LafargeHolcim is a “Conscientious Corporate Citizen” Everywhere But Texas

In Europe, LafargeHolcim is a multinational cement manufacturer based in Switzerland and France – two countries on the cutting edge of climate crisis planning and members of the progressive European Union. The Company portrays itself as a climate-conscientious corporate citizen, to the point of its Swiss CEO declaring the reduction of CO2 emissions as his first, most important priority.
In Midlothian Texas, LafargeHolcim runs the most conventionally dirty cement plant in Texas and is seeking a permit that could make it one of the most climate-hostile one as well. In fact, there’s some reason to believe the Holcim plant in North Texas is preparing to burn by-products from either the Canadian Tar Sands, the Permian Oil Field, or both, as fuel.
Baking rock to make cement takes a lot of heat. Regardless of how new or old a cement kiln is, regardless of the pollution controls a kiln has, every cement maker in the world still has to employ the same age-old process of applying a 2000 degree open flame to a mix of limestone and other ingredients. A third or more of the cost of running a cement plant is keeping that open flame consistently hot enough to do the job.
This is the reason cement kilns will always try to find cheap, free, even profitable sources of fuel for that flame. Hazardous and industrial wastes that c an be diverted from incinerators or landfills can be burned in cement kilns for slightly less money because they don’t have to meet the same standards. Used tires and oil. Lottery tickets. Dashboards from cars. Even municipal waste is now being burned in kilns.
an be diverted from incinerators or landfills can be burned in cement kilns for slightly less money because they don’t have to meet the same standards. Used tires and oil. Lottery tickets. Dashboards from cars. Even municipal waste is now being burned in kilns.
Burning anything causes air pollution. Burning wastes causes lots of conventional and exotic air pollution, including CO2. But just baking limestone rock also releases a lot of stored CO2. Even if there was some was to make cement without a flame, the heat needed would still release tons of CO2.
Worldwide the cement industry is estimated to be responsible for 5 to 7% of the planet’s CO2 emissions – larger then the airline industry. If the industry were a country, it would be the third largest emitter on earth, behind the United States and China.
Companies like LafargeHolcim are facing both public and financial pressures to reduce that number. In July European funds managing $2 trillion in assets called on cement companies to slash their greenhouse gas emissions, warning that a failure to do so could put their business models at risk. The mangers specifically mentioned LafargeHolcim and urged it to adopt the goal of net zero carbon emissions by 2050 and align itself with the Paris Climate Accords.
LaFarge Holcim has responded by initiating a series of technical innovations and pilot projects under the banner of “The Plant of Tomorrow” to prove its forward thinking.
Almost 300 facilities around the globe are targeted for inclusion in one or more of these “Plant of Tomorrow” projects, including a Canadian kiln installing a carbon-capture pilot project, an Ohio kiln building three wind turbines to secure its electrical needs, and kilns burning industrial waste as “low carbon” (if not low toxic) fuel.
Left out of this mix so far is Holcim’s woe-be-gone Midlothian plant. You might call it Holcim’s “Plant of Yesterday.” Despite having lots of stiff competition, Holcim not only operates the dirtiest cement plant out of the three doing business in Midlothian, but it’s the dirtiest in the entire state.
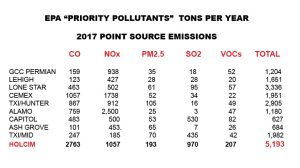
Holcim’s Midlothian plant is the largest Carbon Monoxide (CO) polluter among all 10 Texas cement plants – a sign of poor combustion. It’s the second largest Nitrogen Oxide (NOx) polluter among the bunch, emitting almost twice as much smog pollution as the other two Midlothian cement plants combined. It’s the largest PM 2.5 (Particulate Matter) polluter by far – almost 100 tons a year separate it from second place. It’s the largest Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) polluter by a large margin and releases four times as much Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) than the next highest plant. Almost all 2017 pollution numbers for Holcim have gone up over the last five years. A plant that was already bad is getting worse.
Now add Holcim’s request for a new permit to burn 100% Petroleum Coke in one of its two kilns.
Pet Coke is a byproduct of oil refining. It’s a concentrated carbon solid residue that is left behind after the refining process has converted the bulk of the oil into liquid fuels such as gasoline and diesel.
Pet Coke is like coal, but dirtier. Pet Coke looks and acts like coal, but it has even higher carbon emissions than coal. On a per-unit of energy basis Pet Coke emits 5 to 10 percent more carbon dioxide than coal. A ton of Pet Coke yields on average 53.6 percent more co2 than a ton of coal.
As well as significantly higher co2 emissions, Pet Coke also has high sulfur and toxic metals content than coal.
Because its a waste product, Pet Coke is cheap for Holcim to buy or it could even be free if a refinery wanted to get rid of its supply. And now, thanks to the exploitation of the Tar Sands and the oil boom in the Permian the US has lots and lots of Pet Coke. The heavy oil refining capacity in America is now the largest in the world, with over 40 percent of the global market. Much of that production takes place on the Texas Gulf Coast in huge new expanded refinery complexes like Motiva and Total in Port Arthur. The capacity to produce Pet Coke in U.S. refineries has doubled since 1999. In fact, the annual production of Pet Coke is so large these days, it’s outstripped most of the usual uses for it and is “priced to move.”
Because Holcim wants to burn 100% Pet Coke, and it must have a reliable source to burn it 24/7, there’s reason to believe the company has signed a sweetheart deal with one or more refineries to supply it. Probably from the Gulf Coast, and probably from one of the refineries dealing in Canadian Tar Sands oil or Permian Basin product. Both are poster boys for irresponsible fossil fuel development with the Tar Sands and the Keystone Pipeline igniting modern Climate Crisis activism and the Permian becoming one the planet’s largest sources of Methane as tons of unused natural gas are burned off from thousands of rigs.
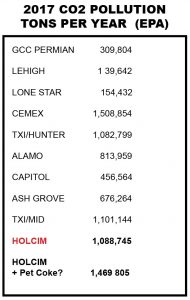 Currently, Holcim is “only” the third largest CO2 polluter among all ten cement plants in Texas, and fourth among all of Holcim’s U.S. plants. But burning 100% Pet Coke in its Kiln #2 could change that rapidly by adding a whopping 400,000 tons more of CO2 to its annual totals. That would send it to #2 in Texas and #2 in the entire US Holcim fleet of cement plants. Not very climate conscientious. And probably not a number you want to tout in trying to sell your “Plant of Tomorrow.”
Currently, Holcim is “only” the third largest CO2 polluter among all ten cement plants in Texas, and fourth among all of Holcim’s U.S. plants. But burning 100% Pet Coke in its Kiln #2 could change that rapidly by adding a whopping 400,000 tons more of CO2 to its annual totals. That would send it to #2 in Texas and #2 in the entire US Holcim fleet of cement plants. Not very climate conscientious. And probably not a number you want to tout in trying to sell your “Plant of Tomorrow.”
At the same time Holcim is trying to project an image of a concerned 21st Century corporate entity to the rest of the world, it’s doing business in Texas like its still 1999.
Officially, the State of Texas doesn’t care about CO2 pollution. Heck, officially it doesn’t even believe there’s a climate crisis. There is no regulatory system for controlling its releases and only the EPA bothers to track CO2 releases at all. So this increase in planet-melting pollution will go completely unaddressed in the permit proceedings themselves.
Also officially, despite the evidence, the State and Holcim both say no other kinds of pollution will increase when 100% Pet Coke is burned at Holcim. No increase in PM 2. 5. No increase in SO2. No increase in metals. Citizens don’t believe them. A group calling itself “Midlothian Breathes” has formed to fight the new permit and has already caught regulators off guard asking tough questions about new emissions.
But trying to get the State of Texas to do the right thing about air pollution is an uphill fight. Instead, perhaps citizens should take these embarrassing numbers directly to LafargeHolcim, who’s claims of new fund corporate responsibility are belied by them. Contrasting its Texas operations with those of the rest of its facilities may be a way to shame the company in its own European backyard. Officially the company may still be able to be embarrassed. Texas state government left that possibility behind years ago.
