustration into what they believe to be meaningful mechanisms for change, you back them into a corner. Take away the reasonable options, and suddenly, the "unreasonable" ones are the only ones available and they have nothing left to lose in taking them. Just Google "Chinese parents + pollution" and see what kind of tactics you push people into pursuing when they don't have a system that responds to their real and present dangers.
Not many people remember the modern American anti-toxics movement was born with a hostage crisis.
Love Canal was a toxic dump for chemical waste used by the Hooker Chemical Company in the 1950s in Niagara Falls, New York. In the next 20 years two schools and 900 homes were built on or near Love Canal. A young housewife, Lois Gibbs, lived there, and led a precedent-setting fight against the federal government to get all the families relocated.
At one point in 1980 when EPA officials visited the community, Lois Gibbs and her group refused to let the officials leave until the federal government promised to relocate the families. That's right, the group held the EPA officials hostage.
"Yes, I say we detained them for their own protection! That’s actually what got us the relocation. EPA had come down and told us all the things we couldn’t do, and then said we had chromosome breakage, and chromosome breakage means that we have a higher risk of cancer, birth defects, and miscarriages. But the thing that really broke the…sort of the straw that broke the camel’s back was when they said it’s not just about the adults in the community, these chromosome breakages could be in your children, and people just panicked. And they all came to this front lawn of the abandoned house where we had our offices, and they’re all looking at me, it’s like, “Lois, what are we going to do?” and I’m thinking like, “My goodness, I’m going to be a target here because people are so angry.” So I called the EPA representatives to the house to explain to the larger group, what does this mean? And when they got there, people said, “you know what? If it’s so darn safe for us, it can be safe for you. And we’re going to hold you in this house until President Carter does the right thing”.
So they were in the house and 500 people literally encircled the house and sat down, so they couldn’t get out. But after a while, it got really rowdy out there, people were feeding off of one another and they were getting angry. The FBI said they were going to come in and they were going to take the hostages from us if we don’t let them go. So we gave the White House…we let them go, kept them for five hours, and we let them go and gave the White House an ultimatum. They had until Wednesday at noon to evacuate us, or the hostage holding as it was coined, would look like a Sesame Street picnic to what we would do Wednesday at noon. We had no plan for Wednesday at noon! We had no clue what was going to happen Wednesday at noon, but I didn’t go to jail, and in fact, one of my hostages sent me a telegram – which young people today may not know that is – but sent me a telegram that said, “I hope you win everything you guys are fighting for. Thank you for the oatmeal cookies. Your happy hostage, Frank.”
