Study: Combusted PM Pollution Up to Five Times as Lethal As Non-Combusted Kind. Burning is Bad.
 Long term exposure to small particulate pollution from combustion sources, specifically coal-fired power plants, is up to five time more likely to kill you through heart damage than other forms of natural or human-made "PM."
Long term exposure to small particulate pollution from combustion sources, specifically coal-fired power plants, is up to five time more likely to kill you through heart damage than other forms of natural or human-made "PM."
That's the conclusion of new comprehensive study comparing risks from breathing-in the tiniest specs of soot from combustion sources for over 450,000 Americans in 100 cities from 1984 to 2014. Published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives this month to coincide with the Paris climate talks, the study has ten co-authors and promises to be a milestone in the long fight to reduce this form of pollution.
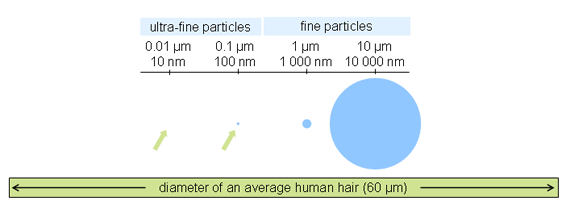
Combustion of any sort releases fine and ultra-fine particles of soot, or "Particulate Matter" in the often antiseptic regulatory-speak of environmental regulation. These specks differ from dust particles or fireplace soot in that they're much, much smaller and so can be inhaled deeper into the lungs, and then, even pass from the lungs into the blood steam to affect other organs and systems. It's their tiny size that makes PM pollution dangerous on its own. Over the last 30 years, scientists and public health officials have gone from being worried about PM 10 (10 microns or less), to PM 2.5 (2.5 microns or less – about 100th of the width of a human hair), to Ultra-fine Particles.
But soot from combustion also carries residues of whatever was being burned in the facility it came from, and this makes it doubly toxic. If you're burning coal, the soot might carry bits of Mercury, Arsenic, Cadmium and Lead, for example. The new study says that difference is what really drives up risk for people breathing-in coal plant PM.
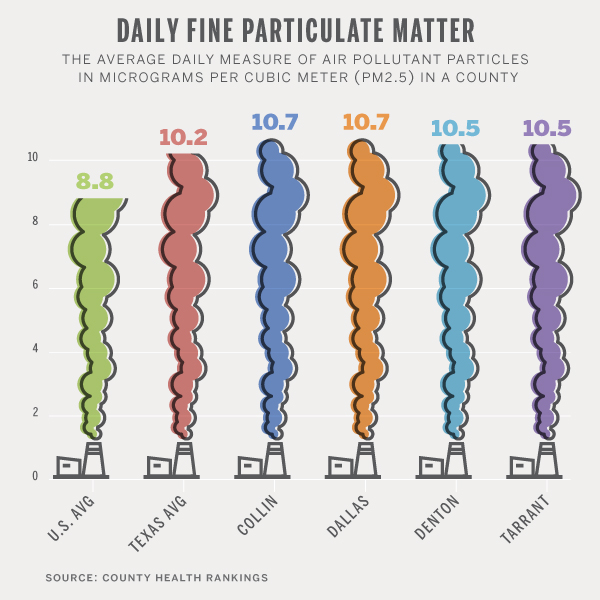
Locally, DFW is chock full of large industrial sources of combustible PM.
We're surrounded by five coal plants in an arc on its northeastern to southeastern side. That means we're downwind of their pollution, including their particulate matter pollution, most of the year. Their impact on local smog levels has recently been chronicled by Downwinders' study from UNT.
PM Pollution would follow approximately the same patterns although heavier particles fall closer to the source, while the really fine particles drift for hundreds or thousands of miles. Luminant’s 2013 Emissions Inventory submission reports 1400 tons of 2.5 particulate matter in a single year at its Big Brown plant. And that may be a severe underestimate. Big Brown’s two Units have exceeded the Texas SIP’s opacity limit of 30 percent on thousands of occasions over the past decade.
Luminant's Martin Creek plant released 2,018 pounds of mercury into the environment in 2013, according to the Toxic Release Inventory, and in fact Texas hosted the top three mercury polluters among all coal plants in the US that year.
Closer in, there's the three Midlothian cement plants with a total of four kilns now. Modernization and controls forced by 20 years of campaigning by Downwinders have brought the numbers down dramatically, but they're still huge facilities that deal in both a dusty raw material, and burning lots of coal and industrial wastes like tires and used oil, and even car parts, to turn that into a higher grade of raw material. When you burn exotic materials with coal, you turbocharge the toxicity of the PM pollution even more. In 2013, the last year the state has numbers posted online, the three cement plants released approximately 440 tons of 2.5 PM pollution.
But cement plants weren't included in the study and so the risk evaluations in it for DFW are underestimated.
Midlothian is also the home to the very large French-owned Amersteel (formally Chaparral Steel) secondary steel mill and steel mills were included as a source category in the study and were also associated with a higher mortality rate. Just about every 18-wheeler trailer you see on local highways loaded with crushed cars is headed to this facility – across the street from the TXI cement plant. Imagine the residues on the soot from melting down thousands of used cars into liquid metal. In 2013, the plant released 133 tons of PM 2.5.
But by far, the largest PM polluter in the DFW area, bar none is the Owens-Corning fibreglass plant in north Waxahahchie, along I-45. It released a whopping 300 tons of PM 2.5 pollution in 2013 alone. No other facility comes close – not the cement plants or the steel mill down 287. Not the GM plant in Arlington. It's not known how much of Owens-Corning PM is combusted however. It could be from the manufactiuring process.
Diesel engines in vehicles were also included, and the study found they has an association with higher mortality, but not nearly as significant as coal plants or steel mills. There's been a steady stream of studies tying highway pollution to respiratory and neurological illness among near-by populations, especially children. Most of the risk is assigned to PM pollution, and most of that is coming from diesels.
Just as important as the conclusion that coal-combusted particulate matter is significantly more dangerous than your average speck of dust is the study's indictment of current EPA risk assessments that operate on exactly the opposite assumption. The authors are critical that the Agency still weighs the risk of desert dust the same as combusted soot in computing long-term human health effects.
There are potentially enormous public heath and policy implications for North Texans in the study's conclusions.
First, the campaign to get the most modern anti-smog controls included in the latest DFW air plan has the side benefit of reducing PM pollution too. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) on the cement kilns and coal plants decreases smog-forming pollution by up to 90%, and makes an effective additional PM catcher as well, increasing soot capture by 30-50%. The technology is particularly effective on the kind of PM that carries dangerous heavy metals like Mercury. Of course, retiring already-obsolete coal plants would eliminate the threat all together.
Likewise, electrification of compressors would not only lead to decreases in smog-forming emissions, but PM pollution from those sources as well.
Next, it means the already large public health costs of bad air in DFW just published by Dr. Robert Haley of UTSW in his own study are severely underestimated, since they were based on the EPA's own risk assessment software that doesn't weigh the harm of coal power plant PM differently from any other speck of PM 2.5. Adjust those numbers for the exposure to toxic soot and you could see a huge increase in lives lost, illness caused, and dollars spent.
Finally there are implications for almost very other source of combustion around – burning is bad. Where's there's a flame, a boiler, a furnace, a process that means burning something to get something in return, there's going to be PM pollution. What you burn is as important as how you burn it. Burn coal and get the residues of coal on the PM. Burn hazardous waste, and you get the residues from those wastes on the PM. Burn diesel fuel in your truck or car and get residues from that fuel mix packed away in your particulate matter.
As one of the major authors of the study said, if you want to do something about this kind of pollution – start with the most toxic forms of combusted PM. Those mostly come from large industrial sources – the coal plants, cement kilns, and compressors already in our sights because they're also smog polluters. We knew they were a problem. Now we know even more about why they're a bigger problem.
