Not So Freindly Skies: Another Study Finds Airport Air Pollution Problems
 For the second time in as many weeks, a new study shows dramatic air pollution problems surrounding one of America's major airports. Last week, it was the fact that Particulate Matter was four to five times higher surrounding LAX, adding up to more annual pollution than more than half of the Los Angeles freeway system.
For the second time in as many weeks, a new study shows dramatic air pollution problems surrounding one of America's major airports. Last week, it was the fact that Particulate Matter was four to five times higher surrounding LAX, adding up to more annual pollution than more than half of the Los Angeles freeway system.
This time, it's Logan in Boston, where an epic, 14-year long effort by the Massachusetts Department of Health and Human Services shows that children living adjacent to the airport suffer respiratory problems at levels as much as four times higher than those who live further from from the runways. Adults living nearby are twice as likely to experience chronic obstructive pulmonary disease than their peers living in more distant Boston neighborhoods.
According to the study's authors, the findings are “statistically significant” and take into account pollution from vehicle traffic and socioeconomic factors such as smoking rates and poverty. It's the first research to try to explore specific health effects surrounding an American airport, relying on interviews with more than 6,000 adults, who also provided health information for more than 2,200 children in 17 communities within a 5-mile radius of the airport.and combined them with advanced air modeling data to estimate exposure to airport-related emissions.
In response, Airport officials and city leaders are working on plans to use more hybrid and natural gas-powered vehicles in and around the airport, including maintenance vehicles and rental cars, as well as requiring planes to use only one engine while taxiing.
DFW Airport long ago required electrification of all ground vehicles because of North Texas' chronic smog problems.
Boston's study was prompted by complaints from residents about pollution and health concerns. The 17 communities within the study area were Boston, Brookline, Cambridge, Chelsea, Everett, Hull, Lynn, Malden, Medford, Melrose, Milton, Nahant, Quincy, Revere, Saugus, Somerville, and Winthrop.
Show Me the Money: Putting a Dollar Value on Climate Change
 How do you monetize a human life? How about when that life is impaired with an illness? What's it worth to you not having to rush your child to the emergency room when they're turning blue during an asthma attack? What about to prevent a heart attack?
How do you monetize a human life? How about when that life is impaired with an illness? What's it worth to you not having to rush your child to the emergency room when they're turning blue during an asthma attack? What about to prevent a heart attack?
These days we live in a cost-benefit world that demands this kind of accounting for things that should be accepted at face value. Want to talk about the advantages of cleaner air? You have to be able to put a price tag on it. And, with a small slight of hand, that's what the Obama administration did when it touted all the economic reasons why its new carbon capture rule for existing power plants was a plus for the country.
Carbon pollution itself doesn't directly cause the kind of death and suffering among humans that the Clean Air Act was written to address. Oh sure, it might doom countless species, raise sea levels, and cause global catastrophe, but there's not a way to tie it directly to more mundane respiratory diseases or early mortality that we (well, everyone but the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality) associate with "air pollution."
Instead of pricing catastrophic planetary effects, no matter how self-evident their true costs might be, the EPA instead sought out to tag the out of pocket expenses saved by Americans in cutting pollution associated with carbon, like Particulate Matter and smog. Most of the $55 to $93 billion in economic gains cited by the EPA last week came from these co-benefits, rather than from added spending and jobs in renewable energy or preventing massive crop failures. Otherwise, the new rules might not have been "worth it" from a regulatory point of view. The administration projects the new rules will cause the loss of between 79,900 and 80,400 full-time equivalent jobs in power generation versus 111,800 full-time equivalent jobs in renewable or energy efficiency work, basically a wash.
Want to know the price of an asthma attack? $58. Multiply that by 140,000 to 150,000 across the country and you have the approximately $9 million saved over the next 15 years by reducing soot and smog – a side effect of reducing carbon pollution under the rules.
Non-fatal heart attacks cost an average of $98,000 in health care costs and lost earning power among under-25-year-olds versus an average of $200,000 among 55- to 64-year-olds, because this later demographic is supposedly reaching its peak earning power. Preventing a six-day bronchitis episode is valued at $430.
By far the largest single health impact from the carbon rules seems to come from the forecasted reduction in deaths associated with PM pollution, quickly becoming the most insidious and widespread air pollution threat in the world, and smog. EPA economists estimated savings of between $27.3 billion and $66.7 billion from lower levels of PM 2.5 (fine particles smaller than 2.5 microns in size) and Nitrogen Oxide by preventing 2,700 and 6,600 early deaths.
Most of these numbers come from anticipated cleaner or closed coal plants. It's not unusual for EPA to do accounting this way for the rules it's proposing, although it's the first time it's used it to justify carbon pollution regs.
Will these kinds of arguments win over the skeptics? Doubtful, but that's not who they're aimed at. Instead the administration is using these numbers as talking points to the media and the public in hopes of creating momentum the skeptics can't reverse or rationalize. After all, it's hard for even Rick Perry to call out your child's asthma attacks as unimportant or inconsequential.
Study: LAX Pollutes More Than Half of SoCal Freeways
 Researchers at the Keck School of Medicine and the University of Southern California have just published a report in the American Chemical Society's Environmental Science & Technology journal that shows air traffic from Los Angeles International Airport is responsible for more air pollution than half of all the city's notoriously congested freeways with a plume extending at least 10 miles downwind.
Researchers at the Keck School of Medicine and the University of Southern California have just published a report in the American Chemical Society's Environmental Science & Technology journal that shows air traffic from Los Angeles International Airport is responsible for more air pollution than half of all the city's notoriously congested freeways with a plume extending at least 10 miles downwind.
LAX is the world's sixth largest airport, with 40-60 take-offs an hour. DFW averages 46 according to the airport's own website.
USC Scientists spent a month driving around the LA airport taking air samples for Particulate Mater pollution and found that downwind communities had twice the routine background level of PM in the city. Nine miles out, they found PM levels five times higher than background. Two miles from LAX, PM levels were almost 10 times higher. For comparison's sake, that's equivalent to 174 to 491 miles of freeway traffic. The entire area of Los Angeles County has a total of about 930 miles of freeways. Based on their calculations, scientists concluded that within the area they found to have elevated pollution from the airport, automobiles contributed less than 5 percent of the PN levels. “Therefore, the LAX should be considered one of the most important sources of PN in Los Angeles,” concluded the ACS piece
Why is that a public health concern?
"Ultrafine particles, which form from condensation of hot exhaust vapors, are of particular concern because they deposit deeply into the lungs and can enter the bloodstream. The oxidative stress and resulting inflammation appear to play a role in the development of atherosclerosis (blocked arteries) and can make other health conditions worse, especially for people with existing cardiac or lung conditions including asthma."
As far as we know there's been no study of PM pollution from DFW Airport – no federal highways dollars at stake – but this one from California should prompt one.
Big Green Discovers It Needs More Than A DC Office to Win
 In 2010, there was a very large and coordinated push by the nation's largest environmental groups and President Obama to get climate change legislation through Congress. Even with a "Democratically-controlled Congress" it failed.
In 2010, there was a very large and coordinated push by the nation's largest environmental groups and President Obama to get climate change legislation through Congress. Even with a "Democratically-controlled Congress" it failed.
Four years later, the president has ditched Congress and is resorting to his executive authority under the Clean Air Act to initiate a cap and trade system for CO2 that reportedly will demand a 30% drop in emissions from 2005 levels from the country's existing power plants. There are lots of potential land mines in this approach – if it can survive the gauntlet of legal challenges form industry. And if it does?
"It's going to be like eating spaghetti with a spoon. It can be done, but it's going to be messy and slow," said Michael Gerrard, director of the Center for Climate Change Law at Columbia University.
As for Big Green, it's discovered that DC lobbyists and think tank policy analysts do not a movement make. Prompted by their own failure, a soul-searching New Yorker article in 2013 questioning the wisdom of a corporate-like top down approach, as well as new groups that were filling the vacuum of leadership – like the more radical and highly decentralized Keystone campaigns, a change in perspective begin to occur.
“The national environmental groups said, ‘We need to do more in-your-face activism,’ ” said Gene Karpinski, the president of the League of Conservation Voters. “You can’t just lobby members of Congress with a poll that says people support you.”
As a result the big groups have re-tooled to catch-up. They're now sponsoring more direct actions, including divestment campaigns at universities, and public protests, as well as spending big bucks in targeted state elections. They're decamping from the Capitol and spreading out their resources. In doing so, they're building new organizing models for themselves, models that take cue from smaller, more dynamic, more effective grassroots groups. It's a change for the better.
Sierra Club Sues EPA Over Delayed “Bump Up” for DFW Smog Status
 DALLAS, TX – The U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) missed a key deadline in 2013 to classify smog air pollution in Dallas-Fort Worth as ‘severe,’ prompting the Sierra Club to file suit against the agency yesterday afternoon in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia for failing to properly act to protect the health of the people of North Texas.
DALLAS, TX – The U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) missed a key deadline in 2013 to classify smog air pollution in Dallas-Fort Worth as ‘severe,’ prompting the Sierra Club to file suit against the agency yesterday afternoon in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia for failing to properly act to protect the health of the people of North Texas.
The levels of smog in Dallas-Fort Worth are among the highest in the country, and only smoggy California, Houston and Baltimore have levels higher than North Texas. Ozone is the main ingredient in the smog in Dallas-Fort Worth. It triggers asthma attacks in children and is responsible for the red and orange bad air alert days the region sees every year.
“While we recognize that the Environmental Protection Agency has many priorities, nothing is more important than protecting our children from the dangers of smog and the asthma attacks that it can trigger,” said Dr. Neil Carman of the Lone Star Chapter of the Sierra Club. “The Clean Air Act has mechanisms in place to reduce pollution for areas with long-standing smog problems like Dallas-Fort Worth, but those mechanisms don’t get triggered unless EPA acts.”
The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) had a federal deadline to meet the public health standard by 2009, and when the state’s clean air plan failed to reduce pollution levels to meet the protective standards of the Clean Air Act, regulators received an extension to meet the standard by the end of the 2012.
State regulators again failed to develop a plan that would lower smog levels to protect people living in the region. After both failures, the law required EPA to classify Dallas-Fort Worth as having a “severe” ozone problem and publish the notice in the Federal Register in 2013. This action would have required polluters to take additional steps to clean our air. Unfortunately, U.S. EPA missed the deadline, prompting the Sierra Club to file suit late Tuesday, May 20, 2014.
"The Clean Air Act requires polluters to take extra steps in places like Dallas-Fort Worth that have been chronic violators of smog standards," said Jim Schermbeck with Downwinders at Risk, a clean air group based in Dallas-Fort Worth. "But asking Rick Perry to enforce the Clean Air Act in 2014 is like asking Wall Street tycoons to care about low-income families. That's why six million residents need the EPA to do its job and guarantee North Texas safe and legal air."
Because the EPA missed the 2013 deadline to properly classify the Dallas-Fort Worth area as a “severe” ozone smog area, industries are being allowed pollute more than they would otherwise, delaying the protections children, the elderly and people with respiratory illnesses in the region need.
"Today's action is the first step in requiring the EPA to finally solve the ozone problem in D-FW. Too many Texas children end up in the emergency room or miss school because of asthma and other breathing difficulties. We have to hold EPA to its legal requirements to give these families a chance to breathe easier," said Nia Martin-Robinson, Beyond Coal organizer with the Sierra Club in Texas.
Coal-fired power plants across Texas, cement plants in Midlothian and fracking in the Barnett Shale are significant contributors to smog-forming pollution to the region. State regulators have failed to require the most up to date pollution controls on these sources, contributing to the repeated failure of state clean air plans.
Air Pollution is “an overlooked risk factor” for Heart Disease
 Over the last decade we've seen plenty of studies linking air pollution, and specifically Particulate Matter, or soot pollution, to heart disease and attacks. Now Dr. François Reeves,a Canandian cardiologist has a new book "Planet Heart: How an Unhealthy Environment Leads to Heart Disease," that puts those studies in context.
Over the last decade we've seen plenty of studies linking air pollution, and specifically Particulate Matter, or soot pollution, to heart disease and attacks. Now Dr. François Reeves,a Canandian cardiologist has a new book "Planet Heart: How an Unhealthy Environment Leads to Heart Disease," that puts those studies in context.
“You can sum it up like this: more pollution, more major adverse cardiac events. Pollution of the city is as toxic as cigarette smoke. It has different stuff in it, but the difference is that with pollution, you get it all through your life, from your birth to your death. If you live in a polluted milieu, as soon as you’re a baby you’ll take it in through every breath.”
Reeves' interest as a cardiologist in air pollution issues was triggered by a 2008 World Health Organization report that tracked mortality rates for cardiovascular disease in European countries. In nations with relatively clean air like Norway or even France, the levels were approximately 25 to 70 per 100,000 men. In Russia and the Ukraine it was 600-750 per 100,000. “I was blown away by those numbers,” Reeves says. “We know the classical and well-demonstrated risk factors for heart disease, like smoking and obesity and inactivity. But that’s when I realized the environment has a huge impact."
Just like lead, and benzene, and dioxin, and so many other kinds of pollution, there appears to be no "safe level" of exposure to PM pollution. Any amount is capable of doing some harm, and the more you're exposed, the more harm is likely to happen. That's why fence-line communities are particularly vulnerable to higher rates of illness. In DFW, where PM levels are considered under control, there are still lots of hot spots for the pollutant. If you live downwind of the Midlothian cement plants, you're inhaling a lot of soot. the closer you live – Cedar Hill, South Grand Prairie, South Arlington, Mansfield – the more soot you're inhaling.
In his new book Reeves gives a list of heart-healthy things an individual can do to reduce their risk of heart disease, including increased bike riding, more public transit, or walking and weaning yourself off of internal combustion engines with electric cars and hybrids. “Look at everything you’re doing to minimize your footprint and do whatever you can to have an impact on global footprint,” Reeves says,
But he recognizes the limits of this kind of advice if a person is living in a smoggy city or region and offers overarching policy advice for officials. Cities and governments must continue their efforts to be green, if only out of their own self-interest.
If those governments need any convincing, Brauer points to a financial argument: fewer health problems mean less strain on the public system. “If you improve air quality, everybody benefits,” he says. “It’s really, really cost-effective.
Have You Seen This Bucket of Hazardous Waste ?
 It's 2014. Distant parts of the globe are connected within micro seconds. Some of us are driving electric cars. Our phones are more powerful than all the computers it ever took to put a human being on the Moon, combined.
It's 2014. Distant parts of the globe are connected within micro seconds. Some of us are driving electric cars. Our phones are more powerful than all the computers it ever took to put a human being on the Moon, combined.
And we use five gallon buckets from Academy to collect and store industrial hazardous waste.
Or at least the Exide contractors that are in charge of "cleaning-up" Frisco's Stewart Creek do. And they not only use them, they lose them.
On May 8th, workers for Apex-Titan Inc. were collecting battery casing chips and bits of lead slag from fields near the Creek a the intersection of Legacy and Stonebrook and putting them into the bucket. For decades before it closed in 2012, the Exide lead smelter dumped waste into and around the Creek, leaving a still-contaminated trail from the plant site all the way to Lake Lewisiville, approximately five miles away.
After collecting a full load of Exide waste, the contractors placed the bucket in the back of a pick-up truck and drove off – apparently without securing the tailgate first. Despite two staff from the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality on the scene to "document field activities" and the City of Frisco's own contractor present – nine people in all – no one noticed when or how the bucket fell off the truck on he way back to the plant site.
When they discovered the loss, the workers retraced their route. They searched the parking lot of a city park located across the street from a school – one of two in the immediate vicinity. No bucket. More than two weeks later the bucket of hazardous waste is still missing. But we're only now finding out about it.
This would be funny if it weren't for the possibility of this bucket ending up with kids or in a garden or as a water container. As a memo from the City of Frisco puts it:
"We believe it is a reasonable assumption that the bucket was found in the street by a person who picked it up for their own use; without realizing the contents might be hazardous waste."
With that in mind, did the City of Frisco inform the Frisco School District? Did any warnings get issued to students and parents at the two near-by schools? Not as far as we know. Did the City put out an All Points Bulletin for the bucket? No it did not. Embarrassment often keeps officials from doing the right thing about public health. So there's hazardous lead waste out there in a Frisco neighborhood that could be diminishing kids' IQs even as you're reading this, even as officials are too embarrassed to ring the alarm.
Now maybe you're thinking this whole Frisco lead cleanup fiasco now has a new mascot. And you' be right. This bucket pretty much sums up the FUBAR'd state of things. A bankrupt company entrusted to clean-up its own mess. A city council seemingly intent on making sure it ends up with a Superfund Site in the middle of the "second-fastest growing city in America." A state and federal government asleep at the wheel. It's all nicely summed up by that lost five gallon Academy bucket. That's the image. Here's the caption, however, thanks to Jack Fink at Channel 11:
"Mack Borchardt of the city of Frisco said he’s surprised, since they were assured going into this process by Exide that there wouldn’t be any problems with the system in place. “Obviously, that didn’t turn out to be the case,” said Borchardt."
City officials were shocked! Shocked they tell you, that Exide screwed up.
Frisco City officials handed the job over to Exide and expected the same company that ran an outlaw smelter operation to provide an excellent clean-up of their own mess. They had faith! The City is handing over the toxicology and assessment to the state and EPA. They have faith! They're handing the decision about what to do with the waste in Frisco to their lawyers, who are recommending the city host a toxic waste landfill by Stewart Creek in front of the new Grand Park. They have faith! What they don't have is any faith in their own citizenry. After 2 years there's still no transparent, civic dialog on the fate of the thousands of tons of lead waste that remains in the heart of the central business district.
There's no question that given a choice, most Frisco residents would vote to haul the waste completely out of town to a hazardous waste disposal site and develop the property as any other prime piece of real estate. And yet the Frisco City Council is still on course to approve a permanent toxic landfill of its own…… that would be monitored by the same state agency that didn't see that five gallon bucket falling out of the contractor's truck.
What's needed now more than anything else is homegrown vision and leadership. The city needs to take its fate into its own hands instead of entrusting others to look out for its self-interests. There's millions of dollars in state-collected battery fees that are supposed to be going to communities impacted by lead smelting. Frisco certainly qualifies. Instead of arguing with its own residents over a permanent landfill, the Council should be proposing legislation for the next session in Austin to finance a full clean-up.
This incident is a five-gallon splash in the face. Following instead of leading can only result in many future "problems with the system."
Downwinders at Risk Joins Groups in Filing EPA Petition Demanding Federal Limits on Toxic Oil & Gas Air Pollution from Well Sites
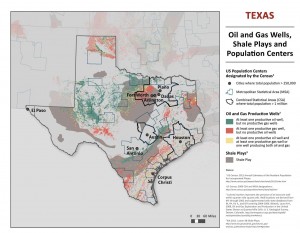 Downwinders at Risk and over 60 other local, state and national groups filed a petition Tuesday urging the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to protect public health by setting pollution limits on oil and gas wells and associated equipment in population centers around the U.S.
Downwinders at Risk and over 60 other local, state and national groups filed a petition Tuesday urging the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to protect public health by setting pollution limits on oil and gas wells and associated equipment in population centers around the U.S.
Led by the public interest law organization Earthjustice, the nationwide alliance also includes The Clean Air Council, Clean Air Taskforce, Environmental Defense Fund, Global Community Monitor, Natural Resources Defense Council, Physicians for Social Responsibility-Los Angeles, Sierra Club, and WildEarth Guardians.
Making the case to require oil and gas companies to limit toxic air pollution from oil and gas wells in urban, suburban and other populated areas as the Clean Air Act expressly provides, the petition urges the EPA to act quickly to protect public health.
In recent years, the pace of oil and gas drilling has increased drastically. As of 2011, oil and gas wells in the U.S. numbered more than 1.04 million. Current estimates project that as many as 45,000 new wells could be drilled each year through 2035.
Available data suggest that at least 100,000 tons per year of hazardous air pollution from oil and gas well sites—such as benzene, formaldehyde, and naphthalene—are currently going freely into the air. These pollutants have been linked to respiratory and neurological problems, birth defects, and cancer.
“More than 150 million Americans now live near oil and gas wells or above shale areas where companies are looking to drill or engage in hydraulic fracturing, and EPA needs to set standards that restrict the hazardous air pollutants they put into the air,” said Earthjustice attorney Emma Cheuse, who filed the petition on behalf of the groups.
A significant number of those millions are Texans, who are hosting at least four large gas and oil plays in the state, including the Barnett Shale that overlaps large sections of the DFW metropolitan area.
"Almost a decade of un-and-under-regulated fracking has transformed North Texas into a sacrifice zone for the gas industry, with conservative estimates of over 1,000 tons of hazardous air pollution being released annually from industry sources. Breathing this toxic air pollution has left a well-documented trail of illness and disease throughout the Barnett Shale. EPA needs to do its job and protect frontline victims of fracking by reducing the toxic fallout from the practice," said Downwinders at Risk Director Jim Schermbeck.
Besides the DFW Metropolitan area, Houston, Austin, San Antonio, Corpus Christi, Beaumont-Port Arthur, Waxo, Lubbock, Amarillo, Laredo, College Station-Bryan, Killeen-Temple-Fort Hood, McAllen-Edinburg-Mission, Longview, Tyler, Abilene, Wichita Falls, Odessa, Midland, Sherman-Denison, Victoria, San Angelo, and Texarkana would also be protected by the new regulations.
Facilities presently not regulated for their toxic air pollution that would be covered under the petition include new and existing oil and gas wells, existing hydraulically fractured gas wells (unless modified), new hydraulically fractured gas wells that are exempted, most equipment associated with wells, including: many storage vessels, pneumatic controllers, compressors, and equipment leaks.
The petition filed today, as well as a list of the groups filing, can be found at: http://earthjustice.org/documents/legal-document/2014-petition-for-federal-limits-on-toxic-air-pollution-from-oil-gas-wells
To see the population centers that would receive protection under new EPA rules, look at Table 5 of the petition, or the maps listed below.
Human-Induced Earthquakes and Cooking the Planet: We’re Living the Next Hollywood Sci-Fi Blockbuster
 "Environmentalism" as a cause in America has its roots in the wilderness, the "otherness" a person can discover when he or she is separated from their own kind and put among crowds of the planet's non-human inhabitants. Walden Pond. National Parks. These were all meant to be meditative retreats from "civilization," from which you could escape. Environmentalism was a revelatory and individualistic experience.
"Environmentalism" as a cause in America has its roots in the wilderness, the "otherness" a person can discover when he or she is separated from their own kind and put among crowds of the planet's non-human inhabitants. Walden Pond. National Parks. These were all meant to be meditative retreats from "civilization," from which you could escape. Environmentalism was a revelatory and individualistic experience.
Then came the understanding of environmentalism as a way to affect collective public health. Air pollution we breathe into our bodies causes lung cancer and asthma. Swallowing water with toxins in it when you're pregnant can cause birth defects. Eating foods with pesticides in them can affect a child's hormones. Still, the impacts were mostly seen person by person, and they depended on lots of variables – genetics, location, exposure. Not in my backyard.
Now however we're in a whole new age of cause and effect. The scale is planetary. The sky we live under as well as the ground we walk on.
Imagine Hollywood makes a movie about alien invaders who want to reshape the Earth for their own purpose, say like "Battleship." They begin pumping in massive quantities of CO2 and methane, driving up the temperature way beyond anything in recent history and setting-off all kinds of chain reactions among species and weather conditions. They begin extracting minerals by poking deep holes in the earth and then setting off large explosions, the waste of which causes not-insignificant earthquake activity when they pump it back into the ground under tremendous pressure. Their huge spaceships sometimes leak radioactivity, and if they just happen to be sitting beside oceans that can be used as industrial-size septic tanks, all the better.
That's what it feels like now, in 2014.
In case you missed it, the United States Geologic Service issued its very first "Earthquake warning" for Oklahoma:
"A new study found that earthquakes in Oklahoma rose by 50 per cent over the last seven months, leading researchers to warn that the risk of a damaging earthquake measuring a magnitude of more than 5.5 has increased significantly in the state. Agencies reported 183 earthquakes of magnitude 3.0 or higher from October until April 14th, compared with an average of only two per year from 1978 to 2008."
Usually reserved for places like California or Alaska to warn residents of the risk of damaging aftershocks, this is the first time the USGS has issued an earthquake warning for a state east of the Rockies. In the Sooner State, the aftershocks are thought to be caused by fracking waste injection wells. A Cornell University study released this week showed a link between waste wells and earthquakes up to 50 kilometers away.
"A new study of the Jones earthquake swarm, occurring near Oklahoma City since 2008, demonstrates that a small cluster of high-volume injection wells triggered earthquakes tens of kilometers away. Both increasing pore pressure and the number of earthquakes were observed migrating away from the injection wells.
"The existing criteria for an induced earthquake do not allow earthquakes associated with the well activity to occur this far away from the wellbore," said Katie Keranen, assistant professor of geophysics at Cornell University, who led the study of the Jones earthquake swarm. "Our results, using seismology and hydrogeology, show a strong link between a small number of wells and earthquakes migrating up to 50 kilometers away" said Keranen. "
Moreover, we're just beginning to understand the threat to infrastructure from human-induced earthquakes…
"Last week scientists attending the Seismological Society of America annual meeting in Anchorage, Alaska called for more research into the relationship between fracking wastewater disposal and earthquake activity.
Gail Atkinson, an earth sciences professor at the University of Western Ontario, presented research at the conference highlighting the “significant and as-yet-unquantified risk” to the integrity of critical infrastructure, such as major dams and nuclear power plants posed by induced seismicity.
Part of the problem is that fault lines in the areas most affected by fracking operations are often poorly and incompletely mapped. Texas, Ohio, Colorado and Oklahoma, which have in recent years experienced unprecedented seismic activity, have never been made a priority like California and other states where quakes have long been a threat."
SMU and USGS scientists looking into the Azle earthquake swarm were also at this same Alaska conference presenting their paper showing the vast majority of recent earthquakes near that city were centered between two injection wells, including a large XTO one. Expect to see some follow-up as reporters and citizens take their first look. And while we really do expect an alien invasion to occur before the State of Texas voluntarily does anything to stop the problem in Azle, there's a House Energy Committee, Seismic Activity Sub-Committee hearing next Monday May 12th, where only invited testimony will be heard. Sharon has the details for folks that want to make another trip to Austin.
Meanwhile, April saw new highs in atmospheric poisoning.…
The end of April has arrived, and with it, the record for the first month in human history with an average carbon dioxide level in Earth’s atmosphere above 400 parts per million has been set.
With a little more than 24 hours left in the month, the average for April can't slip below 400 ppm. “Every day in April has been over 400 ppm,” said Pieter Tans, a climate scientist with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
The levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are monitored from a site atop Hawaii’s Mauna Loa volcano, where they have been measured continuously since 1958. The long record has charted the steep rise of the greenhouse gas — the most prevalent in Earth’s atmosphere — as a result of human emissions.
The first measurement in excess of 400 ppm was made on May 9, 2013. This year, the level rose above that mark a full two months earlier, and has remained above 400 ppm steadily since the beginning of April.
And lest you think you'll be long gone before the effects of this change affect you and yours, yesterday's new National Climate Assessment report wants you to know that,
"The effects of human-induced climate change are being felt in every corner of the United States, scientists reported Tuesday, with water growing scarcer in dry regions, torrential rains increasing in wet regions, heat waves becoming more common and more severe, wildfires growing worse, and forests dying under assault from heat-loving insects.
Such sweeping changes have been caused by an average warming of less than 2 degrees Fahrenheit over most land areas of the country in the past century, the scientists found. If greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane continue to escalate at a rapid pace, they said, the warming could conceivably exceed 10 degrees by the end of this century.
“Climate change, once considered an issue for a distant future, has moved firmly into the present,” the scientists declared in a major new report assessing the situation in the United States."
Conscience-ridden scientists making dire warnings about the threat. A government too slow or self-interested to act to thwart the threat. We know this movie. From the POV of the moving camera, we see the same forces of darkness making things go boom underneath us are also filling up our thin layer of atmosphere with gunk. This is no longer something we can escape from, nor is it a matter of local public health. After years of hearing that the sky is falling, now it really is. Only instead of aliens causing it, it's us treating the planet as if we were.
In such a Hollywood Blockbuster, the heroes would be the scrappy, common-sense fueled citizenry who had managed to outrun and outsmart the aliens in various small and large ways while governments fumbled and greedy privateers made deals with the newcomers. With some imagination, a rag tag group of locals fighting a single alien ship out in the boondocks would finally find an out-of-the-box way to disrupt, confuse, and eventually defeat the enemy. As the credits begin to roll, you can see word of this grassroots strategy spread across the globe and its effectiveness showing up in Paris, Moscow, Nairobi, Mexico City, and Hong Kong.
This is that movie. We're in it. Are you a member of the scrappy resistance or an anonymous uncredited crowd extra? Quick, the tide's coming in.….
Thank You. Citizens Might Have Just Saved The Local Air Planning Process…From Itself
 A year from now, last Thursday' meeting in Arlington may be seen as a turning point.
A year from now, last Thursday' meeting in Arlington may be seen as a turning point.
Local residents refused to let the air quality planning process die, showing up in numbers that forced officials to switch to a larger room, and making sure their opposition to another state "do-nothing" air plan was heard loud and clear.
Their participation had already changed the day's agenda. Included was a breakthrough UNT study that directly challenges the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality's claim that natural gas emissions don't increase DFW smog.
UNT's Dr. Kuruvilla John's presentation of the new study received quite a bit of media coverage, before, during, and after Thursday's meeting. You can find some of the best coverage by clicking on the links below.
UT-Austin Study Reveals "Underestimates"
Dr. John's presentation influenced another researcher's slide show as well. Scheduled to speak about older, more generic ambient air measurements for ozone, Dr. David Allen of UT Austin instead presented more recent research into gas pollution as well.
Overlooked in the debut of the UNT study, Allen's constant monitoring of one drill site in Fort Worth revealed that the TCEQ was underestimating emissions from the pneumatic valves at the site by 159%.
That was news to both citizens and TCEQ, who said they hadn't looked at Allen's research and hadn't corrected their inventories to account for such underestimates. Valves like these are powered by natural gas, are quite numerous on gas equipment, and account for a large percentage of VOCs released from a fracking site.
A Better Picture of Oil and Gas Pollution
Citizen cross-examination of TCEQ staff members present at the meeting also revealed a different look at the volume of Oil and Gas industry pollution in the 10-county DFW "non-attainment area"
Up to Thursday, TCEQ was dispersing Oil and Gas pollution across several categories, making it impossible to show the true total impacts.
Here's an example of the way TCEQ likes to present the info:
SOURCES OF SMOG-FORMING NITROGEN OXIDE POLLUTION (NOx)
IN DFW's NON-ATTAINMENT AREA
1. "On Road" vehicles 113.21 tons per day
2. "Non-Road" vehicles" 39.87 tpd
3. "Area" 30.76 tpd
4. "Other Point Sources" 24.95 tpd
5. "Locomotives" 18.90 tpd
6. "Cement Kilns" 17.60 tpd
7. "Electric Utilities" 15.02 tpd
8. Oil and Gas Production 12.21 tpd
9."Airports" 11.77 tpd
10. Oil and Gas Drill Rigs 5.83 tpd
TOTAL 290.12 tpd
This makes it look like Oil and Gas pollution is not that big a deal.
But it turns out TCEQ is hiding 28.44 tpd of NOx gas compressor pollution in the "Area" and "Other Point Source" categories.
This was brought out in questioning on Thursday. Once you add these figures to the other Oil and Gas emission numbers spread out over different categories, this is what you get:
SOURCES OF SMOG-FORMING NITROGEN OXIDE POLLUTION (NOx)
IN DFW's NON-ATTAINMENT AREA
1. "On Road" vehicles 113.21 tpd
2. Oil and Gas Industry 46.48 tpd
3. "Non-Road" vehicles 39.87 tpd
4. "Locomotives" 18.90 tpd
5. "Cement Kilns" 17.60 tpd
6. "Area" 15.93 tpd
7. "Electric Utilities" 15.02 tpd
8. "Other Point Sources" 11.34 tpd
9. "Airports" 11.77 tpd
TOTAL 290.12
(Earlier today we put out an e-mail alert that left 10 tons off the "Area" category in this second chart, greatly affecting its ranking. That mistake is corrected in this version of the chart and we apologize for any confusion that might have caused)
When you quit playing the state's shell game with Shale pollution, the Oil and Gas industry becomes the region's second largest source of NOx pollution – the kind of pollution TCEQ says is the main driver of smog in DFW (not even counting all the pollution from O&G fracking trucks still hiding in the "On Road" category).
There have been control measures for cars to reduce NOx. There have been controls on heavy duty equipment and trucks to reduce NOx. There have been new controls on locomotives to reduce NOx pollution. There have been controls on airport ground equipment to reduce NOx pollution. There's even been middling controls to reduce the NOx from the Midlothian cement kilns. But where's the controls to reduce NOx from the Oil and Gas industry – the one source in this list that hasn't had the same kind of regulatory attention? Good question – save it for next time.
Citizen Participation is Crucial
This is the kind of close examination the TCEQ hopes to avoid by limiting debate on this new clean air plan, scheduled to be submitted to EPA by July next year. And it's exactly why citizens need to keep showing up.
Because of the momentum and interest coming out of Thursday's meeting, citizens also got the next scheduled pow-wow of the local air planning process moved up to late May or early June instead of waiting until July.
We're already taking suggestions for what you want to see on that agenda, so don't be shy. And thank you again for restoring some tiny amounts of integrity into a process that's been swamped by Rick Perry's indifference.
You're making a difference, and that's all anybody can do. This last Thursday it was a big difference. Let's try to do the same in May.
Some Coverage of Thursday's Air Planning Mtg.
Channel 8: "UNT researchers say fracking a contributor to North Texas smog problem"
Texas Observer: "Studies: Links Between Fracking and Smog Pollution Stronger Than State Claims"
Star-Telegram: "Natural Gas Production Contributing to Higher Ozone Levels, study Finds"
Denton Record Chronicle: "Officials: No New Plans to Clean Up Air"
HOW YOU CAN SAY "THANK YOU" BACK
Here's what Downwinders at Risk did this past week to make sure Thursday's air quality meeting wasa success:
1) Pressed for and got the UNT study linking fracking to smog on the meeting agenda after being told it would not be included.
2) Sent out releases to the media advertising the UNT presentation.
3) Sent out alerts to you and others to let you know about the new UNT study and the meeting itself.
4) Sent out a "Citizens' Guide to the Meeting" so you could be prepared for Thursday.
5) Showed-up at Thursday's meeting with handouts showing the lack of air quality progress in DFW and the lack of a complete plan by TCEQ
6) Used our questions to reveal how TCEQ was hiding Oil and Gas industry pollution totals in their data
7) Pressed for and got an earlier "next meeting" of the local air quality planning group
8) Sent out this follow-up so that everyone knows what went on and what the news is from the meeting
A local forum for clean air issues was about to disappear.
Only the last month's mobilization of citizens prevented that from happening on Thursday.
Who began that mobilization?
We did.
We really need your financial help to keep doing this. We don't get state or national funding – just local money from people like yourself.
Thanks. We very much appreciate it.
