EPA Interpretation of Soot Regs Under Fire
 In an important challenge to the way EPA has gone about regulating the tiniest and most harmful forms of soot, or "Particulate Matter" pollution, attorneys for environmental groups seem to making some headway in the courts.
In an important challenge to the way EPA has gone about regulating the tiniest and most harmful forms of soot, or "Particulate Matter" pollution, attorneys for environmental groups seem to making some headway in the courts.
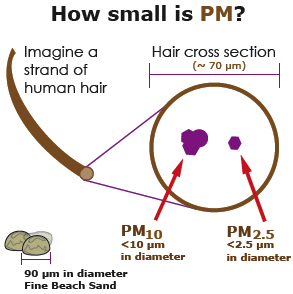
Currently, EPA is about to recommend new PM pollution rules that will reportedly lower the exposure standard for "PM 2.5" – that is, soot that's 2.5 MICRONS or less in size. A human hair is about 10 microns wide, so we're talking incredibly small particles that can easily find their way into your lungs, and then pass through directly into your blood stream.
However, when the Clean Air Act was amended in the early 1990's, the danger of PM pollution was confined to "PM 10" – particles 10 microns or less in size. So called "Coarse PM." But research over the last 20 years has pointed to the greatest danger to human health coming from the smallest kinds of PM pollution – the stuff that's 2.5 or smaller. It's been linked at very low levels of exposure not only to respiratory disease, but to heart attacks, strokes, and brain diseases similar to Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. In fact, the consensus among researchers now is that there is no level of exposure to PM 2.5 pollution that's not capable of doing some harm, that is, there is no "safe level" of exposure.
In another example of how regulations don't keep pace with science, EPA is still regulating PM 10 standards stricter than they are PM 2.5 standards, even though we now know that it's the smallest stuff that is more harmful. EPA is actually using another part of the Clean AIr Act to regualte PM 2.5 pollution than it uses to regulate PM 10 pollution. And the provision it uses for PM 2.5 allows states a lot more wiggle room than the tougher PM 10 provisions.
PM 10 pollution pouring out of a smokestack includes all PM 2. 5 pollution. But "PM 2.5 polluiton"excludes the larger coarser soot. Clear?
One of the three judges of the US Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia, David Tatel, had a hard time with the fact that EPA went outside it's own PM 10 rules to regulate a sub-set of more dangerous PM 10.
"I don't see why it makes much sense to separate out the fine particles," Tatel said. "I don't understand why the agency would do this.' Tatel indicated he did not believe the Clean Air Act required EPA to handle fine particulate matter differently than the coarser pollutants. References in the statute to PM 10 seemed to indicate Congress was referring to particulate matter in general, which would include PM 2.5, Tatel said."
This is exactly the argument EarthJustice lawyers were using. When the Clean Air Act says "fine particles" it means PM 10 and PM 2.5 – you can't regulate PM 10 without also regulating PM 2.5. But this is a law of physics that EPA is trying to undo. The Agency is actually arguing that Congress only meant to apply the standards to PM 10 pollution and no other "fine particles." It's also arguing that the challenge is a decade too late, since the original rules were passed in 1997. The judges didn't seem to be buying that defense either.
With brand new EPA regs for PM pollution expected to be announced shortly, one could reasonably assume this is mostly an academic exercise. but it's not. First, these old rules will still be in play for some time as the new ones are phased-in. It's important to get it right in the intervening period. These old regs affect PM emissions from cement kilns, boilers of all types, power plants and even cars and the public health impact of a stricter standard could be significant. Second, the interpretation EPA uses to establish the new rules could rest on whether the courts agree that it used the right provisions and language last time out.
We've been saying this a lot lately, but it's true. PM pollution is the most insidious, dangerous, and widespread form of air pollution in the world today. It is the ozone of the 21st Century in terms of how pervasive its effects are, and the size of the regulatory response to counter that harm.
