2nd TCEQ Clean Air Plan in Four Years Fails, Leaves Air Dirtier
 For the second time in four years a state-designed clean air plan to bring safe and legal air to DFW residents has failed, missing its goal by an even wider margin than on its first try, and leaving local air quality worse than when it started.
For the second time in four years a state-designed clean air plan to bring safe and legal air to DFW residents has failed, missing its goal by an even wider margin than on its first try, and leaving local air quality worse than when it started.
November 1st marked the official end of the eight-month 2012 ozone season. According to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, or TCEQ, its plan was supposed to deliver record-breaking clean air to DFW this summer on its way to bringing the region into compliance with the Clean Air Act for the first time in two decades.
Instead, six of the 20 ozone monitors in North Texas recorded levels of smog at or above the now-discarded 1997 standard of 85 parts per billion (ppb), while 17 of them recorded violations of the stricter new health- based 75ppb standard that will take effect in 2018.
Clean air activists were anything but surprised.
They accused the state plan of being designed to fail by a politicized TCEQ to avoid any new pollution controls on industry at a time when Governor Perry was running for President. Relying mainly on new car sales projections, TCEQ engineers assured local leaders that pollution levels would go down as older vehicles were traded-in for newer, cleaner ones.
"Since this 'plan' primarily rested on the hope that lots of people would buy new cars, no serious-thinking person thought it would work " said Jim Schermbeck of DFW-based Downwinders at Risk."Unfortunately, after 12 years of Rick Perry's leadership, the TCEQ is in short supply of serious-thinkers."
The margin of error between what TCEQ computer modeling predicted pollution levels would be at DFW air monitors in 2012, and the actual levels of smog they recorded this summer is over 20% at some locations.
The average error of all 20 monitors is 10 ppb. None of the 20 area monitors came closer than 4ppb to reaching its predicted TCEQ target.
A first attempt at reaching the 85ppb target fell short in 2009 -10, but gave the region its lowest-ever smog readings, albeit still illegal. Since then, air quality in DFW has been getting worse, not better.
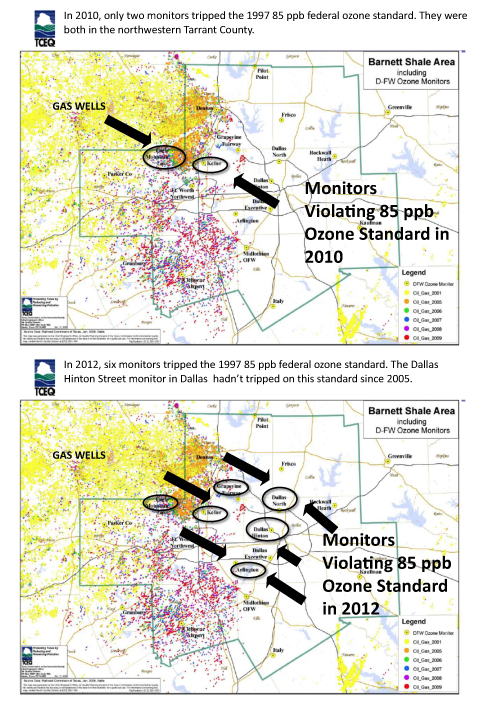
In fact, air pollution is worse now than when the state started drafting its latest plan in 2010. Two years ago, there was only one monitor recording violations of the 85ppb standard. This year there are six.
"Only TCEQ could write a clean air plan that actually makes the air dirtier," remarked Schermbeck.
Some of the critical numbers from 2012 were slightly lower than 2011, when North Texas smog levels reached seven-year highs. The slip was large enough to allow Houston to retake a share of the title of "Smog Capital of Texas" that DFW claimed solely for itself last year.
In 2012, DFW has a rolling three-year worst average of 87ppb of ozone while Houston clocked in at 88ppb. Houston had 17 days over the old 85ppb limit. DFW had 12. But while Houston experienced 28 days when it was in violation of the new stricter 75 ppb standard, DFW recorded 36. A third of DFW's 20 monitors were over 85ppb. Only a fifth of Houston's 47 monitors were. Likewise, 85% of the monitors in DFW had violations over 75ppb – the same as 2011, while Houston had 87%.
Perhaps just as embarrassing to TCEQ as its continued failure to get DFW into attainment with old federal smog limits is Houston's continued backsliding. After a period of progress that saw it reaching compliance with the 85ppb ozone standard in 2009, things have going backwards ever since.
Like DFW, Space City was supposed to be on its way to meeting the new standard, not struggling with trying to meet the 15-year old one. Clean air plans for both regions to meet that new 75ppb standard will have to be drafted by the state and submitted to EPA by 2015.
Schermbeck said for any new DFW clean air plan to be successful, it must do more to reduce pollution from East Texas coal plants, the Midlothian cement kilns, which are applying for new permits to burn industrial wastes, and the smog-forming pollution caused by natural gas mining and processing
"TCEQ continues to underestimate the impact of industrial sources of pollution while overestimating the impact of car pollution. It's all about blaming drivers and ignoring the smokestacks and flares."
Schermbeck pointed to the fact that over the last three years, the location of monitors violating the 85 ppb limit has moved further and further east as gas drilling has moved in the same direction.
After being confined to one or two northwest Tarrant County sites, the number of problem monitors has risen to half a dozen and reaches all the way into central Dallas. A TCEQ monitor near Mockingbird and I-35 violated the 85ppb standard for the first time since 2005.
Schermbeck speculated that the state hadn't adequately estimated the air pollution impact of new gas facilities in the Barnett Shale itself, as well those being built southeast, or directly upwind, of DFW. He blamed TCEQ's monopoly on the computer modeling that drives the entire air planning process for painting a deceptively cleaner future.
"Garbage in, garbage out. As long as this TCEQ is exclusively in charge of the little black box that spits out the results, you're always going to get more political answers than scientific ones. Local officials must understand this and begin to search for their own expertise. Austin just isn't a reliable source of information or advice on how to fight smog."
