Nitrogen Oxides
Summer Isn’t Coming, It’s Here. Ozone Season Arrives with a Vengeance.
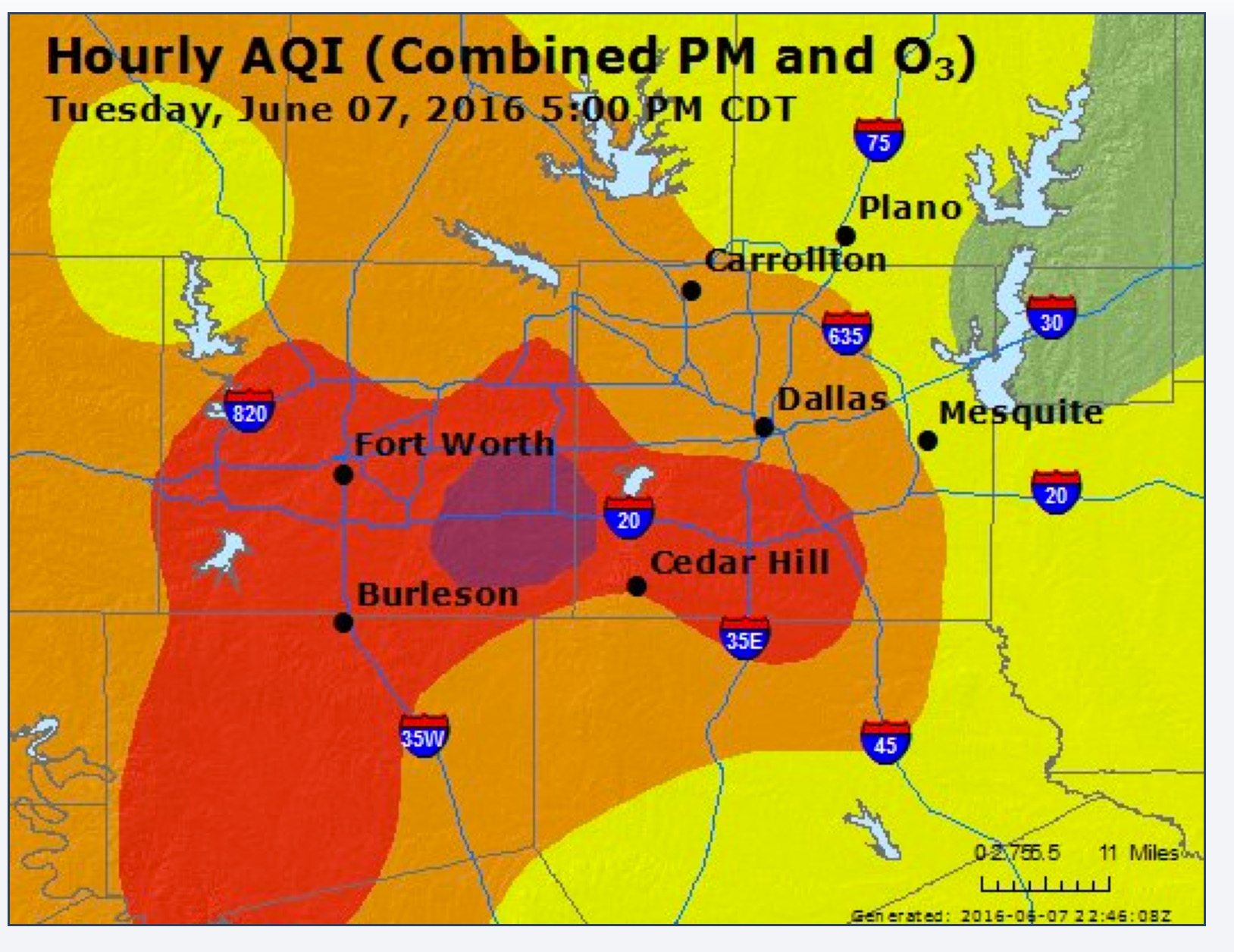
 Yesterday was the single worst day for DFW smog in the last three years.
Yesterday was the single worst day for DFW smog in the last three years.
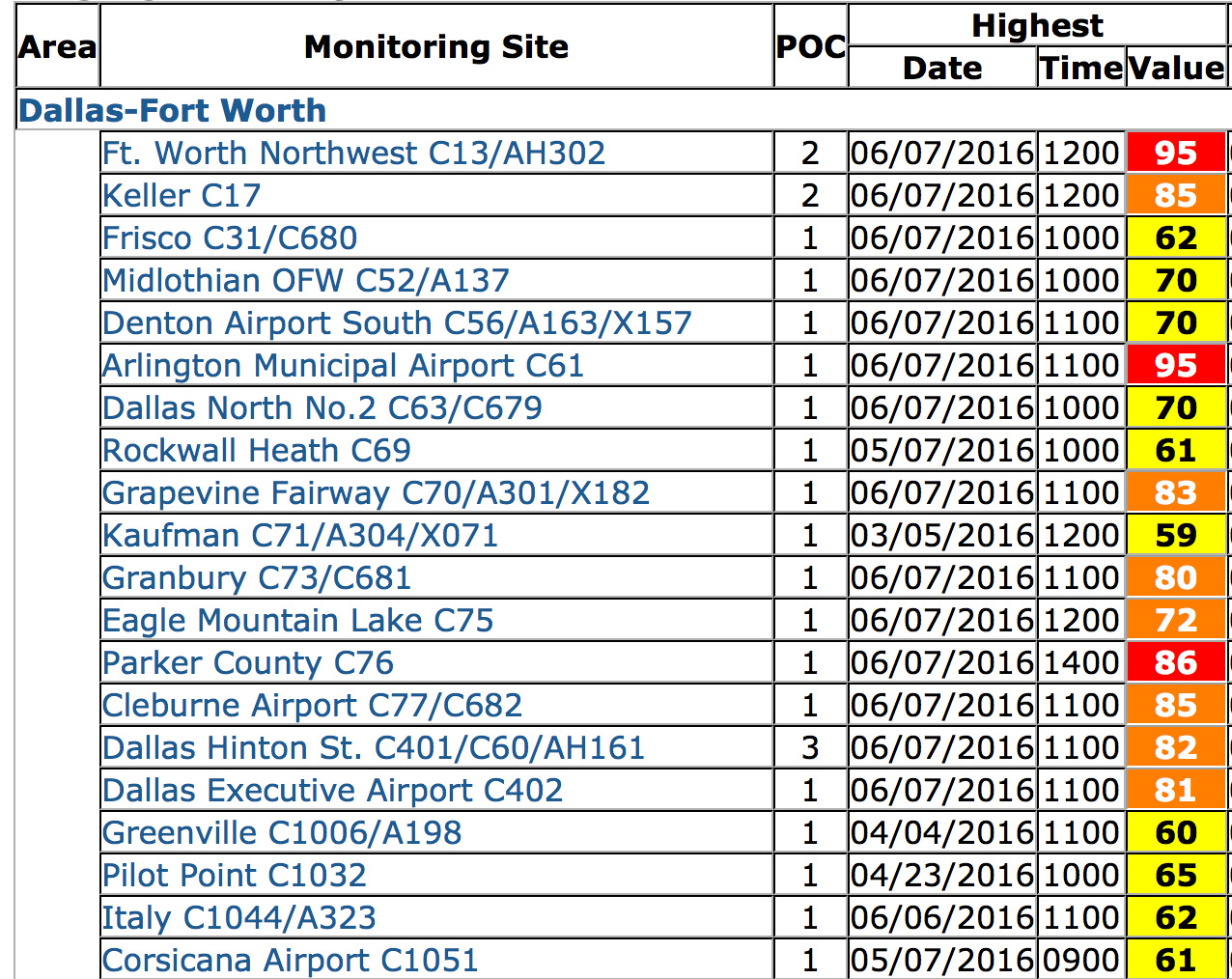
Seven monitoring sites stretching from central Dallas to Weatherford saw hourly averages of 90+ parts per billion. Three sites in Arlington, Northwest Fort Worth and Keller saw levels reach 100 + ppb. Two of those sites saw hourly levels climb to 113 ppb. To give you some idea of how bad that is, the original dreadful, obsolete standard during the 1980's and early 90's was 125 ppb in a single hour. We probably came within an hour or two of reaching a level of air pollution at not one, but two sites yesterday that would have exceeded a 40-year old smog standard.
14 out of the 20 DFW monitors recorded average ozone "exceedences" that violated the current 75 ppb 8-hour standard (what you see above). Two sites saw 8-hour averages of 95 ppb, the worst showing since September 2013.
It became a hazard to breathe for hundreds of thousands, maybe millions of DFW residents, yesterday afternoon. South Arlington residents experienced unhealthy levels of air pollution from 12 noon to 7 pm. In Keller it was 2 to 7 pm.
The good news? It could have been worse. The only thing preventing even higher numbers was the changing wind direction in mid-day. Monitors located in Dallas were recording high smog levels in the morning and lunchtime from northerly winds, but then they turned east and the pollution headed west, raising smog levels across broad swaths of Tarrant, Johnson, and Parker Counties. Had the wind been coming from the east all day, you would have seen the numbers those monitors reached at 2 -5 pm happen sooner, with more room to grow.
Wednesday also looks to be a bad day, as does the rest of the week of full-bore summer sunshine. Bad as they were, none of yesterday's exceedences actually count as a Clean Air Act violation…yet. It takes four bad days where the 8-hour average exceeds the 75 ppb standard over the course of the ozone season to make a violation. Regulators only use the fourth highest smog level recorded at each site to determine the annual average and whether an area is meeting the Clean Air Act standard (you can keep track of those here). Yesterday, nine monitors recorded their first exeedence of the year. Only three more to go.
However, the region's current reigning bad air champ, the Denton airport monitor, uncharacteristically remained out of harm's way and saw levels barely above the 75 ppb standard in mid-afternoon. It'll have it's chance. Summer is only beginning.
 Tuesday's smog attack put an exclamation point in front of next Wednesday's Dallas City Council scheduled vote on Councilwoman Sandy Greyson's air quality resolution rejecting the current state plan – ain't it working out swell!? – in favor of a plan to eliminate days like yesterday.
Tuesday's smog attack put an exclamation point in front of next Wednesday's Dallas City Council scheduled vote on Councilwoman Sandy Greyson's air quality resolution rejecting the current state plan – ain't it working out swell!? – in favor of a plan to eliminate days like yesterday.
Greyson's resolution requesting a new and better clean air plan, as well as the staff presentation that provided background information, can be reviewed here. It's similar in content to one passed earlier in May by Dallas County.
Supporters can sign-up to speak for 3 minutes each when it comes up on the agenda and as always, we'll have plenty of lapel pins with the DFW Clean Air Network logo on them so you can non-verbally support the resolution as well.
If you want to speak at the Council meeting in favor of clean air, please contact the City Secretary beginning at 8:15 am tomorrow, Thursday, June 9th at (214) 670-3738 to reserve a 3-minute speaking slot or Item #12 on the "consent agenda."
Consent agendas are tricky things. They require complete unanimity among all 15 council members and are usually reserved for the most benign, non-controversial subjects. So at first glance, it's a good thing our resolution is on the list because it implies support from all 15 members.
But, and it's a big but….any member who doesn't agree it should be on the consent agenda can ask that it be taken off and placed in the "Items for Individual Consideration" bin – kind of like going to the back of the line and waiting for all the other business to get done before re-visiting the matter.
If there's industry opposition, or any opposition for that matter, it would give a council member an excuse to take it off the consent agenda and send it to the back of the line in hopes us cooling our heels and losing speakers as the day wears on. And it only takes one council member disagreeing to do so. This is why we need you to send emails to ALL 15 council members.
Since it's on the consent agenda, at least for now, it'll be among the first orders of business next Wednesday. Supporters need to show up at 9 am sharp.
Dallas passing this resolution would mean that the most populous city in the DFW "non-attainment area" for smog is rejecting the anti-science "do-nothing" approach of the State and demanding a better strategy to actually clean up chronic air pollution.
That's exactly the kind of statement local governments have to send EPA in order for the federal agency to screw-up enough courage and reject the current state proposal in favor of something better.
And after yesterday, is there anyone outside of Austin who believes we don't need something better?
Dallas City Council Clean Air Vote
Wed. June 15th 9am
Dallas City Hall 1500 Marilla
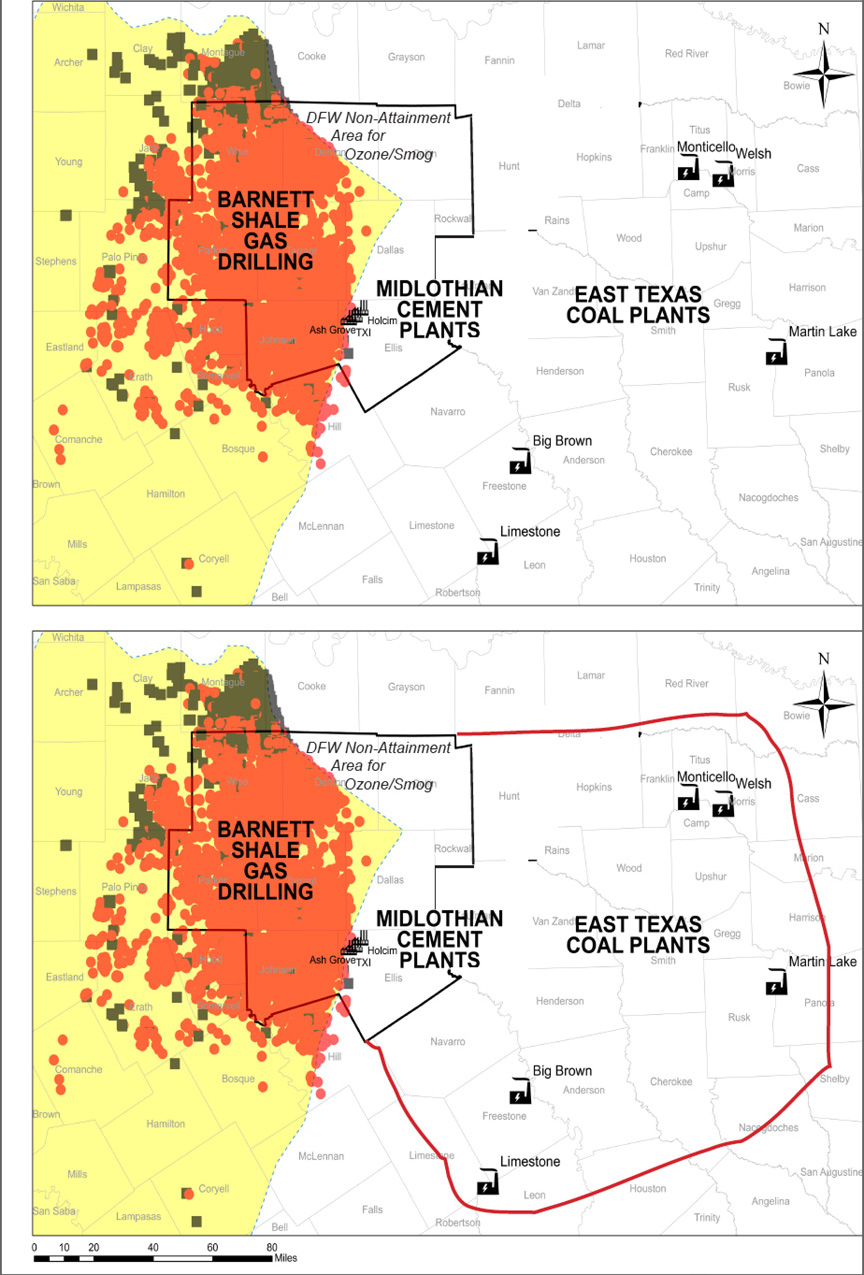
Why a small variance could mean a big increase in DFW smog
Thousands of gas wells, pipelines, storage tanks, compressors, and other pieces of infrastructure in oil and gas patches, which individually don't emit the huge volumes of air pollution coming from a single cement kiln or a coal plant can, when combined, easily total tonnage larger than both.
And that's what has happened in DFW over the last decade. As the Barnett Shale boom crept further into the region's "non-attainment" area" for smog, all the air pollution from all those thousands of individual sources begin adding up and having an impact on air quality.
While other large sources were actually decreasing their pollution, the oil and gas sector was going the opposite direction. It ballooned. To the point where it's now the fourth largest category of air pollution in that "non-attainment area." The three sources that outrank it? 1. All vehicles on the road. 2. All vehicles off-the-road, and, 3."area sources" a catch-all term including everything from backyard BBQs to small paint shops, and probably some oil and gas sources itself. Oil and Gas air pollution is, by volume, now the largest source of industrial air pollution in the North Texas area, exceeding the Midlothian cement kilns, local power plants (now all gas-fired), and large manufacturing plants like the GM truck and SUV factory in Arlington. Only the East Texas coal plants emit more and their 90-100 miles outside the nonattainment boundary (another problem that needs fixing).
At the same time oil and gas air pollution rose from Barnett Shale development, DFW smog levels, which had been declining, began to plateau. For a decade now the annual smog average has hovered on either side of 85 parts per billion (ppb) – the obsolete 1997 standard that we were supposed to reach in the early Oughts. We were at 86 ppb of smog in 2008 and we're now at 83 ppb.
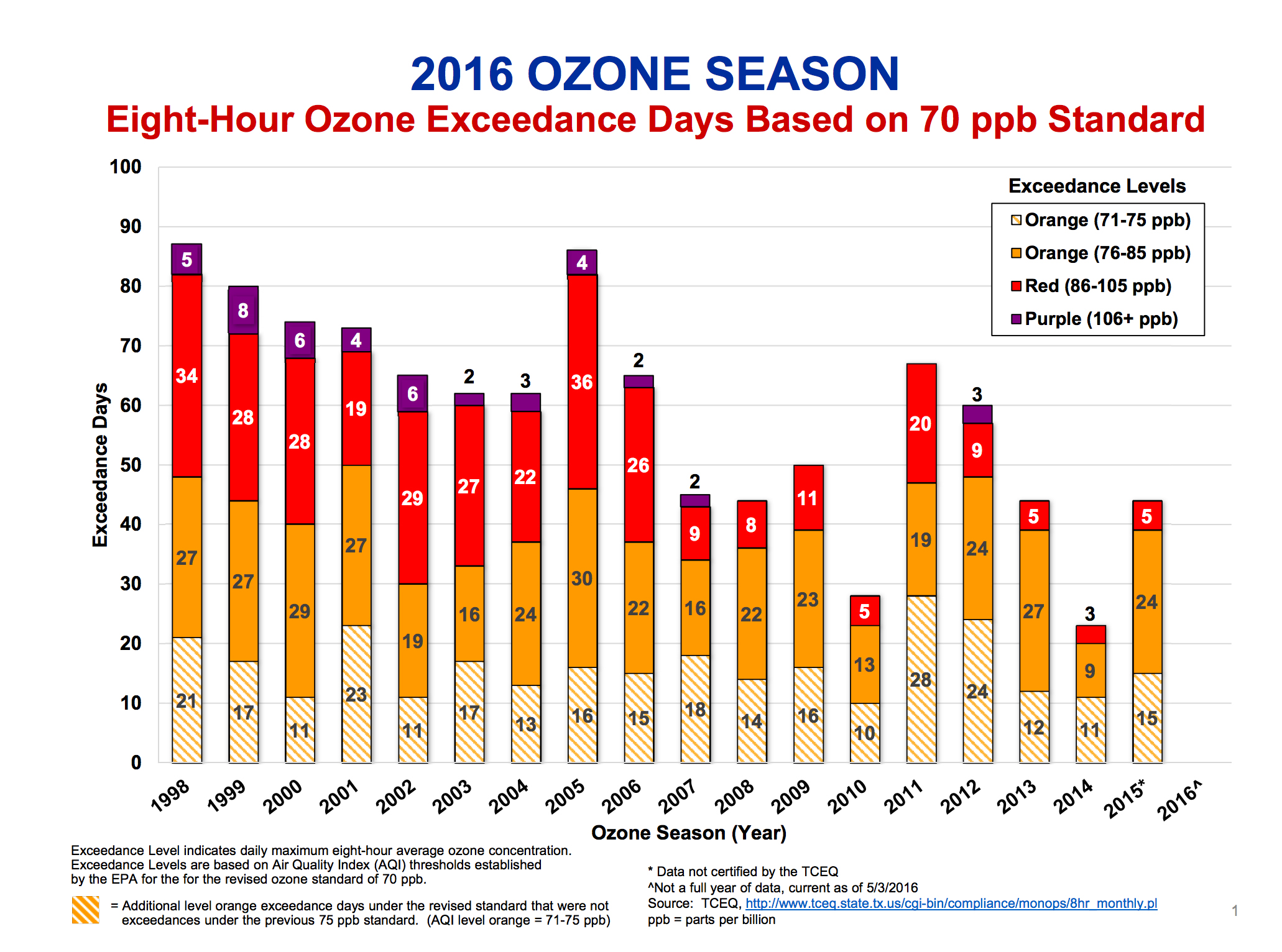
Look at the chart below, generated by the North Texas Council of Governments. In 2007 DFW had 45 "exceedence days". In 2015, DFW had 44 "exceedence days." There's a very good case to be made that oil and gas air pollution has prevented DFW from making the kind of air quality progress it might have otherwise made without that burden.
For the last five years, the State of Texas has been on a mission to deny any link at all between the oil and gas industry in the Barnett Shale and DFW smog. It's gone out of its way to hide the real volumes of pollution emitted by these sources, as well as avoiding or downplaying the significance to regional air quality of decreases in that pollution. That's not hyperbole, it's the record.
In looking ahead with its proposed DFW air plan now in the pipeline, the State has predicted that a drop in the number of new wells in the Shale will equal a drop in the amount of air pollution coming from O&G sources. Sounds logical doesn't it? Yet the industry's own text books say that it ain't necessarily so.
A drop in new wells is the tip of the O&G iceberg in DFW. Just because there were no new wells drilled last month doesn't mean there's no new pollution being released this month. Some 20,000 wells, almost 1000 large compressors, untold thousands of smaller compressors, millions of gallons of storage capacity, miles of pipelines – these all continue to operate and emit huge amounts of air pollution 24/7.
And when production-per-well drops, and the densest parts of the patch begin to play out, as is occurring now in the Barnett, investors don't usually go with the flow. They want to increase the flow. And so they install more "lift compressors" to squeeze every last molecule of gas they can out of a well. These compressors, powered by gas or diesel, increase air pollution. Not by a lot by themselves, but when you start putting them together, by the thousands, then yeah, they have an impact. And so, even when O&G production is declining, you can have increases in O&G air pollution.
Downwinders at Risk and the Sierra Club made this argument in our comments about the state's plan, providing sources from industry to show exactly how this has taken place plenty of times before. We told Austin it was underestimating the impact of O&G air pollution – again. The State dismissed our concerns and said no problem.
Which brings us to Mansfield in Tarrant County, scene of the last pre-HB40 gas ordinance fight in the state.
Last week, there was a small headline in the Fort Worth Star-Telegram a lot of people probably ignored. It concerned a routine variance to zoning code being requested by (notorious) gas well operator EagleRidge. At issue was whether the company could keep using gas powered lift compressors instead of electric-powered ones as the city's year-old ordinance required. EagleRidge made an argument in favor of the variance which sounded very familiar to some of us….
EagleRidge first noticed a dramatic decline in natural gas production at 15 of its wells last year, as it went from 8 million to 2.5 million cubic feet of natural gas per day. Low natural gas prices, trading about $2.10 per British thermal unit Monday, could make the wells economically unfeasible, according to Mark Grawe, executive vice president of EagleRidge.
That prompted EagleRidge to try a new strategy, using small gas lift compressors that increase production on the wells. Last year, Mansfield granted a six-month variance to allow the compressors on a trial basis.
Grawe said the compressors have already improved production on three of the wells, but addition tests are needed on EagleRidge’s other wells.
Eagle Ridge got its variance. And besides the three lift compressors it's operating on the site now, at least two to three more or expected, and all of those might one day be replaced by two giant-sized compressors. And, Eagle Ridge told the council, it's experience in Mansfield will be repeated at "hundreds of wells in Southeast Tarrant County" that have also seen declining production.
Eagle Ridge's ratio was approximately one lift compressor for every two wells. There are 15 wells as part of this one variance, "hundreds" in SE. Tarrant County waiting their turn, and 20,000 more throughout the part of the Barnett Shale in the DFW non-attainment area for smog. That's thousands and thousands more lift compressors emitting lots more air pollution even as Barnett Shale production is declining – and most will be located in cities or counties where there's not even a requirement for electric power to get a variance from. In other words, this is exactly the scenario Downwinders and the Sierra Club warned about in their comments, but which the state dismissed.
That's in addtion to the thousands of lift compressors already located in DFW, the exact number and location of which are unknown to EPA and Texas because they don't require indivdual permits. Austin "estimates" the total amount by using, you guessed it, production numbers. Here'a map from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality guestimating where all those existing lift compressors are now:
If you think there might be a correlation between O&G pollution and stagnating DFW smog levels, what's the answer? It's pretty straight-forward. Stricter emission standards for all equipment, leak detection, electrification of large and small compressors. These are all things the industry is either doing in fits and starts in North Texas and elsewhere, or being required by the new EPA methane rules, but they're not being applied across the board in the Barnett Shale, or they don't apply to existing facilities, or both.
Who's going to make that happen? Local governments were doing some of it – up until the passage of HB40. For example, Dallas, Mansfield, and other cities required electric-powered compressors and state-of-the-art leak detection. But that's off the table, as is any action from Austin. That leaves the EPA as the one regulatory entity that could, if it wanted, impose uniform emission standards on all O&G facilities in the 10-county non-attainment area, including Denton, Johnson, Parker, Tarrant, and Wise counties. It could do so as part of it's own anti-smog plan for the region.
But before it can start writing its own plan, the EPA must first reject the state's. And for it to do that we must give the EPA the political support it needs to stand up to the backlash from Austin you know will come. Thus the need for resolutions from DFW cities and counties asking the EPA to reject the State plan. Thus the need to show-up this coming Monday morning at City Hall and support an effort by Dallas City Councilwoman Sandy Greyson to have the City of Dallas join Dallas County in calling for EPA intervention in DFW air quality: 9am Room 6ES, Quality of Life Committee.
Don't let the Mansfield variance become the regional template.
Next Week: Two Events Put DFW Greens on the Front Lines of Change…Again
GET OUT OF YOUR RUT AND JOIN THE FIGHT!
MONDAY, MAY 23rd
9am Dallas City Hall
1500 Marilla Downtown Dallas
Room 6ES (6th Floor, South)
Dallas City Council's Quality of Life Committee Considers/Votes
on the DFW AIR QUALITY RESOLUTION
WEDNESDAY, MAY 25th
7:30 am – 10 am
Morton Meyerson Symphony Center
2301 Flora Downtown Dallas
EXXON – MOBIL SHAREHOLDERS MEETING
MONDAY, the 23rd
Dallas could follow Dallas County and be the second North Texas local government to say they want the EPA to reject the state's air plan for DFW.
Think about that. In "Red" Texas, local governments are asking the EPA to intervene and give them cleaner air because of their own State's failure to do so.
Just like our Green Cement Campaign, and our Dallas Drilling Ordinance, an EPA- written air plan for DFW would be setting an important national precedent from right here in the Belly of the Beast.
 Sandy Greyson is Chair of this Committee, which includes:
Sandy Greyson is Chair of this Committee, which includes:
Tiffini Young
district7@dallascityhall.com
Mark Clayton
mark.clayton@dallascityhall.com
Philip Kingston
Philip.Kingston@dallascityhall.com
Adam McGough
adam.mcgough@dallascityhall.com
Rickey Callahan
rick.callahan@dallascityhall.com
Please email these council members and tell them you support Ms. Greyson's air quality resolution.
This is a Committee hearing. There is no public comment allowed, but public shows of support are encouraged and the council members may ask questions from experts in the audience.
We'll have plenty of DFW CAN BREATHE CLEAN AIR lapel pins. Feel free to wear one and/or show your support through other means.
If this Committee votes in favor of the resolution, it'll probably go to the full council for a vote in June.
Show up Monday and let the City Council know you care about clean air.
WEDNESDAY, MAY 25th
The national spotlight will be on Dallas again on Wednesday as Exxon-Mobil, our own hometown corporate Poster Child for climate change denial, will be holding its annual shareholders meeting in downtown Dallas.
Because of new revelations the company secretly knew about the dangers of climate change in the late 1970's, but continued to publicly deny the phenomenon, this year's annual meeting in Dallas is especially important. More than 500,000 people across the United States have called on the Department of Justice and State Attorneys General to look into Exxon's cover-up. So far, Massachusetts, U.S. Virgin Islands, New York, and California have launched official investigations.
350.org, the Sierra Club and other national groups have been leading the call to show up at the Exxon-Mobil meeting and make sure the company is held accountable for its past and current behavior.
Most of us never get to go to international conferences and protests like Paris last year, or even ones in DC or New York. But next Wednesday the 25th, the epic global fight against self-destruction comes to your own doorstep.
What are you going to do?
Don't let your activism end once you go off-line. Turn your "like" into an action.
Show up Wednesday morning bright and early and represent.
They'll be coffee and food. They'll be banners. They'll be media.
But we need you to be there too.
Help us show the rest of the world that we can do our part.
Help us keep the pressure on.
Help us win.
WEDNESDAY, MAY 25th 7:30 am – 10 am
Morton Meyerson Symphony Center 2301 Flora Downtown Dallas
Bring the East Texas Coal Plants into DFW’s Smog “Non-Attainment Area” and See How Long They Last……
 Want the Coal Plants to Face the Kind of Regulation
Want the Coal Plants to Face the Kind of Regulation
They've Been Avoiding for Decades?
Click here and send a formal comment letter demanding the coal plants
be included in the new DFW non-attainment area for smog.
Even as we're all waiting to see what EPA decides to do about the current Texas air plan for DFW under the current 75 ppb ozone standard, the regulatory process is gearing-up to administer the new 70 ppb standard.
One of the things which must be decided by the EPA are what geographical boundaries to use for the new standard when it comes to the DFW airshed and its chronic smog condition. Should they stick with the current 10-County configuration or should it be different and/or more inclusive?
The history of DFW's smog fight is a lengthy chronicle of bringing new counties into the fold despite official resistance. Originally, the DFW non-attainment area was only Tarrant, Dallas, Collin and Denton. Then Rockwall, Parker, and Johnson Counties came in because of their commuter traffic.
Downwinders had to petition the EPA to bring Ellis County and its cement industrial complex into the non-attainment area early in this century after being told repeatedly by state officials that its pollution had no impact on DFW air quality.
More recently, the state argued against the inclusion of Wise County, despite its huge inventory of oil and gas pollution, population of commuters, and more than likely, the highest ozone levels of anywhere in North Texas. EPA decided to bring it in anyway.
We're once again at a crossroads, and it could be the most significant one in a decade.
 New evidence shows the huge impact the East Texas coal plants have on DFW air quality. Every scenario run by the UNT Engineering Department with the state's own DFW air computer model as part of Downwinder's Ozone Attainment Project demonstrates there's no more effective smog fighting strategy than reducing or eliminating the pollution from these coal plants.
New evidence shows the huge impact the East Texas coal plants have on DFW air quality. Every scenario run by the UNT Engineering Department with the state's own DFW air computer model as part of Downwinder's Ozone Attainment Project demonstrates there's no more effective smog fighting strategy than reducing or eliminating the pollution from these coal plants.
In fact, with a few other measures within the DFW area itself, controlling or eliminating their emissions could bring us in compliance with the 75 ppb standard, something that's not likely to happen otherwise.
Why is it so important to officially bring them into the DFW non-attainment area? Because major sources of pollution like coal plants are regulated differently inside than they are outside the area.
Right now, many DFW businesses are having to pay to operate and maintain pollution control equipment although most emit a tiny fraction of the pollution coming from the coal plants. That's because they're located in one of the ten counties in the DFW non-attainment area. They're held to a higher standard of control than their peers doing business outside those ten counties.
On the other hand, despite their large contribution to DFW's chronic ozone problem, the East Texas coal plants remain untouched by the same regulations and are not held to that higher standard. What sense does that make?
As much sense as it made to keep the cement plants out. As much sense as it made to try and exclude Wise County.
As per usual, the EPA is letting the state have first crack at defining a new DFW smog zone. The state has decided to leave the boundaries the way they are.
 Now, it's your turn to comment on that state decision, and tell Austin and the EPA – which will review the State's recommendations – what you think needs to happen.
Now, it's your turn to comment on that state decision, and tell Austin and the EPA – which will review the State's recommendations – what you think needs to happen.
The state is accepting comments on its decision until April 15th. This time, you can send your comments directly by e-mail instead of having to go through the official Texas Commission on Environmental Quality website
If you want to use our ready-to-send letter, all you have to do is CLICK HERE , sign the letter and add your own comments if you want. Then one more click and it's on it's way to Austin.
If you want to write your own comments:
EMAIL: kristin.patton@tceq.texas.gov
SNAIL MAIL: Kristin Patton, MC 206, State Implementation Plan Team, Office of Air, Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, P.O. Box 13087, Austin, Texas 78711-3087,
FAXED:(512) 239-6188.
All comments should reference "2015 Ozone NAAQS Designation Recommendations."
DFW One of Only Ten Areas Nationwide Not Expected to Meet New Smog Standard by 2025
 There was a lot of coverage of last week's announcment of a new, more protective national smog standard by EPA. Most of it centered on the reaction by both sides that it was either not enough progress (public health advocates), or Western Civilization was about to collapse under the weight of all the controls necessary to meet the standard (National Chamber of Commerce, et al.).
There was a lot of coverage of last week's announcment of a new, more protective national smog standard by EPA. Most of it centered on the reaction by both sides that it was either not enough progress (public health advocates), or Western Civilization was about to collapse under the weight of all the controls necessary to meet the standard (National Chamber of Commerce, et al.).
But if you read deeper into the articles, many of them mentioned computer modeling EPA had already done that demonstrated, given current trends, only 14 counties, representing 10 separate areas, wouldn't be able to meet the new standard by the target year of 2025. Unfortutantely, none of those articles mentioned which 14 counties, or which 10 areas.
Now, given all that you already know about our state and regional track record for meeting clean air deadlines, your first question might be: how many of those are in Texas? We'll give you a minute or two to start a pool and pick a number….
And the answer is: Three. Brazoria and Harris Counties in the Houston "non-attainment area" for smog, and Tarrant in DFW's non-attainment area. (The ten areas are: Baltimore, Dallas-Fort Worth, Denver, Fort Collins, Houston, Louisville, Milwaukee, New Haven, New York, and Pittsburgh).
Of course, for the purposes of regional smog record-keeping, EPA doesn't separate Tarrant County numbers from Dallas County, or Denton County, or any of the other nine counties in the non-attainment area. If one monitor is out of compliance in the area, the whole region is considered in violation. So EPA is conceeding that both DFW and Houston will still continue to be in continual violation of the Clean Air Act for another decade.
This is discouraging but not surprising. The State refuses to put new-generation controls on large major polluters like the Midlothian cement plants, East Texas coal plants, and gas production facilities, while painting the rosiest scenarios with its own modeling.
But this new revelation means it's that much more important to get EPA to override the state and act now to include controls on those major polluters, while the current smog plan is in the pipeline. It may be the only chance we have in the next 5-10 years to adequately address these sources. This can only be done if the EPA decides to revoke Texas' authority to write and implement these plans – to commit to a Federal Implementation Plan of its own.
PLEASE….
1) Sign our Change.Org petition urging the EPA to reject the state's clean air plan for DFW and substitute one of its own, and
2) Send an e-mail to the Chief EPA administrator in Washington and the Regional Administrator here in Dallas saying you want them to take responsibility for a new DFW air plan.
Thanks.
US Cement Plant Using SCR Pollution Control Device Achieves 80% Reduction. Texas Says It’s Still Not Feasible.
 EPA has released the results of the first test of a full-scale Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit on a US cement plant and the numbers look good.
EPA has released the results of the first test of a full-scale Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) unit on a US cement plant and the numbers look good.
As many of you know, SCR is just an industrial-sized version of the catalytic converter in your car. It can capture up to 90% or more of the smog-forming pollution from a cement plant. In use on cement kilns since 2001, there are at least a half a dozen cement plants in Europe that use SCR successfully, but the technology has been slow to arrive in the US because of regulatory laziness and industry resistance.
But after 15 years, that's finally changing.
in 2013, LaFarge Cement entered into a consent decree with the EPA and the US Justice Department as part of a settlement over a string of environmental violations, including excessive smog-forming Nitrogen Oxide (NOX) emissions. As part of that settlement, Lafarge was to retrofit its Joppa, Illinois "dry process" cement kiln with an SCR unit, record its effectiveness during stack testing, and report on the results of those tests by 2015.
This last week, those results were finally made available by EPA and they show SCR was able to reduce NOx by 80%.
That's approximately twice as effective as SNCR technology, (Selective NON-Catalytic Reduction), the current pollution control device for NOx most often used in U.S. cement plants.
Moreover, according to LaFarge, "the SCR control technology performed well and no operational problem was encountered."
In fact, the control technology worked so well, LaFarge is now getting a permit from the Illinois state environmental agency to operate SCR past the EPA-mandated settlement period.
But while LaFarge is getting its SCR permit, Holcim's Midlothian cement plant has already applied and been granted one by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality for construction and operation of its own SCR unit. It should be up and running by this time next year.
So that makes two U.S. cement plants with permits to run full-scale SCR units. One that was forced into the choice by EPA and now wants to keep using it, and another voluntarily adding it.
But according to the TCEQ, even though it gave a permit to Holcim to install SCR, and even though Holcim's SCR unit will be operational in a year, and even though the LaFarge test was a success, and even though SCR has been used for 15 years by European cement companies – SCR is "not economically or technically feasible." That's exactly what the Commission said in response to comments from both citizens and the EPA in its new clean air plan for DFW a couple of months ago.
That's right. One the one hand the Commission has granted a permit to Holcim to build an SCR unit in its own backyard, and on the other it's still calling the technology infeasible. It's the stuff of Monty Python sketches.
And that's not all. There is no mention of the Holcim Cement SCR permit in the TCEQ's own official arguments against SCR in its DFW clean air plan. Not one. Since Holcim's building of an SCR unit would tend to empirically disprove TCEQ's contention that the technology wasn't practical, the state just pretends it's not happening. As with climate change and smog, any facts that conflict with the pre-determined ideologically-correct premise must be ignored.
Presumably, Holcim is building the SCR unit because it's made the business judgment that the technology is not only both economically and technologically feasible, but beneficial to the company's bottom line. Presumably LaFarge is pursuing a permit for its SCR unit because it has made the same practical decision. Yet, in a strange role reversal, a Texas state government agency is now telling business it's making the wrong choices. It's overruling the industry's decision to reduce pollution through SCR use by saying "not so fast."
This is how bad its gotten: the Texas approach to clean air is now so backwards that the cement industry is more aggressive about reducing pollution than Austin.
So how many U.S. cement plants have to be operating with SCR before the State of Texas concludes it's a feasible technology? Two? Four? A Dozen?
Fortunately, the TCEQ isn't the last word on this. The Clean Air Act says any and all reasonably available technology must be used on major pollution sources like the Midlothian cement plants when a clean air plan is being drafted. TCEQ hasn't done that. We think they're breaking the law. There are signs that EPA thinks so as well.
EPA is ultimately in charge of enforcing the Clean Air Act, and if it doesn't do it correctly, then the courts step in.
The best hope for safe and legal air in DFW is for EPA to rigorously enforce the law. The State of Texas will not do so. If you agree then please take a minute to:
1) sign this petition to EPA
2) Send this e-mail to EPA
Thanks.
Going Backwards: DFW’s Annual Smog Average Went Up Twice in Two Days Last Week
 State officials and industry PR types thought they'd caught a break last summer when two things produced a much lower annual smog average, called a "Design Value."
State officials and industry PR types thought they'd caught a break last summer when two things produced a much lower annual smog average, called a "Design Value."
Since it's a three-year rolling average of smog numbers, past years roll off as new ones come on. Smog numbers from 2011 that had been so high they'd sent the average soaring, were finally rolling off and wouldn't be included in the average.
Second, unusually cooler temperatures and rain kept a new round of numbers lower. Combined, these factors resulted in a significant decrease in the smog average for 2014.
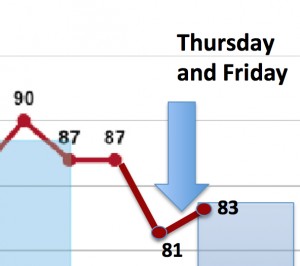
But in 2015, a more typical summer, or at least August, is bringing the average back up (Over 60% of the 100 highest recorded levels of smog this summer occurred in the last 30 days). Smog levels are higher across the board this year than last. There are more monitors recording more "exceedences" of the national smog standard. Leading them all is the Denton monitor, which saw ozone levels rise on Thursday and then skyrocket on Friday. The numbers were so high on both days they moved the needle of the annual smog average, the DFW Design Value, up from 81 to 82 parts per billion (ppb) on Thursday and up to 83 ppb on Friday. The standard is 75 ppb.
Even though Houston has recorded higher smog numbers than DFW this year, 2014's lower smog numbers was even more anomalous for that city than for North Texas. Last year's much lower numbers in the Bayou City are canceling out this year's much higher numbers. So that in 2015, DFW's Denton monitor's annual average of 83 ppb is the highest in the State of Texas.
And that means that according to the official accounting of the Clean Air Act, DFW has dirtier air than Houston. And not for the first time.
It also means we're rolling backwards in terms of air quality progress. With at least a whole month of "ozone season" to go, DFW's smog average is now only a little lower than it was in 2009. It would only take one or two more bad days to raise the average again.
This is the second time in four years that DFW's smog average has increased during the implementation of a state clean air plan for the area. Neither plan required new controls on large industrial polluters significantly contributing to the problem, like the gas industry, East Texas coal plants, and Midlothian cement kilns. There may be some connection there.
Given the state's stellar two decade-old track record of never meeting a clean air plan deadline, its latest plan was always likely to fail. But a federal court roll back of the deadline to get to the 75 ppb standard at all DFW monitors, from 2018 to 2017, plus these new 2015 smog numbers, make it DOA in the real world.
However, in the regulatory world governing these things officially, the plan is still being reviewed by the EPA and, believe it or not, could get approved if citizens don't make a big stink.
That's why you need to sign our Change.org petition to EPA to reject the state's plan and send an email to EPA officials requesting they write a new clean air plan instead of the state of Texas.
Many clean air advocates cautioned that 2014 should be seen as a outlier, and this summer is justifying that caution. If the experts are right, climate change will mean future summers will be more like 2011 than 2014. We've got to have a more realistic approach to the goal of safe and legal air. The State of Texas will not provide that. EPA can.
Expect Obama’s New CO2 Plan to Close Those Nasty East Texas Coal Plants? Don’t.
 By this point, most of you will have been inundated with opinions and factoids about what President Obama's new "Clean Power Plan" will and won't do about climate change. Bottom Line: while it sets a precedent and an emissions floor for the largest sources of CO2, it does so in a way which turns out to be not so challenging for most states – including Kentucky deep in Coal County.
By this point, most of you will have been inundated with opinions and factoids about what President Obama's new "Clean Power Plan" will and won't do about climate change. Bottom Line: while it sets a precedent and an emissions floor for the largest sources of CO2, it does so in a way which turns out to be not so challenging for most states – including Kentucky deep in Coal County.
That's also true for Texas, where besides being Ground Zero for the fracking boom, we also have plenty of wind power and some solar. According to the EPA, the state must cut an annual average of 51 million tons of carbon to reach its target, a reduction of about 21 percent from 2012 emissions. We're well on our way to achieving most of that reduction with current or planned wind, gas, hydro, and solar. (In what might be a first concession that natural gas shouldn't be a long-term "bridge fuel," some analysts think tweaks performed by EPA prior to the Plan's release give more incentives to adopt real renewables earlier rather than leaning on gas in the interim.)
This is mostly good news. We want the wind and solar economies to grow. The trade-off is that, under Obama's Clean Power Plan, the rise of these technologies and their emissions reductions lets the obsolete East Texas coal plants off the hook because you don't need them to close to meet your CO2-cutting goals.
Five of those obsolete coal-fired power plants surround DFW's eastern side in a half circle (Big Brown, Martin Lake, Monticello, Limestone, and Welsh). They are, without a doubt, the worst examples of fossil fuel-generated pollution in Texas. They're huge emitters of Mercury, Particulate Matter (PM), Sulfur Dioxide (SOx), and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx).
These five East Texas coal plants are projected by the state to still be releasing 150 tons a day of smog-forming NOx pollution in 2018. Because of wind direction and volume, that pollution has a very large impact on DFW air quality – probably more than any other single phenomenon. We need those coal plants to either modernize or close ASAP to help solve our chronic smog problem. But from the initial survey of the policy, the Clean Power Plan is not going to force that outcome.
While the Plan probably signals the end of any new coal plants any time soon, or at least none without CO2 solutions like sequestration or capture, the fate of existing coal plants, especially in a state like Texas, is more ambiguous. More likely, they'll continue to linger on, beneficiaries of friendly state-created policies designed to nullify the requirements of the Clean Air Act, like loosening their PM limits by magnitudes.
Now, you might think that a federal goal that's been mostly accomplished without doing anything new would be a no brainer in Austin, but there are increasingly fewer and fewer brains in Austin. Because the state's environmental agencies are now completely ideologically driven, common sense just isn't a factor anymore. Instead of asking "how can we best solve this problem?" the response is now to deny there's a problem at all and go about ginning up anti-federal hyperbole to better position yourself in the Republican Primary.
Consequently, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality is seriously considering not turning in a required state plan of how to get the reductions needed by the deadline of 2030. If the state doesn't submit one of its own, then the EPA would write one for them. This has the business community in Texas a little nervous, since they have a lot more influence here than in DC. But citizens, which kind of anti-climate change plan would you rather have Texas abide by – one written by a state agency that denies climate change is happening and is doing everything it can to obstruct policies to prevent it, or one written by a federal agency that's actually acknowledging the obvious and doing something about it?
Regardless of whose plan does what by when, the East Texas coal plants look to be able to ride this federal policy out thanks to an almost two-decade homegrown drive to open up the state to renewables. If we want these coal plants to stop causing problems for us, we're probably going to have to find other leverage points.
One of these leverage points is demanding the state of Texas follow the law and require the coal plants install modern Selective Catalytic Reduction controls as part of the new DFW clean air plan it submitted to EPA this summer for approval. SCR could reduce smog pollution from these plants by 90%. So far, Texas has refused to even acknowledge the need to do so. EPA has requested the state change its mind – without success.
If it wants to, EPA can reject the state's plan for not including these new controls on the coal plants. But we have to encourage them to do so – by petition, and by e-mail.
Consider the five East Texas coal plants the energy sector equivalent of the obsolete "wet" kilns in Midlothian that burned hazardous waste for 20 years. They're technological dinosaurs, on their last legs, but still churning out tons and tons of harmful air pollution as they plod their way to the bone yard. The Clean Power Plan insures they'll be the last of their kind, but it's not a silver bullet.
Ready to Fight Back and Win? Downwinders is about to launch its most ambitious campaign in years

Mercifully, the 2015 Texas Legislative Session is almost over. Since January we've seen cities stripped of their traditional zoning power over oil and gas facilities, citizens' ability to challenge new pollution permits further suppressed, and renewable energy sources singled-out for financial punishment.
But the circus leaves town on June 1, and shortly after that Downwinders at Risk will be gearing up for the largest clean air campaign we've taken on since our fight against hazardous waste burning in the Midlothian cement kilns.
It'll begin with the mid-summer release of the results of a years-in-the-making project that turns the tables on the recent trend to transfer all pollution decisions from local governments to Austin. For the first time, city and county officials in North Texas will have the power to do what, up until now, only state agencies could do.
We don't want to give away too much too soon, but this is by far the single most costly project we've ever sought funding for, and it will have an impact on every major industrial source of pollution affecting Dallas-Fort Worth air quality – the cement kilns, the oil and gas industry and the obsolete East and Central Texas coal plants. And It's being done in a way that makes its results unimpeachable by a hostile state government and industry.
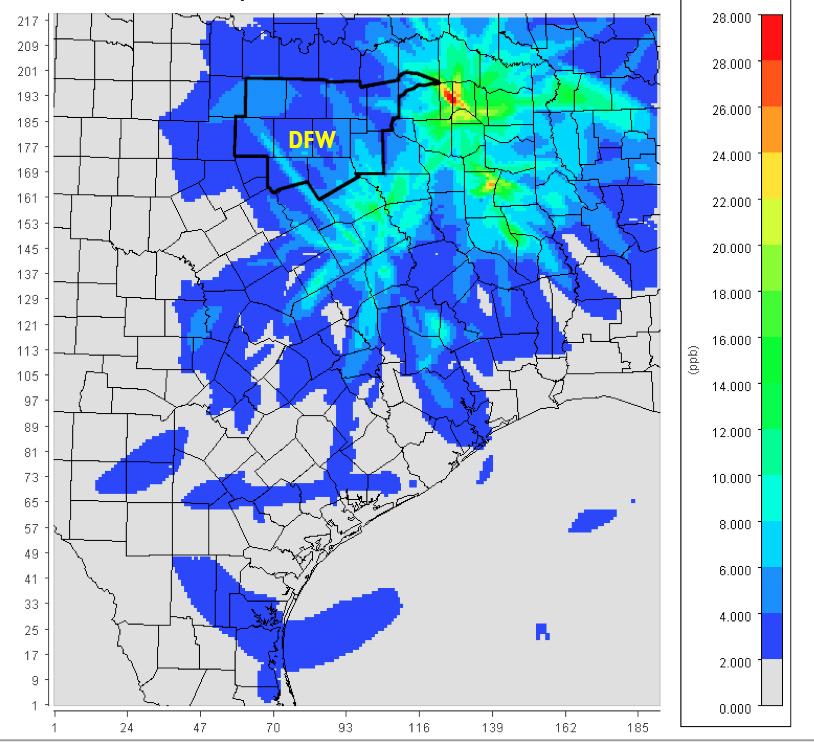
As a kind of sneak peak, below is a small sample of what we're talking about. It's a map of our half of Texas with the DFW metropolitan area outlined in black near the top. It shows the reach and intensity of smog pollution from the five coal plants closest to us. Even though they're 90 to over 100 miles away, they're still able to raise smog levels in central DFW by 4 to 8 parts per billion or more – a huge amount that could make or break our compliance with the Clean Air Act.
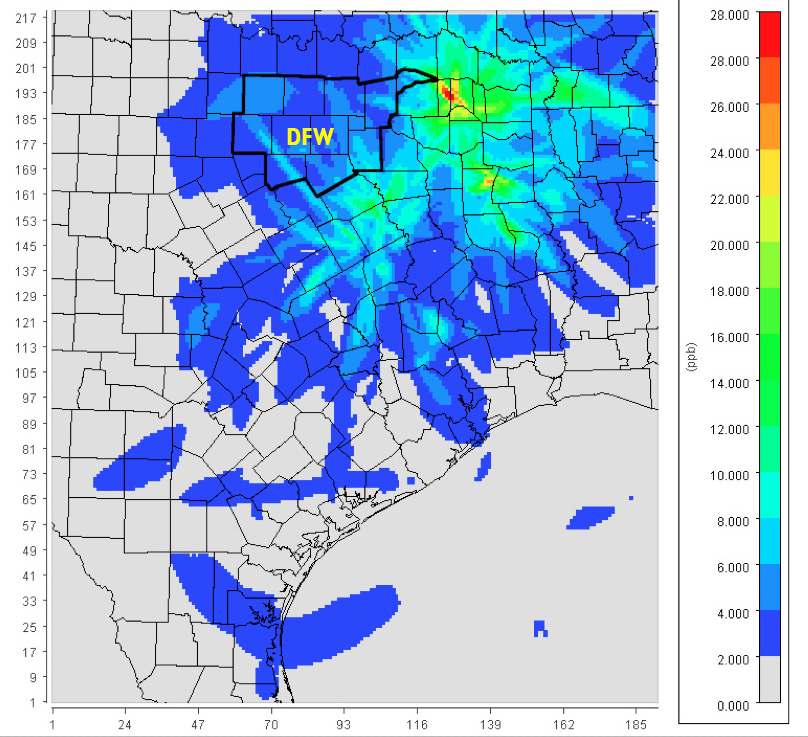 This is a map the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality has the ability to produce, but refuses to. Now, we have the same ability. And we can aim it at any large industrial source of pollution in the region. And we have.
This is a map the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality has the ability to produce, but refuses to. Now, we have the same ability. And we can aim it at any large industrial source of pollution in the region. And we have.
Moreover, the results of our study are being released in tandem with an associated project by Dr. Robert Haley and the University of Texas – Southwestern Medial Center. Together, they'll represent the opening salvos to a sustained, multi-organizational campaign to address DFW's chronic bad air problems.
Armed with this new evidence and having identified some chinks in the armor of the Status Quo, we see a chance to strike a powerful blow for cleaner air and citizen power. We see a chance to win a significant victory. We don't know about you, but after the last five months, we could sure use some victories.
That's not to say winning will come easy. It's still Texas. But we hope you'll agree that one of they keys to our long track record of success is picking the battles and the battlefields that give us better odds.
Every dollar you give goes to fight
for cleaner air right here in N. Texas
Even a Single Day of Air Pollution Increases Stroke Risk
 When environmental health advocates speak about the dangers of dirty air, the effects are often categorized as long term and cumulative. But the more scientists delve into the subtleties of the human body and what outside influences can do it, the more they realize that even short term exposures can be harmful. That's been especially true lately when looking at pregnant moms and the exposure to fetuses in certain stages of development. Not it turns out to true when looking at the other end of the age spectrum.
When environmental health advocates speak about the dangers of dirty air, the effects are often categorized as long term and cumulative. But the more scientists delve into the subtleties of the human body and what outside influences can do it, the more they realize that even short term exposures can be harmful. That's been especially true lately when looking at pregnant moms and the exposure to fetuses in certain stages of development. Not it turns out to true when looking at the other end of the age spectrum.
A new examination of 103 studies involving 6.2 million stroke hospitalizations and deaths in 28 countries published online at the BMJ (British Medical Journal) found that almost every type of industrial air pollution contributed to a higher risk of stroke. And the higher level of exposure to the pollutant, the higher the risk of stroke.
Increases in the levels of Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide, Carbon Monoxide and fine Particulate Matter were all associated with increases in strikes and hospitalizations. Not surprisingly, the strongest correlations were on the day of actual exposure, but the effects of PM, otherwise known as soot, were longer lasting. Missing from the list is ozone, or plain old smog, which studies have shown increases asthma and heart attacks on its own.
According to the report, strokes account for five million deaths worldwide every year and cause en even greater number of disabilities.
The lead author, Dr. Anoop Shah, from the University of Edinburgh, said that there was little an individual can do when there's a bad air day going on but stay indoors
“If you’re elderly, or have co-morbid conditions, you should stay inside,” he said. But policies leading to cleaner air would have the greatest impact, he said. “It’s a question of getting cities and countries to change.”