Nitrogen Oxides
Study: Less Smog Means Healthier Kids
 Up to this point almost all studies about air pollution have tracked increasing levels of air pollution with decreasing levels of health. Respiratory problems, strokes, heart disease, Autism, Parkinson's-like symptoms – they've all been linked to exposure to high levels of air pollution vs exposure to less severe air pollution.
Up to this point almost all studies about air pollution have tracked increasing levels of air pollution with decreasing levels of health. Respiratory problems, strokes, heart disease, Autism, Parkinson's-like symptoms – they've all been linked to exposure to high levels of air pollution vs exposure to less severe air pollution.
Now, comes a new study that approaches the problem from the opposite end of things. It associates healthier kids, specifically, increased lung capacity, with cleaner air over time in Southern California. It provides much needed evidence that pollution controls mandated by the Clean Air Act over the last 40 years have had their intended effect and improved public health.
On Wednesday, the results of the effort were published in the New England Journal of Medicine by researchers from the Keck School of Medicine at the University of Southern California (USC).
Over two decades, researchers at USC studied air pollution levels as they declined in five smog-plagued local communities, while also measuring breathing capacity in 2,120 school children from those same communities during three separate time periods: 1994-1998, 1997-2001 and 2007-2011.
The last group of kids tested showed improved lung growth of about 10% between the ages of 11 and 15, compared with children at the same age in 1996. Overall, the percentage of children with abnormally low lung function at age 15 dropped from nearly 8% in 1994-98, to 6.3% in 1997-2001, to just 3.6% in 2007-11. The positive effects were observed in boys and girls, and regardless of race and ethnicity.
This increase in lung function tracks with improvements in air quality in the LA Basin. According to the ALA, despite a higher population and more cars, Los Angeles had 68 fewer high-ozone days last year than in 1996, and 75 fewer high-particulate-matter days than in 2000. By the study’s conclusion in 2011, fine particulates had fallen by 50 percent and nitrogen dioxide levels by 35 percent in the communities being studied.
Those communities had fewer bad air days because of the pollution controls introduced by government beginning in the mid 1970's with the introduction of the automobile catalytic converter, and continuing to this day with emissions restrictions on everything from shipyards to power plants to lawn mowers.
According to the USC study, those controls and the decrease in smog they produced, have led to fewer stunted lungs and fewer children susceptible to asthma and a host of other respiratory disorders.
According to USC's James Gauderman,
“Improved air quality over the past 20 years has helped reduce the gap in lung health for kids inside, versus outside, the LA basin.”
Consensus in the scientific community (outside TCEQ) seems to suggest that this kind of study wil be important in proving the efficacy of new pollution controls across the country.
Morton Lippmann, a professor of environmental medicine at New York University School of Medicine, said the research would be influential and predicted that within the next few years, when federal emission standards are due for review, “this kind of information will play a major role.”
“It provides confirmation that the work we’ve done to improve air pollution has made a difference in kids’ health,” said Dr. Joel Kaufman, a physician and epidemiologist at the University of Washington, who was not involved in the research. “There are more kids comfortable running around.”
The caveat here is that while new controls benefited public health, it was not necessarily the controls on ozone pollution alone that caused the benefits. During the two decades of study, ozone levels declined only modestly. Ozone has been associated with acute health problems, such as asthma attacks, but the researchers concluded that its reduction does not have the long-term effects on overall lung function that reductions in fine particulates and nitrogen dioxide do.
Pollution controls for ozone, or smog, often have the side effect of reducing particulate matter (PM) and NO2 (one of the forms of Nitrogen Oxide that form ozone), as well. It may well be that these side effects have more impact on public health than previously believed. Certainly the accumulating evidence about the variety of insidious harms caused by even low levels of particulate matter exposure give credence to this idea. Based on the scientific literature, many local downwinders have believed that the single most dangerous kind of pollution being emitted by the cement plants in Midlothian are their voluminous amounts of PM pollution.
One of the reasons Downwinders at Risk has been so insistent on getting Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) on the kilns is that, besides being able to reduce NOX pollution by 80-90 % or more, the equipment is also able to make sizable dents in Dioxins, Volatile Organic Compounds, and yes, Particulate Matter pollution.
Both Gas Industry Spinmeister and Mansfield Compressor Spew During Thursday’s EPA Hearing
 There was at least one truth uttered by Steve Everley, the professional PR spokesperson for Energy in Depth, itself the PR arm of the Gas Industry, during his testimony at last Thursday's EPA ozone standard hearing in Arlington:
There was at least one truth uttered by Steve Everley, the professional PR spokesperson for Energy in Depth, itself the PR arm of the Gas Industry, during his testimony at last Thursday's EPA ozone standard hearing in Arlington:
"…natural gas producers will be significantly impacted by EPA’s proposal to reduce the National Ambient Air Quality Standard for ozone from 75 parts per billion to between 65 and 70 ppb."
Indeed. At the rate things are going in Austin and DC, it might be the only thing to impact the industry's large emissions of pollution for many years to come. Left unsaid by Everley was why the industry would be impacted by such a lower ozone standard – because in many parts of the country now, including the DFW area, smog-forming pollution from the gas industry is contributing significantly to higher ozone levels.
Even the governmental affairs branch of the gas industry, otherwise known as the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, admits that facilities like compressors, storage tanks, pipelines, and de-hydrators found by the thousands in the western part of the Metromess contribute more smog-forming Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) than all the "on-road" vehicles in North Texas combined. This is true not only at the present time, but will be true at least three years into the future, according to TCEQ's own estimates.
Gas facilities also account for the third largest source of smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide pollution in DFW, according to TCEQ numbers included in their recent air plan submitted to EPA – only a ton per day less than all "non-road" vehicles in North Texas like construction equipment, and well ahead of "point sources" like the Midlothian cement kilns and local power plants.
In all, TCEQ predicts that 35,335 tons per year of smog-forming pollution will still be coming from the region's gas industry in 2018. That's a lot. It's so much that, as the TCEQ also demonstrates with its computer modeling, even a tweak here and there in gas pollution estimates can make big differences in the levels of ozone at monitors in places like Denton and Keller and Eagle Mountain Lake – traditionally the worst-performing air quality monitors in North Texas.
And that's why a lower ozone standard is a threat to the industry. The very air quality monitors the industry affects most with its pollution are the ones driving the region's high smog levels. Lowering the ozone standard means it would have to spend money to reduce those emissions significantly. It means it would have to spend money to prevent the kind of huge "accidental" releases of smog-forming pollution released by the Mansfield compressor on Thursday even while Steve Everley was testifying to EPA.
After giving her own testimony to EPA on Thursday morning, Earthworks' Sharon Wilson and Mansfield Gas Well Awareness board member Lance Irwin headed out to the Summit Midstream Partners Compressor Station behind Mansfield's Performing Arts Center, with an infrared, or FLIR "thermal imaging" camera. Such a device is capable of recording the kinds of VOC emissions that are often smelled and inhaled by surrounding residents, but can't be seen with the naked eye.
The Summit compressor and the two nearby Eagleridge gas wells have been the scene of many different complaints from the surrounding Mansfield neighborhood – everything from airborne foam landing in backyards to oily deposits landing on car finishes. On Thursday, Wilson and Irwin were responding to a new series of complaints about awful smells. When they showed up, what the two recorded was a massive "emergency blowdown" (versus the "planned" kind). While filming the event, Wilson suffered health effects familiar to gas facility neighbors and was overwhelmed by the obvious hydrocarbon fumes. Once you see her video, you understand why:
Such a blowdown was exactly what Lance Irwin had warned the Mansfield City Council about only three days before, during comments directed at slowing down or denying the permit for a new compressor, 34 wells, 12 tanks and a assortment of other facilities at an Edge pad site near Debbie Lane in town. He pointed out that industry and government estimates about emissions never take these kind of catastrophic events into account – form a short-term toxic exposure perspective, or as it turns out, from an air quality, smog-creating perspective. And he's right.
In this regard, these kinds of accidents are no different than the infamous industrial "burps" from refineries and chemical plants along the Houston Ship Channel that lead to smog spikes downwind. There are 650 large compressor stations in the DFW "non-attainment" area. How many are experiencing blowdowns on any given day? How many are affecting ozone levels in the spring and summer? The TCEQ estimates included in its DFW air plan don't even try to quanify them.
Because gas facilities like compressors are subject only to "standard permits," are located diffusely around a region, and don't officially emit a de minimus amount of air pollution, they're not subject to the federal rule of off-setting. That's when a new polluting facility locates in an already smoggy area like DFW and has to pay to cut smog pollution elsewhere if it wants to emit the stuff itself. If a new cement plant or power plant were to locate in DFW, it would have to pay to reduce a ton and a half of smog-forming pollution for every ton it wanted to release. Gas facilities don't have to do this – even though collectively they emit more smog-forming pollution than all the cement plants and power plant in the non-attainment area!
EPA has tried to argue that a company's different facilities are all tied together and should be counted as a single source, and so subject to off-setting regulations. But the courts have ruled against them.
Rising gas industry pollution and the absence of any official brake on its growth like off-setting is a large reason, maybe the primary reason, why DFW hasn't seen the kind of air quality progress it should have by now. Until this last summer's cooler and wetter weather gave us relief, ozone levels had been stagnating or even rising since 2009 – or about the time the industry invaded North Texas in large numbers. There's no question that had the Barnett Shale boom not happened, we'd have much cleaner air by now.
But it did and we don't. And so that's why a lower ozone standard is perhaps the only way that the gas industry will ever be forced to clean-up its act – especially on the widespread regional level we require to get to safe and legal air. Just like it has with the Midlothian cement plants, the need for lower smog levels can force the state's and industry's to act to add controls. It's a long-term fight, but one of the only paths to across-the-board change versus the city-by-city slog activists have had to rely on.
National Resources Defense Council lawyer John Walke has a great takedown of Steve Everley's spin on Thursday. And the tireless cross-country DeSmogblog reporter and photographer Julie Dermansky has a good read on the Mansfield fight that you should check out. But the most compelling rebuttal to both industry PR and local governments who want to ignore their own responsibility in this mess is probably Wilson and Irwin's two and a half minutes of video.
After a 14-year Campaign, State-of-the-Art Pollution Control Finally Coming to Midlothian
 (Midlothian) After a 14-year effort by local citizens, Holcim US Inc. is applying for a permit to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to install a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit in their Midlothian facility. It's the first application for commercial use of SCR technology in any U.S. cement kiln.
(Midlothian) After a 14-year effort by local citizens, Holcim US Inc. is applying for a permit to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to install a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit in their Midlothian facility. It's the first application for commercial use of SCR technology in any U.S. cement kiln.
DFW-based clean air group Downwinders at Risk has been advocating the use of SCR in the three Midlothian cement plants located just south of I-20 since 2000, when a German cement kiln first operated the technology successfully.
Together, the TXI, Ash Grove, and Holcim plants represent the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the country and are a major contributor to DFW's historic smog problem.
"We need this pollution control technology in North Texas, and we're pleased to see Holcim's application," said Downwinders Director Jim Schermbeck. "But we wish residents could enjoy its results sooner than Holcim intends."
The SCR unit is planned for Holcim's idle Kiln #2 while a more common Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer will be built for its operating Kiln #1. Both technologies are being installed to meet new EPA emission standards for hydrocarbon pollution from cement plants. Those standards themselves were championed by Downwinders and other citizen groups in 2009, with over 200 people showing up at an EPA hearing the the DFW Airport Hotel to support them.
The deadline for compliance with the new standards is September 2016. However, restarting of Kiln #2, and the introduction of SCR in Midlothian, is dependent on local demand for Holcim's cement, which is still recovering from weak demand during the recession. That lack of demand could delay the technology's inauguration until after 2016.
Nevertheless, according to Schermbeck, Holcim's application for a permit to install SCR makes it's more likely that all of the Midlothian cement plants, and others in EPA "non-attainment areas" for smog pollution around the country, will be adopting it sooner rather than later.
"Holcim's application sets a precedent that's hard to ignore by regulators in Austin and Washington. For the first time a US cement plant has expressed enough confidence in SCR to make it a technically and economically-viable choice for pollution control. There's no going back."
SCR is widely considered to be the most advanced form of pollution control for cement manufacturing, capable of reducing smog-forming pollution by 90% or more, along with significant reductions in Particulate Matter, metals, and Dioxins.
Although about half a dozen European cement kilns are successfully operating the technology, U.S. plants have refused to endorse it. Two EPA-sponsored pilot tests of SCR are being conducted at Indiana and Illinois cement kilns as part of court-ordered settlements. Holcim's application for its Midlothian kiln is the first time and American cement plant is voluntarily approving SCR use.
Although it's not coming in time to impact the current DFW clean air plan, due to go to public hearing in January of next year, Holcim's application will put SCR on the agenda for the next such plan.
Just two weeks ago, EPA staff recommended a new ozone, or smog, standard of between 60 and 70 parts per billion over an eight hour period versus the current limit of 75 ppb. Adoption of a stricter standard is expected to occur by late next year, meaning a plan to meet that standard will be gearing up sometime in the next three to five years. By that time, Holcim's SCR unit should have a track record that can be cited as a reason for all the Midlothian cement plants to use it.
Schermbeck noted that just last month representatives of the TCEQ told a regional air quality meeting in Arlington that SCR was neither an economical nor technically feasible pollution control option for the Midlothian cement plants. He said Holcim's application belies that claim.
A public meeting on the Holcim permit application is being scheduled for early November.
Arrival of SCR on the scene marks the latest and the most dramatic milestone in the transformation of the local cement industry since Downwinders at Risk was founded 20 years ago to stop the burning of hazardous wastes in the Midlothian kilns.
After a 14-year battle, TXI halted its hazardous waste-burning operations in 2008. Downwinders then pursued a six-year "green cement" campaign to replace all seven obsolete and dirtier wet kilns with newer "dry kiln" technology. That campaign ended in 2012 with the announcement that Ash Grove would shutter its three wet kilns and build a new dry kiln in their place. That plant is due to go on line this year.
Adoption of SCR remained a goal of the group through four different DFW clean air plans going all the way back to 2000. Schermbeck said his group made incremental progress each time, winning small and large battles that directly lead to today's news.
"Holcim's application for SCR is the latest testament to the persistence and focus of a small group of committed citizens who have pulled and pushed the U.S. cement industry into the 21st Century one step at a time."
TCEQ: Link Between Fracking and Air Quality, No Cement Controls Just “Because”: Highlights From Tuesday’s Air Meeting
 Dallas Resident Liz Alexander showed up at the Council of Governments meeting room on Tuesday to lend her support to the effort to get more out of an anemic state ant-smog plan than the state wants to give. She was a warm body whose presence would be its own statement of concern. She was being a good trooper by just showing up.
Dallas Resident Liz Alexander showed up at the Council of Governments meeting room on Tuesday to lend her support to the effort to get more out of an anemic state ant-smog plan than the state wants to give. She was a warm body whose presence would be its own statement of concern. She was being a good trooper by just showing up.
At first she sat far from the action amidst the rows of seats for bystanders and, despite encouragement, was resigned to just listening, because as she explained, "she didn't know enough to ask questions."
Then someone urged her to move up to the rectangle of tables where the presenters stand and deliver, where there are microphones to raise the volume of concerns and questions that might be posed by mind-numbing reassurances that everything is going hunky-dory. As more of these air quality meetings have occurred, citizens have been less and less shy about taking up these front row seats that look more official than the rest; look like they should be reserved for guys in suits. Increasingly they're occupied by people in street clothes.
And then, after much information had been paraded in front of Liz, she did something she did not think she was qualified to do only about 90 minutes earlier. She asked a question. It was about what assumptions had been included in the information about unspent air pollution clean-up dollars that are piling up in Austin. She got an answer from a local COG staff person in real time that satisfied her. In the space of one meeting she moved from spectator to participant.
And she wasn't the only one. More than any other meeting so far, this one involved more citizens asking more questions about more subjects – and it revealed just how thin the state's rationale is for doing nothing.
As predicted, it was a day for the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality to explain why its new DFW anti-smog plan was really going to work this time – unlike the five previous failures – and why it wasn't going to be considering any new controls on the Midlothian cement plants or on gas compressors – a refutation of the case Downwinders at Risk had made in its June 16th presentation.
But here's what really happened: For the first time in these proceedings the state admitted that oil and gas emissions have a big influence on regional air quality. And when a former County Judge asked an TCEQ's Air Quality Manager specifically why anti-smog controls already being used on cement kilns in Europe were not being considered for the Midlothian kilns, the staffer couldn't say, offering up only the longest, most pregnant pause by any state staffer in the history of these meetings.
After being heavily criticized for months for leaving at least four monitors above the 75 ppb federal smog standard even after its plan had ended in 2018, the state came back to this meeting saying they only had three sites above 75 ppb now, and by margins that didn't exceed the standard by more than 1 part per billion. Between June and August, there had been a remarkable drop in future estimated smog levels at the area's monitoring sties in the state's computer modeling – particularly at the historically most stubborn monitoring sites in Denton and Northwest Tarrant County.
What had caused this drop? A relatively modest decrease in Nitrogen Oxide pollution of around seven tons a day and a decrease in Volatile Organic Compounds of about 15 tons per day. That's not a lot of pollution to produce such a large decrease in monitor readings in the computer model.
A more important question is: where did the decreases in air pollution come from that could produce such dramatic results in the modeling? The answer: primarily from oil and gas industry sources. Based on TCEQ's own formula relying on the declining number of new wells being drilled in the Barnett Shale.
For the moment forget the methodological qualms you might have about that declining well assumption. Instead, appreciate the fact that the same state agency that couldn't bring itself to ever say the Barnett Shale was producing air pollution holding DFW back from meeting Clean Air Act smog standards now says that it's decreases in that very kind of pollution that are having such a substantial effect on the monitors in the western part of the Metromess that have been the most resistant to other control strategies. TCEQ has just proven a causal link its been denying for over seven years now.
It can't be just a one-way street. If declining oil and gas air pollution equals better air quality in the TCEQ's computer model, so increases in oil and gas pollution must lead to worse air quality.
There are all kinds of reasons to doubt that the drop in total oil and gas air pollution will happen at all or drop as fast or as sharply as the TCEQ predicts. Afterall, they're 0 for 5 in such matters. They may be underestimating the amount of total air pollution from all gas and oil sources and so the drop will not be as sharp. They may be underestimating the impact of lots of new lift compressors that will be showing up to squeeze the last bits of gas from older wells even as new wells are not drilled as often. But as of Tuesday the link has been made by TCEQ itself that such a drop results in big decreases in smog levels in Denton and Northwest Tarrant County. That's something that citizens can use to argue as proof of the impact of oil and gas facilities on local air quality.
Of course, it only took the span of about 30 minutes for the TCEQ to internally contradict itself about those results.
According to TCEQ computer modelers, natural gas Compressor Stations large enough to be considered "point sources" just like cement kilns or power plants will be responsible for over 17 tons of Nitrogen Oxides, and 26 tons of VOCs a day in 2018 – well over the amount of oil and gas pollution decreases that resulted in those lower monitoring numbers in Denton and NW Tarrant County. But according to the TCEQ staff responsible for suggesting new controls in the new smog plan, those numbers are not large enough to have an impact on improving DFW air quality or warranting a policy of electrification for those compressors that could reduce their air pollution to a fraction of those volumes.
So while 7 tons of NOx reduction from Oil and Gas sources is large enough to bring some of the most stubborn monitors down a whole part per billion, reducing air pollution from Oil and Gas sources by another 17 tons of NOx reduction would have no effect on DFW air quality at all and it's just not worth it to make them electrify compressors. Honest, that was the logic in play on Monday, and it didn't hold up very well under questions from people like Liz Alexander.
And that was all before you got to why the Midlothian cement kilns could not, no way, no how, possibly, under any circumstance, be required to install Selective Catalytic Reduction controls, just like their European counterparts have done over the last 15 years.
Turns out, it's just because.
Oh, the TCEQ staffer cited four criteria for any new control measure to meet before it could be considered. Let's see, there was "technological feasibility." Since there are at least seven full-scale SCR units up and running in Europe, that couldn't be a problem. It's accepted technology by some of the same companies operating kilns in the US – including LaFarge-Holcim.
There was "economic feasibility." And since there are all those SCR examples already in the European market and no company has gone bankrupt running them, that's also off the table. Plus the fact that the TCEQ's own 2005 study of SCR concluded it was "available technology" then that would only cost $1000 to $3,000 per ton of NOx removed – versus the up to $15,000 per ton of NOx removed ratio allowed in the state's own official diesel engine replacement program. Coming in at one-fifth the cost of what the state already said was economically feasible, it certainly ruled out that one.
There was the third criterion – that controls couldn't cause ‘‘substantial widespread and long-term adverse impacts.’’ The state said that wasn't the reason they couldn't be considered either, although the TCEQ staffers seemed to hedge a bit here, seemingly wanting to say that, really, they didn't want to cause themselves adverse impact by admitting that they had been wrong for over a decade about this stuff.
The proposed control cannot be ‘‘absurd, unenforceable, or impracticable.’’ Clearly, if the Europeans are doing it on their kilns, it's none of those either. It's quantifiable, and up and running in power plants, cement kilns and incinerators.
And it has to speed the attainment deadline by a year. No problem. SCR could do that if it was installed in a timely fashion.
So at the end of the state's presentation, former Dallas County Judge Margaret Keliher asked the TCEQ staffer exactly why SCR wasn't considered a possible pollution control measure since none of these criteria that had been presented seem to rule it out. And the TCEQ's staffer's response was…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
No, really, that was the response. She couldn't say. It was that embarrassing. Because the rejection of SCR by TCEQ isn't based on any of those criteria. It's based on a political decision that's been made that no new pollution controls will be sought on the kilns or any other major industrial polluter as long as Rick Perry is running for President. Or "just because."
How ridiculous is this? At this point the TCEQ is taking an even more regressive view of SCR controls than the cement industry itself. In June, Holcim Cement's Midlothian plant requested a permit from the state that would allow it to build either a Thermal Oxidizer or an SCR until for the control of VOC pollution. Being the free market fanatics the Perry Administration claims to be, doesn't the fact that one of the Midlothian cement plants is asking for a permit that includes the possibility of installing SCR mean it's automatically technologically and economically feasible? The market is never wrong, right? Are the folks at Holcim so enamored of kinky, off-the-wall green technology that they'll just include it in a permit for laughs? These guys are Swiss engineers. They have no sense of humor.
Denial of SCR as a viable control measure that could reduce smog pollution is making the TCEQ contort into sillier and sillier positions. It's making them deny the conclusions of their own almost-decade old report that said it was available to put in a kiln in 2005. It's making them deny the fact that SCR is up and running at over half a dozen kilns in Europe. It's forcing them to once again use the "Midlothian limestone is magically special" defense that has been used to forestall any progress in pollution control there over the last 25 years. The arguments used against SCR are exactly the same as were used against the adoption of less effective SNCR technology before it was mandated. In case you hadn't noticed, they're still making cement in Midlothian despite the burden of having to nominally control their air pollution.
The state wants to power through this anti-smog plan just like they did the last one in 2011. They don't want to have to make industry do anything. But at this point the denial of SCR as a control measure to be included in the next DFW anti-smog plan is so absurd, as is the justification for electrification of gas compressors, that it might be fodder in the next citizens lawsuit over a DFW anti-smog plan, which usually follows these things like mushrooms after a rainstorm.
Want to get involved in this fight and make it more difficult for the state to get away with doing nothing at all about DFW smog – again? Please consider attending our next DFW Clean Air Network meeting – THIS SUNDAY, AUGUST 17th, from 3:30 pm to 5:30 pm at the offices of the Texas Campaign for the Environment across from Lee Park in Dallas, 3303 Lee Pkwy, Suite #402 (214) 599-7840. Citizens are the only force that can make this plan better. Be there, or breathe bad air.
Power of the Press: Week after Trib Report on DFW Smog, First “Exceedences” of 1997 Standard
 It was only eight days ago the that online Texas Tribune did the first real overview of DFW air quality for this "ozone season." Borrowing heavily from the June 16th Downwinders at Risk presentation to the North Texas regional air quality committee, it concluded that there had been no discernible progress in regional air quality for the past five to six years despite a new state anti-smog plan aimed at getting the area below the 1997 standard of 85 parts per billion.
It was only eight days ago the that online Texas Tribune did the first real overview of DFW air quality for this "ozone season." Borrowing heavily from the June 16th Downwinders at Risk presentation to the North Texas regional air quality committee, it concluded that there had been no discernible progress in regional air quality for the past five to six years despite a new state anti-smog plan aimed at getting the area below the 1997 standard of 85 parts per billion.
Ironically, up to that point, DFW had been enjoying one of the wettest, coolest, most ozone alert-free summers on record. Not one 100 degree day until July and only one "bad air" days of note on June 11th. It looked like we might actually be able to meet the 1997 standard of 85 ppb for the very first time.
That's all changed with this past weeks' return to familiar form. In just seven days, they've been at least four official "ozone alerts" issued for DFW by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality. Those had produced four "exceedences" of the current 75 parts ppb standard, which the state is now aiming at with another "do nothing" plan under development and due out by the end of the year. On Wednesday the trend got more serious with the addition of the first two "exceedences" of the older 1997 standard we can't seem to conquer – a reading of 88 ppb at the NW Fort Worth monitor at Meacham Field and a 91 at the usually quiet Granbury monitor in Hood County. In the latter case, one mid-afternoon hourly reading reached as high as 113 – just 12ppb short of a violation of an even more ancient standard left over from the 1980's.
For comparison's sake, EPA scientists just sent a letter to EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy recommending that a new, lower federal standard for ozone be set at 60-70 ppb.
It will still take another week of 85 ppb plus days to produce the "fourth highest" readings at the Denton or Keller sites to combine with their 2013 averages and keep DFW in violation of a 17-year old ozone standard. But then again, we have all of August and September to go.
Not surprisingly, two of this summer's hot spots include traditionally troublesome monitors – the Denton and NW Fort Worth site. Tarrant and Denton Counties have historically been the places where the region's highest readings have originated. One reason is wind direction – smog accumulates from upwind sources like the Midlothian cement plants and blows Northwest during the summer. Another more recent reason is the mining of Barnett Shale gas deposits that release huge quantities of smog-forming pollution in the western half of the Metromess, a phenomenon that's been examined in a new UNT study that divided the region's ozone monitors into "Fracking" and "Non-Fracking" areas and found significantly higher readings among those in the Fracking area.
As we went to press with this post, Thursday's readings looked to be producing another round of 75 ppb or higher results. Adding to this year's ozone season irony is that over the last 20 years, July has traditionally been the summer month that produced the fewest number of high ozone readings, book-ended by higher numbers in June and August-September.
Depending on the weather, DFW may still be able to make it over the 1997 standard, 85 ppb hump. But based on this past week's results, that hump just got bigger. Stay tuned.
Ask the State and Holcim To Finally Give DFW “the Holy Grail” of Cement Pollution Control Technology
 Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
Swiss-based Holcim Cement is requesting a permit amendment to add new piece of pollution control equipment to its Midlothian cement plant, one of three cement plants that make the city the "Cement Capitol of Texas" and the largest concentration of cement manufacturing in the U.S. Good news, right? The problem is that the company is asking the state for the permit before deciding what kind of pollution control equipment to install.
That's right. Holcim is asking the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) to OK a permit that will result in a "major modification" of its Midlothian plant and could produce significant amounts of new pollution before it even decides what the major modification is going to be. Anywhere else in the country this might be a bit odd, but hey, it's Texas, where Rick Perry's TCEQ has a rubber stamp standing by for anything industry requests.
Holcim's permit request is being prompted by a problem complying with new federal regulations limiting a kind of pollution called Total Hydrocarbons, or THCs. These are also sometimes referred to as "Volatile Organic Compounds." Think Benzene, and other kinds of hazardous flammable gases. In its permit application Holcim says it needs to add new controls to reduce THC to levels and come under the new federal standard. Fair enough. The company then says that it's still trying to decide between two different types of controls and will make up its mind after getting the permit and seeing how well its choice works out on one of its two separate giant kilns. That's the bogus part.
But wait, there's more! The two technologies Holcim is considering installing in Midlothian are: 1) A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, or RTO, which is a fancy way of saying setting them on fire and flaring them off, and, 2) A Selective Catalytic Reduction unit, or SCR, which is a tower of treated metal honeycombs that pick up pollution as the plant exhaust passes through them. RTOs are already installed on American cement plants, including TXI's huge Midlothian kiln just a few miles down Highway 67 from Holcim. On the other hand, up to now full-scale commercial SCR units have only been installed on European cement plants and in fact, the Portland Cement Association has lobbied long and hard to keep them out of the US for fear of raising the pollution control bar too high for all of the country's cement plants.
That's because SCR is more expensive to build and maintain than most cement plant control devices. But for the money, you get the Holy Grail of cement plant pollution control technology.
Most of the European cement plants that have SCR units install them to remove another type of pollution from their stacks – Nitrogen Oxides (NOx). If that sounds familiar, it's because NOx is a major smog-forming pollutant, and DFW has so much of it that the region has never been in compliance with the Clean Air Act standard for smog. And you'll never guess which facilities are the single largest sources of NOx pollution in North Texas. Or maybe you will: the Midlothian cement plants. That's why Downwinders at Risk has made it a point to campaign to require all three Midlothian cement plants – Holcim, TXI and Ash Grove – to install SCR….since all the way back in 2001, when the first European units were deemed a success at a German cement plant. SCR can remove 80 to more than 90% of all NOx coming out of a cement kiln. The 6500 tons of NOx a year that the Midlothian cement plants are permitted to release could be reduced to 650 tons with the application of SCR.
Now, as it turns out, SCR units are great not only at capturing large amounts of NOx pollution, but all kinds of other industrial pollution coming out of cement plants as well. Like THCs – up to 70% or so, but also Particulate Matter, Metals, Greenhouse Gases, Carbon Monoxide, and Dioxins. It's what's called a multi-pollutant control device because it does such a good job of eliminating a wide variety of nasty stuff from smoke stacks. This is what makes it the state-of-the-art technology for communities hosting kilns. In contrast, RTOs are single-purpose pollution devices aimed just at hydrocarbon removal and aren't designed to remove other kinds of emissions.
So even though Holcim is considering operating SCR because of its hydrocarbon problem, it would have a massive impact on the plant's air pollution across the board. And if Holcim were to set the precedent, the clock would begin ticking on bringing SCR to the other two Midlothian cement plants as well. It would only be a matter of time.
The public comment period for telling the state whether to accept or reject Holcim's permit application ends this Friday, July 11th at 5 pm. (If you're interested in jumping through the hoops to fill out the online form for official comments, you can go here and use Permit Number 8996)
Downwinders is submitting detailed comments praising Holcim for considering SCR, but urging the TCEQ to reject this permit because it's too vague and doesn't commit the company to any partciular technology, including SCR. We've also been collecting letters form local officials and stare legislators that urge Holcim to definitively choose SCR.
Now we're asking you to help us bombard both the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality and Holcim's US headquarters in Dundee Michigan in the next 48 hours with the same message to show public support for the company to do the right thing while rejecting a placeholder permit that doesn't commit it to do that right thing.
We want a permit request from the company that says Holcim will definitely install SCR, becoming the first commercial application of this state-of-the-art technology in America.
Using our "Featured Citizen Action" link, you can send such a message to Austin and Michigan in a matter of seconds right now. All you have to do is click here and then send the e-mails. We guarantee there's no more important or easier thing you can do for clean air in North Texas this week than sending these e-mails to the TCEQ Commisisoners and Holcim Corporate leadership. Please help us get the cement plant pollution control technology DFW deserves. It will only take a matter of seconds for you to help us achieve a goal we've been working toward for 14 years. We can do this. But we need your help. Now. Thanks.
Highlights from Monday: How the State Hides Gas Industry Pollution
 Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
Want to see one example of how low state bureaucrats will stoop to underplay the significance of the impact of oil and gas pollution on DFW air quality? Take a look at some slides that were part of Monday's presentation by Downwinders at Risk's Jim Schermbeck to the regional air planning meeting.
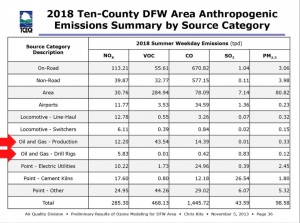
In the first you'll see how the state officially ranks all the "source categories" for human-made, or "Antrhopogenic," smog-forming Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) pollution in North Texas (all the numbers are Tons Per Day):
Yes the pic is fuzzy, (we can land a person on the Moon but can't seem to get charts to show up with a jpeg format online) but if you squint really hard, you'll notice there are two categories for Oil and Gas pollution numbers among the more traditional "Point Sources," Off-Road, "On-Road", etc – "Oil and Gas Production" and "Oil and Gas – Drill Rigs." Looking at these two categories you might think that adding them together would produce total Oil and Gas pollution numbers. You'd be wrong.
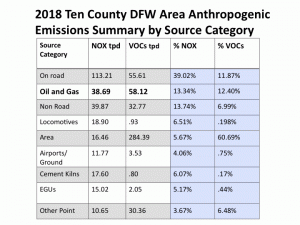
As it turns out, there are other Oil and Gas pollution numbers hidden away in other categories in this chart not labeled "Oil and Gas." For example, in both the "Area" and "Point-Other" categories are the numbers for NOx and VOCs pollution from gas compressors. But wait, you object, aren't gas compressors an integral part of any kind of "Oil and Gas Production?" Yes, yes they are. So why aren't they included in that category instead of being stuffed anonymously in these other categories? Great question. Perhaps it has something to do with the volume of pollution they release. Because when you finally wrestle the numbers from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (the TCEQ didn't voluntarily offer this information), compressor pollution turns out to double the amount of smog-forming NOx released from the Oil and Gas industry in the DFW 10-county "non-attainment area." And NOx pollution is what the TCEQ keeps saying is driving our chronic smog problem. Here's the way Schermbeck presented the same TCEQ "source categories" with the compressor numbers now teased out and added to the ones already identified as Oil and Gas: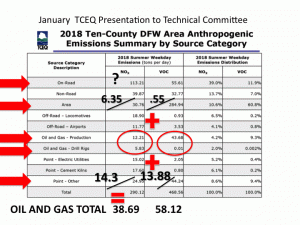
These additions raise the industry's polluter profile significantly. And that's what this next slide is doing. It's totaling all the Oil and Gas pollution and then re-ranking the categories based on these new numbers. Same totals, just different, and more honest, organization of the individual source figures. Instead of Oil and Gas emissions looking relatively small in relation to other sources like cement kilns and power plants and even locomotives, it escalates the Oil and Gas industry into one of the region's foremost industrial air polluters:
And even this much larger number is still underplaying the total amount of air pollution fracking adds to regional air quality because the state hasn't bothered to try to tease-out the "on-road" pollution that all those fracking waste and water trucks adds to the mix. State air modelers shrugged their shoulders and said they couldn't figure out how on earth to do that. Just by "Googling" the subject, Schermbeck found at least two previous studies that did that very thing – a 2005 Denton report and a 2013 Rand Corporation report that even estimated the amount of dust pollution raised by those trucks.
While those truck totals remain a mystery for now, using the TCEQ's own numbers, compressors make up at least 53% of the total NOx pollution released by the Oil and Gas industry in North Texas, and a full quarter of all VOC pollution released. According to Schermbeck, that's why they make such good targets for electrification, an air pollution control measure he was recommending as part of his larger presentation to the regional air planning committee on Monday.
This is just one example of the kind of duplicitous behavior the state of Texas is resorting to in trying to hide the true environmental and public health impact of the Oil and Gas industry. No slight of hand is too petty. Only by diligent digging by citizens is the truth coming out, ton by ton.
Schembeck's entire (unfuzzy) presentation is now online at the North Central Texas Council of Governments website as part of the June 16th agenda. It loses something without his accompanying narration but the jest of it is easily discerned for those who want to plod through it: TCEQ is doing anything but a sincere job of building a serious clean air plan for DFW. But then again, we bet you already knew that.
Rick Perry, with a Smoking Gun, in the COG Headquarters: Monday at 10 am
 The latest chapter in a decades old mystery game of "Get a Clue" happens tomorrow morning, Monday, June 16th when representatives of the Sierra Club and Downwinders at Risk present their case against the current state anti-smog plan during the regional air planning meeting at the headquarters of the North Texas Council of Governments, 616 Six Flags Road in Arlington. Come find out who and/or what keeps the DFW area from ever meeting federal clean air standards year after year and what can be done about it. The meeting starts at 10 am. Citizen groups are expected to do their presentations in the 11 to 12 hour. Then we'll all have a debriefing lunch at the Subway's down the street hosted by State Representative Lon Burnam. Y'all come.
The latest chapter in a decades old mystery game of "Get a Clue" happens tomorrow morning, Monday, June 16th when representatives of the Sierra Club and Downwinders at Risk present their case against the current state anti-smog plan during the regional air planning meeting at the headquarters of the North Texas Council of Governments, 616 Six Flags Road in Arlington. Come find out who and/or what keeps the DFW area from ever meeting federal clean air standards year after year and what can be done about it. The meeting starts at 10 am. Citizen groups are expected to do their presentations in the 11 to 12 hour. Then we'll all have a debriefing lunch at the Subway's down the street hosted by State Representative Lon Burnam. Y'all come.
Thank You. Citizens Might Have Just Saved The Local Air Planning Process…From Itself
 A year from now, last Thursday' meeting in Arlington may be seen as a turning point.
A year from now, last Thursday' meeting in Arlington may be seen as a turning point.
Local residents refused to let the air quality planning process die, showing up in numbers that forced officials to switch to a larger room, and making sure their opposition to another state "do-nothing" air plan was heard loud and clear.
Their participation had already changed the day's agenda. Included was a breakthrough UNT study that directly challenges the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality's claim that natural gas emissions don't increase DFW smog.
UNT's Dr. Kuruvilla John's presentation of the new study received quite a bit of media coverage, before, during, and after Thursday's meeting. You can find some of the best coverage by clicking on the links below.
UT-Austin Study Reveals "Underestimates"
Dr. John's presentation influenced another researcher's slide show as well. Scheduled to speak about older, more generic ambient air measurements for ozone, Dr. David Allen of UT Austin instead presented more recent research into gas pollution as well.
Overlooked in the debut of the UNT study, Allen's constant monitoring of one drill site in Fort Worth revealed that the TCEQ was underestimating emissions from the pneumatic valves at the site by 159%.
That was news to both citizens and TCEQ, who said they hadn't looked at Allen's research and hadn't corrected their inventories to account for such underestimates. Valves like these are powered by natural gas, are quite numerous on gas equipment, and account for a large percentage of VOCs released from a fracking site.
A Better Picture of Oil and Gas Pollution
Citizen cross-examination of TCEQ staff members present at the meeting also revealed a different look at the volume of Oil and Gas industry pollution in the 10-county DFW "non-attainment area"
Up to Thursday, TCEQ was dispersing Oil and Gas pollution across several categories, making it impossible to show the true total impacts.
Here's an example of the way TCEQ likes to present the info:
SOURCES OF SMOG-FORMING NITROGEN OXIDE POLLUTION (NOx)
IN DFW's NON-ATTAINMENT AREA
1. "On Road" vehicles 113.21 tons per day
2. "Non-Road" vehicles" 39.87 tpd
3. "Area" 30.76 tpd
4. "Other Point Sources" 24.95 tpd
5. "Locomotives" 18.90 tpd
6. "Cement Kilns" 17.60 tpd
7. "Electric Utilities" 15.02 tpd
8. Oil and Gas Production 12.21 tpd
9."Airports" 11.77 tpd
10. Oil and Gas Drill Rigs 5.83 tpd
TOTAL 290.12 tpd
This makes it look like Oil and Gas pollution is not that big a deal.
But it turns out TCEQ is hiding 28.44 tpd of NOx gas compressor pollution in the "Area" and "Other Point Source" categories.
This was brought out in questioning on Thursday. Once you add these figures to the other Oil and Gas emission numbers spread out over different categories, this is what you get:
SOURCES OF SMOG-FORMING NITROGEN OXIDE POLLUTION (NOx)
IN DFW's NON-ATTAINMENT AREA
1. "On Road" vehicles 113.21 tpd
2. Oil and Gas Industry 46.48 tpd
3. "Non-Road" vehicles 39.87 tpd
4. "Locomotives" 18.90 tpd
5. "Cement Kilns" 17.60 tpd
6. "Area" 15.93 tpd
7. "Electric Utilities" 15.02 tpd
8. "Other Point Sources" 11.34 tpd
9. "Airports" 11.77 tpd
TOTAL 290.12
(Earlier today we put out an e-mail alert that left 10 tons off the "Area" category in this second chart, greatly affecting its ranking. That mistake is corrected in this version of the chart and we apologize for any confusion that might have caused)
When you quit playing the state's shell game with Shale pollution, the Oil and Gas industry becomes the region's second largest source of NOx pollution – the kind of pollution TCEQ says is the main driver of smog in DFW (not even counting all the pollution from O&G fracking trucks still hiding in the "On Road" category).
There have been control measures for cars to reduce NOx. There have been controls on heavy duty equipment and trucks to reduce NOx. There have been new controls on locomotives to reduce NOx pollution. There have been controls on airport ground equipment to reduce NOx pollution. There's even been middling controls to reduce the NOx from the Midlothian cement kilns. But where's the controls to reduce NOx from the Oil and Gas industry – the one source in this list that hasn't had the same kind of regulatory attention? Good question – save it for next time.
Citizen Participation is Crucial
This is the kind of close examination the TCEQ hopes to avoid by limiting debate on this new clean air plan, scheduled to be submitted to EPA by July next year. And it's exactly why citizens need to keep showing up.
Because of the momentum and interest coming out of Thursday's meeting, citizens also got the next scheduled pow-wow of the local air planning process moved up to late May or early June instead of waiting until July.
We're already taking suggestions for what you want to see on that agenda, so don't be shy. And thank you again for restoring some tiny amounts of integrity into a process that's been swamped by Rick Perry's indifference.
You're making a difference, and that's all anybody can do. This last Thursday it was a big difference. Let's try to do the same in May.
Some Coverage of Thursday's Air Planning Mtg.
Channel 8: "UNT researchers say fracking a contributor to North Texas smog problem"
Texas Observer: "Studies: Links Between Fracking and Smog Pollution Stronger Than State Claims"
Star-Telegram: "Natural Gas Production Contributing to Higher Ozone Levels, study Finds"
Denton Record Chronicle: "Officials: No New Plans to Clean Up Air"
HOW YOU CAN SAY "THANK YOU" BACK
Here's what Downwinders at Risk did this past week to make sure Thursday's air quality meeting wasa success:
1) Pressed for and got the UNT study linking fracking to smog on the meeting agenda after being told it would not be included.
2) Sent out releases to the media advertising the UNT presentation.
3) Sent out alerts to you and others to let you know about the new UNT study and the meeting itself.
4) Sent out a "Citizens' Guide to the Meeting" so you could be prepared for Thursday.
5) Showed-up at Thursday's meeting with handouts showing the lack of air quality progress in DFW and the lack of a complete plan by TCEQ
6) Used our questions to reveal how TCEQ was hiding Oil and Gas industry pollution totals in their data
7) Pressed for and got an earlier "next meeting" of the local air quality planning group
8) Sent out this follow-up so that everyone knows what went on and what the news is from the meeting
A local forum for clean air issues was about to disappear.
Only the last month's mobilization of citizens prevented that from happening on Thursday.
Who began that mobilization?
We did.
We really need your financial help to keep doing this. We don't get state or national funding – just local money from people like yourself.
Thanks. We very much appreciate it.
We Won a Small Victory – Now Come Take Advantage of It
 This is why citizen participation matters.
This is why citizen participation matters.
Last week, local officials were balking at reserving a slot at next Thursday's regional air planning meeting for a presentation by UNT researchers on how gas industry emissions from the Barnett Shale could be adding to DFW's chronic smog.
After reading about the UNT research in the Denton Record Chronicle, Downwinders at Risk and State Representative Lon Burnam specifically asked the local Council of Governments to include the UNT work on the agenda.
At first, we were told that there was already one technical presentation scheduled for the meeting and there wouldn't be any time for a second.
That struck us as strange, since in the past, every such meeting has always had more than one technical presentation.
When we pointed this out in an e-mail with links to past meeting agendas to prove the point, we quickly got a different response. Suddenly, there would be time for the UNT presentation.
That wasn't so hard was it? All it took was a little logical push back. But if we hadn't supplied it, Thursday would be looking a lot different.
Now, we're asking you to please come and help us push back a little more.
State environmental officials are on record as saying the air pollution from gas mining and production in the Barnett Shale is not adding to DFW's smog.
A lot of us think otherwise.
Come next Thursday, on the 17th, you can listen to the new UNT research on fracking air pollution and ask Texas Commission on Environmental Quality officials directly what makes them so sure that gas pollution isn't hurting local air quality.
Because the format of these regional clean air meetings are now so informal, anyone in the audience can ask questions of a presenter. That means you – if you show up.
It doesn't matter if you don't know the technical lingo. This is all about wind direction, weather, and things that pollute. There are no stupid questions.
The new anti-smog plan that the state is building needs all the public scrutiny it can get. It needs tough examination by people who care about clean air and the truth.
Next Thursday, you can help us put the state on the spot.
This is the first opportunity in 2014 to speak up and sound off about our decades-long smog problem. Don't let the TCEQ leave town without hearing from you.
We fought and won the right for you to listen to this research because we thought it was important. Won't you please come and take advantage of this victory?
We need a good showing to prove DFW residents are still mad about breathing dirty air.
NEXT THURSDAY, APRIL 17th
10 am to 12pm
North Central Texas Council of Government headquarters
616 Six Flags Drive
(After the meeting, State Representative Lon Burnam and Downwinders will be hosting a lunch time de-briefing, location to be decided, so stay tuned.)
Look, we know this is a small victory. But state officials don't want to talk about how gas industry pollution may be making our local smog worse, even though there's evidence that it is.
That's exactly why we think we need to keep bringing it up.
Winning the right to hear a new scientific presentation on the connection between gas pollution and smog may not seem like much of a win, but it is when the Powers-That-Be don't want you to hear it.
We know that small victories like this can lead to larger successes.
In the 1990's the same state agency that's now denying gas pollution has any impact on DFW smog was saying exactly the same thing about the Midlothian cement plants.
It took lots of push back from citizens who knew better before we got the state to admit it was wrong.
Now, Ellis County is in the DFW non-attainment area and the cement plants have controls on them they would otherwise never have.
We need the same effort in 2014 to show the state is as wrong about gas industry pollution as it was about the cement plants.
Right now, Downwinders is the only group committed to organizing citizens around clean air issues in DFW.
But we just lost a funding source that was critical to us and we need your help to keep the pressure on. This money paid for staff work in the field.It's very easy to give securely online here, or you can send checks to our P.O. Box at the bottom of the page.
We really need your help. Thank you.